Charts of the Week: This is a crucial period for GCC, including the UAE. How can one decide on the balance between reopening the economy, supporting economic activity, while also containing the spread of Covid19? What policy measures should top the list to support businesses and consumers?
1.Spread of Covid19 in the GCC/ UAE
Confirmed Covid19 cases in the Middle East has crossed 1.75mn, with the GCC nations accounting for 43.7% of total cases. Many of these nations have seen a recent spike in cases, after stay-at-home orders and travel restrictions were lifted in addition to reopening previously constrained activities (e.g. mosques, gyms, salons). Among the GCC nations, the spread of the outbreak is still varied. The chart on the right maps the share in total daily increase in confirmed cases per million persons (x-axis) against the share of the country in overall output (y-axis), with the size of the bubble denoting the 7-day average of the daily increase in cases.
Among the GCC nations, Oman seems to be relatively better off – when it comes to both the 7-day average of daily increase in Covid19 cases as well as the daily confirmed cases per million people; not surprising considering that it is the most “stringent” among the group – the Oxford Covid-19 government response stringency index[1] places Oman at 86.11 vs the least stringent being UAE at 36.11 (Sep 2020). The UAE, which accounts for one-fourth of GCC’s GDP, has the highest 7-day average of daily increase in Covid19 cases (size of bubble). While officials have stressed the need for greater adherence to social distancing measures, no lockdown has been imposed as yet. Within UAE, Dubai is already welcoming tourists subject to Covid19 negative tests.
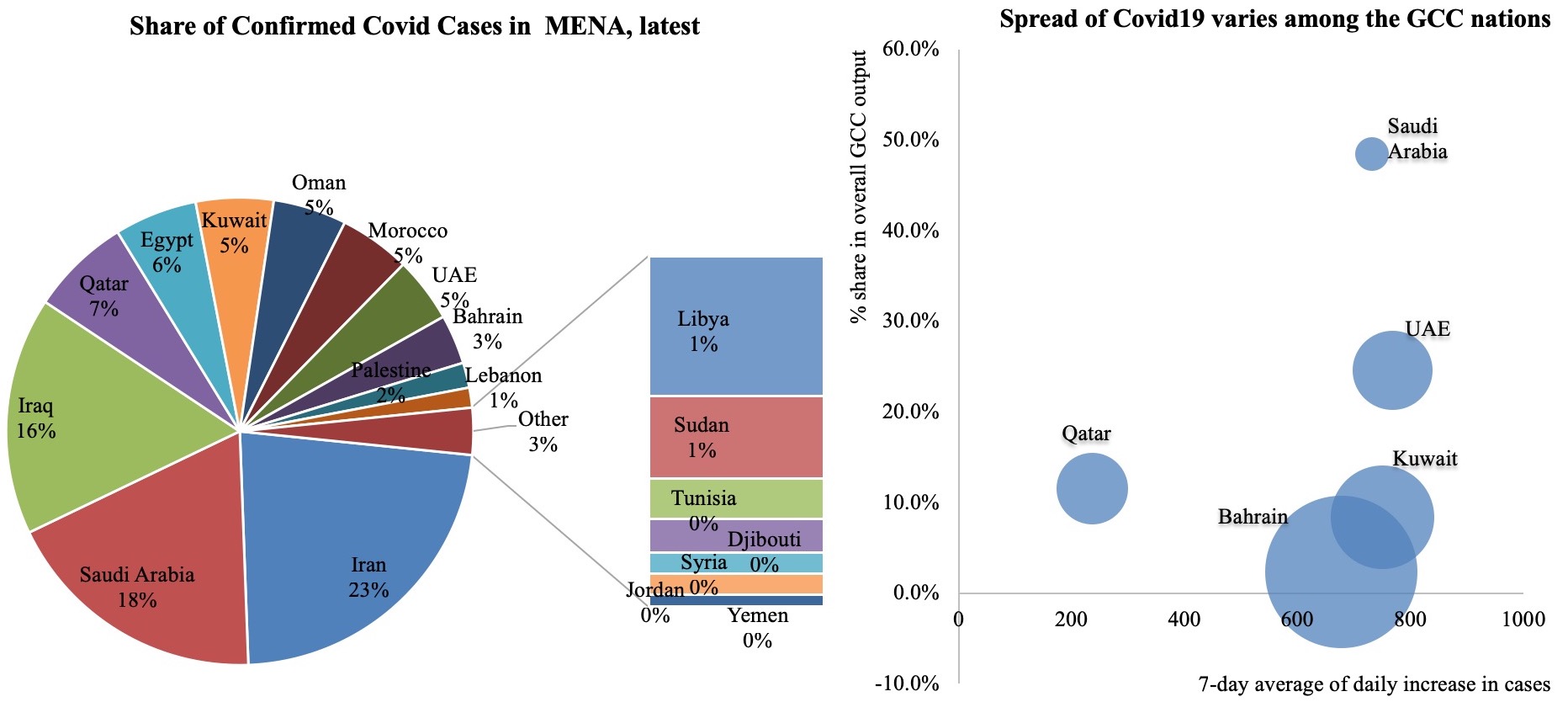
Source: Worldometers, Our World in Data, Nasser Saidi & Associates. The size of the bubbles on the RHS chart denotes the 7-day average of daily increase in cases.
This implies a sharper downturn in GDP this year due to the outbreak, while the effects of lower oil prices and the OPEC+ led cut in oil production will worsen the growth outlook. Given the large proportion of expat population in the country, a dip in growth will also spillover into the labour-importing nations: ranging from job losses (& the return of these residents to home countries), as well as lower remittances. In anticipation of lower growth this year, the government and central bank have rolled out private sector stimulus packages to support the economy, while reducing expenditures (UAE posted a record budget surplus of AED 9.75bn in Q2 this year). The Federal ministries have reduced spending (including compensation of employees), with overall cuts in capital and infrastructure spending will be detrimental to economic growth.
To compensate from lower oil prices and lower non-oil fiscal revenues, borrowing from international capital markets has gathered steam: so far this year, Abu Dhabi issued a USD 5bn multi-tranche bond (that included a 50-year tranche – the longest term for a bond issued by a GCC sovereign issuer) after having raised USD 10bn previously this year, while Dubai government sold a USD 2bn dual-tranche in early-Sep (the prospectus also disclosed that the emirate had raised over USD 3.6bn in debt this year through several instruments, used to support Emirates Airlines and expenses related to the Expo). An important point to highlight is that though Dubai government debt is placed at USD 34bn, the exposure of government-related enterprises (GREs) were not disclosed – an amount estimated at more than USD 120bn by the IMF. A related point was mentioned in the previous weekly insights: bank credit to the public sector and government are rising, threatening to crowd out lending to the private sector (which recorded a 0.1% yoy dip in Jun).
2. Economic Activity in the UAE: PMI, Mobility Indicators & Traffic Congestion
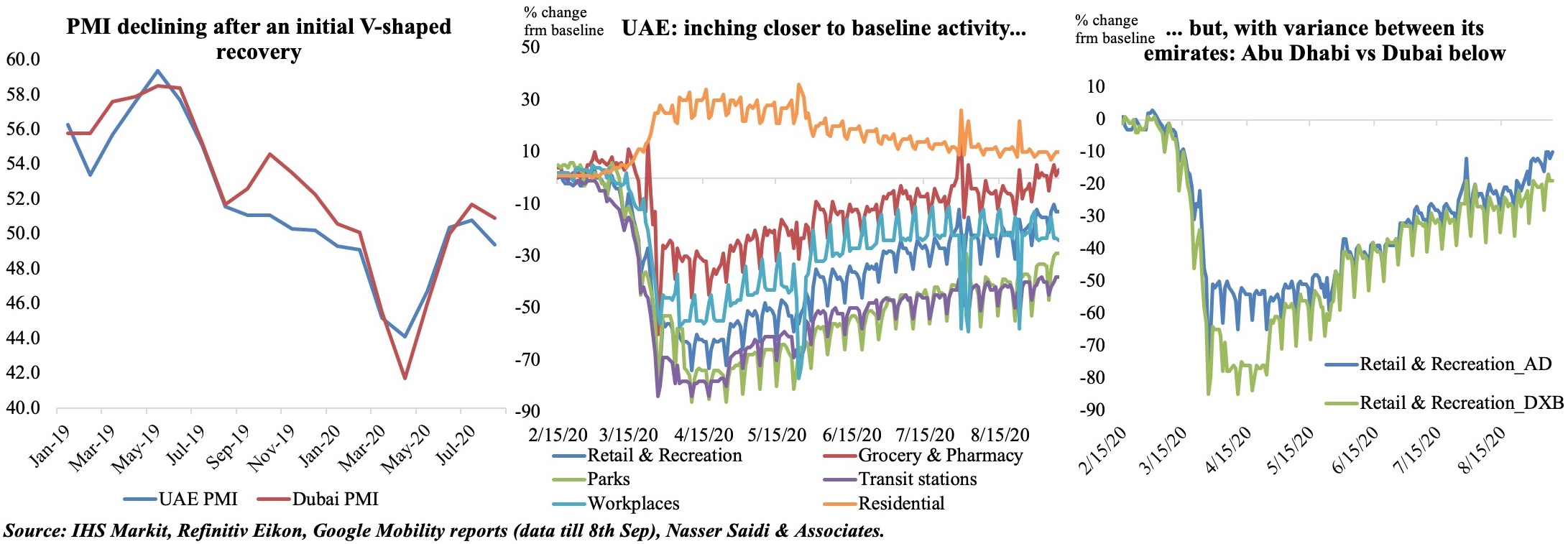
PMI for both UAE and Dubai (most dependent on non-oil sectors) declined the most in Apr – to 44.1 and 41.7 respectively. Following that dip, the PMI readings have been rising in both UAE and Dubai, though it came to a halt in Aug. Employment continues to be the biggest drag on the index (the sub-index was at the lowest in 11 years in the UAE while in a 6th consecutive month of contraction in Dubai) while a rise in sales and related spending was attributed to steeper price discounting (respondent firms generally pointed towards subdued customer demand, not surprising given the wider economic uncertainties).
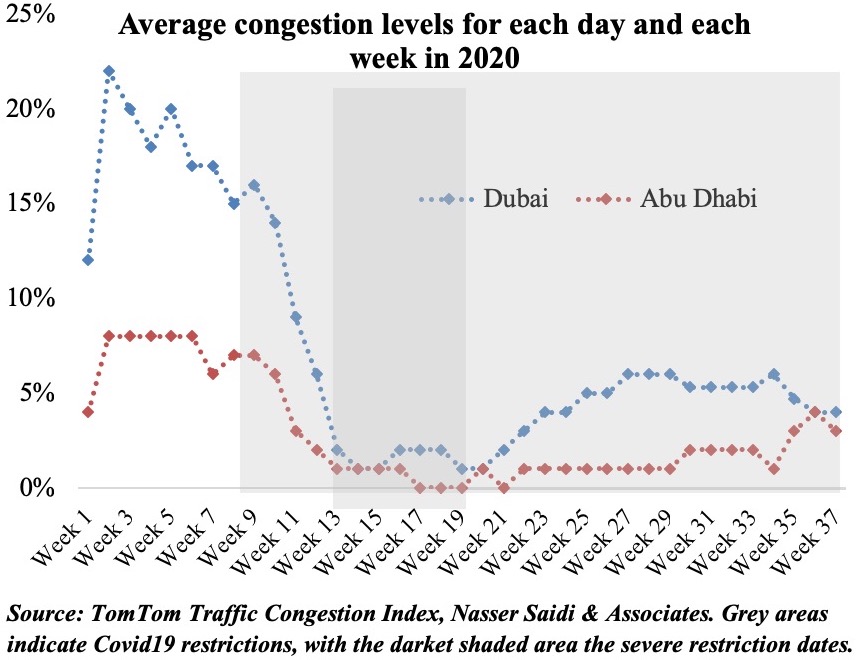
Retail and recreation readings are just under 15% lower than the baseline case in the UAE. There is however a slight difference between Dubai and Abu Dhabi with the latter having recovered faster – probably more confidence as result of specific lockdown restrictions (i.e. need to provide a negative test result to enter the emirate). Workplace is still 25% lower compared to the baseline – possibly the result of working from home policies in many firms. Congestion statistics already show a slow pickup – but below pre-Covid19 levels – more so in Dubai than Abu Dhabi.
3. Policy recommendations for the UAE
As businesses adjust, governments can provide stimulus support to facilitate transition to the new normal. The focus in this section is businesses and consumers. The main immediate concern for firms is operating costs and cash flow: lowering rents/ license fees or offering installment plans for payment of license fees/ rents would help ease financial burdens. Additionally, the government could offer grants to support firms’ digitalization/ roll out of innovative processes. Strains on businesses could have a spillover effect on the banking sector via non-performing loans or increased flight risk of business owners unable to meet repayments. Towards this end, an extension of loan repayments deferment should be considered by the central bank (this has already been done by other GCC nations). Banks should also be nudged to lend to the SMEs and not just already “established” firms with a better financial standing: this could take the form of working capital loans or trade loans, with a SME guarantee scheme (specifying criteria for eligible lenders and the assessment process).
As firms’ lower headcount to adjust, it would be beneficial to remove barriers to labour mobility (e.g. allowing part-time work visas/ freelancing options versus being tied to a specific company): this would allow employees (and families) to remain in the country to search for alternative jobs (and continue school, visit malls and use hospitals among others thereby contributing to overall consumer spending). Ensuring that sudden job losses will not require a move back to their native country, will increase confidence to invest in the economy (be it real estate or starting new business ventures). A longer-term policy would be to establish social security nets and/or unemployment insurance to reduce financial burdens alongside jobs support schemes.
[1] Check https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/covid-stringency-index?year=latest&time=2020-01-22..latest