Markets
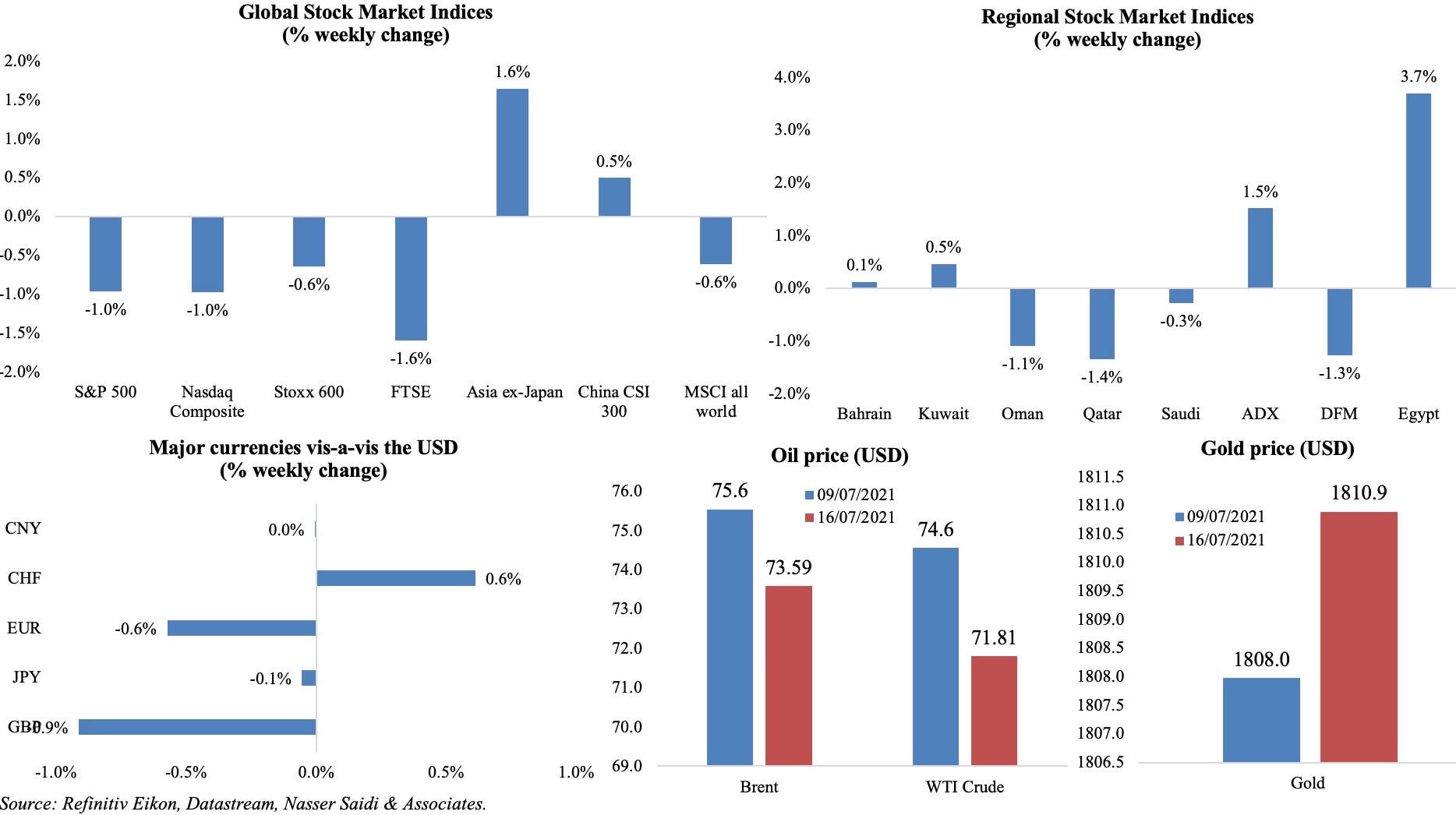
Concerns over the spread of the Delta variant and rising inflation dominated equity market performance globally, amid expectations of a strong Q2 earnings season. In the US, S&P 500 and Nasdaq fell by 1% while in Europe, both FTSE and Stoxx ended the week lower by 1.6% and 0.6% respectively. China’s CSI300 ended marginally higher, though its banking index fell to its lowest level in 6 months during the week. MSCI all country index recorded a peak last week but closed 0.6% lower. Regional markets were mostly down, with Egypt and Abu Dhabi exchanges posting the highest gains. The dollar gained last week, while sterling closed lower (-0.9%). Oil prices declined last week: the OPEC+ meeting held earlier today decided to boost oil supply by a further 2mn barrels per day (bpd) from Aug-Dec 2021 (UAE will see its baseline production increase to 3.5mn bpd from May 2022, while Saudi and Russia’s baseline will rise to 11.5mn bpd each; more in Media Review section). Gold price edged up by a marginal 0.2% over the past week.
Weekly % changes for last week (15-16 Jul) from 8 Jul (regional) and 9 Jul (international).
Global Developments
US/Americas:
- Inflation in the US accelerated to a 13-year high of 5.4% yoy in Jun (May: 5%), with the largest increases recorded for used cars (45.2%) and gasoline (45.1%) among others. Core inflation excluding food and energy also grew by 0.9% mom and 4.5% yoy.
- Producer price index increased to 7.3% yoy in Jun (May: 6.6%), posting the biggest annual gain since Nov 2010. Services, with a 0.8% mom rise in costs (May: 0.6%), accounted for nearly 60% of the increase in PPI. Excluding food and energy, prices were up by 5.6% yoy (4.8%) – this was the largest increase since the series was introduced.
- The Fed Beige book stated that the economy was showing “moderate to robust growth” amid broad-based job gains though finding that prices were rising “at an above-average pace”. It also noted that “while some contacts felt that pricing pressures were transitory, the majority expected further increases in input costs and selling prices in the coming months”.
- Industrial production in the US rose marginally by 0.4% mom in Jun (May: 0.7%): manufacturing continued to be a drag, dropping by 0.1% mom, largely due to a 6.6% plunge in motor vehicles and parts production (given shortage of semiconductors). IP grew by 9.8% yoy but remains 1.2% below pre-pandemic levels.
- Philadelphia Fed manufacturing index eased to 21.9 in Jul (Jun:30.7), as new orders slipped by 5.2 points to 17 and shipments fell to 24.6 (Jun: 27.2). Separately, the New York Empire State factory index soared to a record high of 43 in Jul, on higher new orders (+16.9 points to 33.2) and shipments (+29.6 to 43.8); prices received index also soared to a record high of 39.4.
- Retail sales in the US unexpectedly rebounded by 0.6% mom in Jun (May: -1.7%), thanks to rising demand at electronics (+3.3% mom) and clothing stores (+2.6%) as well as restaurants (+2.3%). Excluding fuel, retail sales were up by 0.4% mom (May: -1.9%). In yoy terms, sales surged by 18% and are well-above pre-pandemic levels.
- Initial jobless claims fell to a 16-month low of 360k in the week ended Jul 10th from an upwardly revised 386k the week before; the 4-week average fell to 382.5k. Continuing claims fell by 126k to 3.241mn in the week ended Jul 3rd.
Europe:
- Industrial production in the eurozone fell by 1% mom in May (Apr: +0.6%), though up by 20.5% in yoy terms. Only consumer goods production increased (+1.6%) alongside declines in non-durable goods (-2.3%), energy (-1.9%), capital goods (-1.6%) and intermediate goods (-0.2%).
- Both inflation and core inflation in the eurozone rose to 0.3% mom in Jun. In yoy terms, inflation rose to 1.9% – energy prices contributed 1.16 percentage points to overall inflation – and core inflation was stable at 0.9%.
- Trade balance in goods the eurozone narrowed to EUR 7.5bn in May (Apr: EUR 10.9bn) as exports eased to EUR 188.2bn and imports stood at EUR 180.7bn.
- Wholesale price index in Germany edged up by 1.5% mom and 10.7% yoy in Jun: the annual increase was the largest since Oct 1981.
- Inflation in the UK rose to 2.5% yoy in Jun, the highest since Aug 2018 (May: 0.6% mom and 2.1% yoy), on higher costs of secondhand cars (+5.6%), clothing (+3.3%), footwear (1.2%) and motor fuel (+20.3%). Core inflation rose to 2.3% yoy from 2% a month before. Retail price index grew to 0.7% mom in Jun (May: 0.3%).
- The ILO unemployment rate in UK remained unchanged at 4.8% in the 3 months to May. Job vacancies in the UK are up by 7% mom to 962k for Jun, with the hospitality sector gearing up for the Jul 19th Average earnings including bonus rose by 7.3% vs 5.3% in the previous 3 months.
Asia Pacific:
- GDP in China grew by 1.3% qoq and 7.9% yoy in Q2 (Q1: 0.6% qoq and 18.3% yoy).
- China’s exports surged by a faster-than-expected 32.2% yoy in Jun (May: 27.9%) while imports grew at a faster pace (+36.7% vs May’s 51.1% gain, partly due to higher raw material prices), posting a trade surplus of USD 51.53bn (May: USD 45.54bn). China’s crude oil imports fell by 3% in H1 this year, their first contraction for the period since 2013, while imports of soybeans, natural gas and iron ore rose.
- FDI into China grew by 28.7% yoy in H1 2021 (Jan-May: 35.4%), with FDI inflow into high-tech industries up by 39.4%. Fixed asset investment grew by 12.6% in H1, easing from the 15.4% rise in Jan-May.
- Industrial production in China accelerated by 8.3% yoy in Jun (May:8.8%). Retail sales grew by 12.1% in Jun (May: 12.4%), with the fastest growing category beverages (+29.1%). The urban survey unemployment rate held steady at 5% in Jun, while unemployment for 16-24 age group climbed to 15.4% (same as Jun 2020).
- China launched its emissions trading system: pollution caps were set for 2,162 big-power businesses (that generate about a seventh of the global carbon emissions). The scheme allows firms to buy the right to pollute from others with a lower carbon footprint. However, the pricing is quite low: trade started off at CNY 7 (USD 8) per ton of carbon. For comparison, a chart on EU carbon price.
- The Bank of Japan held interest rates unchanged, as expected. The apex bank cut growth projections to 3.8% in the current fiscal year ending Mar 2022 (from 4% forecast in Apr) while revising up its inflation forecast to 0.6% (from 0.1%) given recent increase in energy costs. The BoJ will also offer zero-interest, long-term funds its under climate scheme.
- Industrial production in Japan declined by 6.5% mom in May, sharper than the initial estimate of 5.9% drop; shipment declined by 5.5% mom and inventories by 1.1%. IP however grew by 21.1% yoy in May (lower than the initial estimate of 22%). Capacity utilization fell by 6.8% mom.
- Japan machinery orders grew by 7.8% mom and 12.2% yoy in May, posting the 3rd consecutive month of gains. Both manufacturing and non-manufacturing orders increased in mom terms, by 2.8% and 10% respectively.
- India’s industrial output surged by 29.3% yoy in May, with manufacturing up by a higher 34.5%, given the low base effect. In mom terms, industrial output fell 8% in May, a result of the lockdowns imposed due to the spread of Covid19.
- Wholesale price inflation in India stood at 12.07% in Jun (May: 12.94%), on softened fuel (32.83% in Jun vs May’s 37.6%) and food (3.09% vs 4.31%) prices. Though overall retail inflation eased slightly to 6.26% in Jun (May: 6.3%), food and fuel prices were higher.
- India’s crude oil imports fell to a 9-month low in Jun, reported Reuters, citing tanker arrival data: it slipped by 7% mom to 3.9mn barrels per day (it grew by 22% in yoy terms). The share of oil from the Middle East rose to about 59% in Jun (May: 53%): Iraq, Saudi and the UAE were the top oil suppliers to India last month.
- Singapore’s GDP contracted by 2% qoq in Q2, reversing Q1’s 3.1% growth. In yoy terms, it grew by 14.3% yoy in Q2, helped by a low base the year before (Q2 2020: -13.3%).
Bottomline: The more transmissible Delta variant is dominating news, be it in Indonesia – which has the highest test positivity rates globally (more than 27%) and where less than 6% are vaccinated – or in the UK where daily cases passed 50k for the first time since Jan, but relatively better placed given that 68% of the population are fully vaccinated (implying less hospitalization and death rates). Though many European nations were gearing up for summer tourists, some restrictions are back as many including Cyprus, Portugal, Spain and Netherlands are now in the list of code red countries (according to the European Centre for Disease Prevention). Meanwhile, the OPEC forecasts an increase in oil demand, reaching pre-pandemic levels by 2022. This could also seep into inflation numbers which are staying higher longer than expected (though still being labelled “transitory” by major central banks). Lastly, China’s latest GDP numbers and RRR cut indicate a relatively weak momentum – also seen in the latest readings of slowing investment.
Regional Developments
- Bahrain banned entry for travelers from 16 nations including Tunisia, Iran, South Africa and Indonesia among others. Citizens and those with residency visas are exempt from the ban.
- Trade deficit in Egypt narrowed by 13.3% yoy to USD 3.1bn in Apr 2021: exports surged by 47.4% to USD 2.84bn alongside an 8.1% increase in imports.
- The central bank of Egypt’s EGP 100bn mortgage initiative is likely to be launched in Aug: it will allow low- and middle-income homebuyers to access mortgages at a subsidized rate of 3%; eligibility criteria are still unclear though it is expected that subsidized mortgages will be given on houses valued at up to EGP 1.4mn, provided a 20% down payment is made.
- Suez Canal’s revenues hit a record high of USD 5.84bn in the 2020-21 financial year (Jul-Jun): it collected close to USD 3bn in H1 and USD 2.76bn in the second half. This year, about 9763 ships passed through the Canal (+2.3% yoy) till Jun while net shipping loads gained by 3.8% to 610mn tons.
- Egypt’s El-Dabaa nuclear plant project is on schedule and expected to begin operations in 2026, revealed the electricity and renewable energy minister.
- Iraq announced the extension of its oil supply deal with Jordan for another year. During this time, Iraq will supply Jordan with 10k barrels per day of crude oil under preferential terms.
- Occupancy rates in Jordan’s main tourist centres are rebounding: it has increased to 40-50% in the Dead Sea and the Red Sea port city of Aqaba and around 30% in Amman, compared to around 2-3% at the height of the Covid19 crisis.
- S&P cut Kuwait’s rating by one notch to A+ from AA-, citing “persistent lack of a comprehensive funding strategy” for its deficits.
- Kuwait is planning bond sales and indirect taxation to bridge its deficit gap, reported Al Jarida newspaper, citing the finance minister’s response to a parliamentary question. In addition to VAT, selective taxes are likely to be imposed on “selling price of goods harmful to public health and the environment” and “to luxury goods”.
- Kuwait opened its first permanent facility to import LNG – the plant will be able to import as much as 22mn tonnes of LNG. Bloomberg expects LNG use to almost double by 2025, with most of the increase coming from Kuwait.
- The Kuwait Cabinet will close down all activities for children, including summer clubs from July 25 until further notice.
- Lebanon’s Hariri abandoned his effort to form the government stating that he is unable to reach an agreement with the President. The pound weakened even further on this announcement, down to more than 20k from 19k earlier that day.
- Oman’s Sultan visited Saudi Arabia last week, in the first foreign trip since ascension. Economic cooperation on many fronts are likely to benefit – trade, investment and infrastructure in addition to security, cultural & other diplomatic discussions. Our view is that opportunities are multi-fold including cooperation on the move to cleaner renewable energy, privatization programs and listing/ cross-listing opportunities. Read more: https://nassersaidi.com/2021/07/15/weekly-insights-15-jul-2021-covid19-cases-vaccination-beyond-mena-uae-saudi-omani-cooperation/
- Qatar plans to hold its first legislative elections in October to elect 30 members of the 45 in the advisory Shura Council. The rest 15 members will be appointed by the ruling emir.
- A 20-year sale and purchase agreement has been finalized by Qatar Petroleum to supply LNG to Korea: this covers the supply of 2mn tons a year of LNG, starting by Jan 2025.
- Syria, on the heels of an increase in petrol prices, announced higher bread and diesel prices: price of diesel fuel nearly tripled to SYP 500 and the price of bread doubled. This coincided with a move to increase public sector salaries by 50% and set the minimum wage at SYP 71,515 a month (USD 57 at the official rate).
- Funding secured by MENA-based startups accelerated by 64% yoy to USD 1.2bn in H1 this year; this compares to more than USD 1.09bn raised in 2020, according to Magnitt. However, the number of deals fell by 20% to 254 during this time.
- Invesco’s annual Global Sovereign Asset Management Study found that last year, 57% of sovereign funds in the Middle East faced drawdowns (vs. over one-third globally) while portfolio cash reserves of Middle East sovereign funds more than doubled. Climate change risks are a major concern on the agenda in the Middle East: 75% indicating that their asset-allocation decisions are influenced by environmental concerns (vs 62% globally).
Saudi Arabia Focus
- Inflation in Saudi Arabia surged to 6.2% yoy in Jun (May: 5.7%), drive up by transport and food costs (up 22.6% and 8.1% respectively).
- Wholesale prices in Saudi Arabia surged by 19.8% yoy in Jun: other transportable goods posted the highest increase (+25.4), driven by higher costs of basic chemicals (+6%) and refined petroleum products (+28.4%). Other components that surged include metal products, machinery and equipment (+20.5%) and food and non-alcoholic beverages (+10.3%) among others.
- As part of the privatization program, Saudi Arabia raised almost USD 800mn from the sale of two major flour mills.
- Saudi Arabia will permit shops to stay open during prayer times, according to Okaz, citing a circular by the official business federation.
- Fitch revised Saudi Arabia’s outlook to stable from negative while maintaining the sovereign rating at ‘A’, citing “prospects for a smaller deterioration in key sovereign balance-sheet metrics”.
- The Saudi CMA approved the merger of NCB Capital and Samba Capital: the merger is expected to take effect by Q3 2021.
- Saudi Arabia’s PIF has sent banks’ a request for proposals to help develop an ESG framework – this would allow the fund to expand its investor base.
- The number of families benefiting from Saudi Arabia’s “Sakani” housing loan program fell by 24.2% yoy to 48,397 in H1 2021.
- Saudi Arabia will offer SAR 500mn (USD 133mn) in loans for entertainment projects: the plan is to finance at least 50 new entertainment projects in the country.
- The value of online delivery orders in Saudi Arabia surged by 45% yoy to over SAR 1bn in Q1 2021. Overall requests increased by about 33% to nearly 9.2mn while e-payments rose by 128% to 8.1mn.
- Saudi Arabia’s Citizen Account Program deposited SAR 9bn (USD 506mn) into the accounts of 10.5mn beneficiaries for Jul.
- The Saudi Human Resources Development Fund supported the employment of 142k citizens in H1 2021. About 59% of these were women and medium sized firms benefitted most from the support (with 67k employees).
UAE Focus![]()
- As part of the UAE central bank’s 2023-26 strategy, a digital currency will be introduced, in addition to digital transformation of the financial services sector along with adoption of AI and big data.
- Dubai PMI eased by 0.6 points to 51 in Jun, as both new orders and output grew at a softer pace while the rate of job creation posted the fastest pace since Nov 2019. Optimism was high for the future with the 12-month outlook reading at the second strongest since Sep 2020.
- Contrary to reports, the UAE is still in “deliberations and consultations” with the OPEC+ on an extension of the oil supply deal, according to the energy minister.
- A national program was launched in the UAE to train 100k coders, with an aim to establish 1,000 tech companies and increase start-up investments to AED 4bn from AED 1.5bn.
- A Dubai Chamber of Commerce survey showed that business confidence grew to a 7-year high: more than 66% of respondents expect to see a better business environment in the next quarter (vs 51% in Q2), largely due to growing domestic demand, economic stimulus initiatives and the progress of the vaccination drive. Though this was the most optimistic survey reading since Q4 2014, risks could be posed by late payments, debt collection, strong price competition and the high cost of raw materials.
- Abu Dhabi’s DED stated that all eligible private sector claims until end of Q1 had been settled within 15 days instead of 30.
- Abu Dhabi has announced partial overnight lockdown from midnight till 5am effective July 19th; in addition, lower capacity limits of 50% were issued for public beaches, parks as well as restaurants and cafes while shopping malls and cinemas would be restricted to 40% and 30% capacity respectively.
- UAE’s Yahsat expects to launch a new satellite in H2 2023; the company began trading on ADX from Wednesday after a USD 730mn IPO – the first since ADNOC Distribution listed in 2017.
- Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC) disclosed in a filing that it is investing USD 763.7mn to support its production capacity expansion to 5 million barrels per day by 2030.
Media Review
OPEC+ agrees to oil supply boost
https://www.reuters.com/business/energy/opec-meets-agree-oil-supply-boost-prices-rise-2021-07-18/
Central Banking, Fast and Slow: El-Erian
Biden’s new China doctrine
https://www.economist.com/leaders/2021/07/17/bidens-new-china-doctrine
How the EU plans to reshape its economy to limit climate change
https://www.ft.com/content/8800128f-eec6-4272-acc7-a51132c6c931
COVID-19 and women-led businesses: More innovation but greater financial risk
Could Renewed Social Unrest Hinder the Recovery?
https://blogs.imf.org/2021/07/13/could-renewed-social-unrest-hinder-the-recovery/
Powered by:







