Weekly Insights 11 Feb 2021: Will Accelerated Vaccine Distribution Catapult UAE to Faster Economic Growth?
Download a PDF copy of this week’s insight piece here.
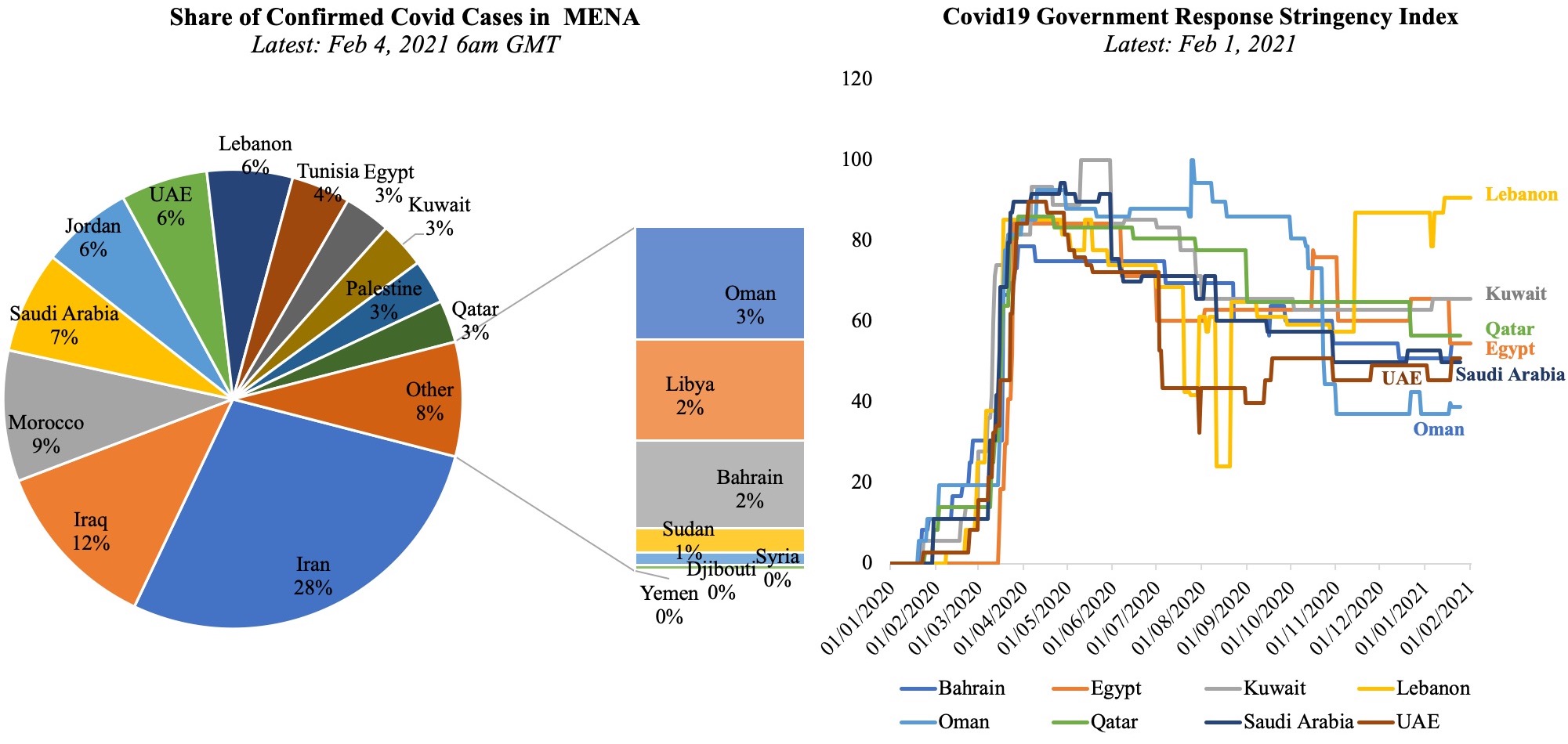
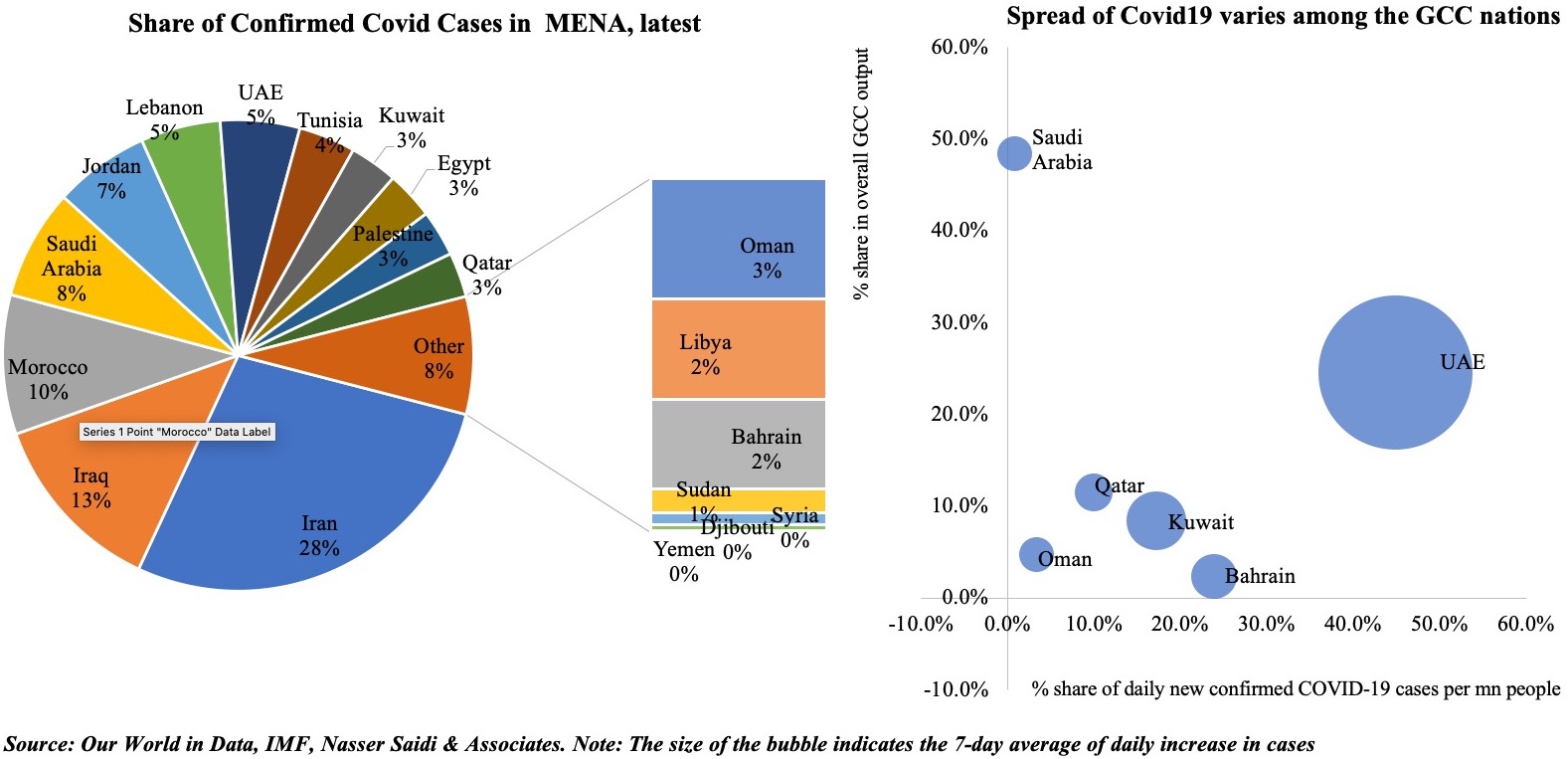
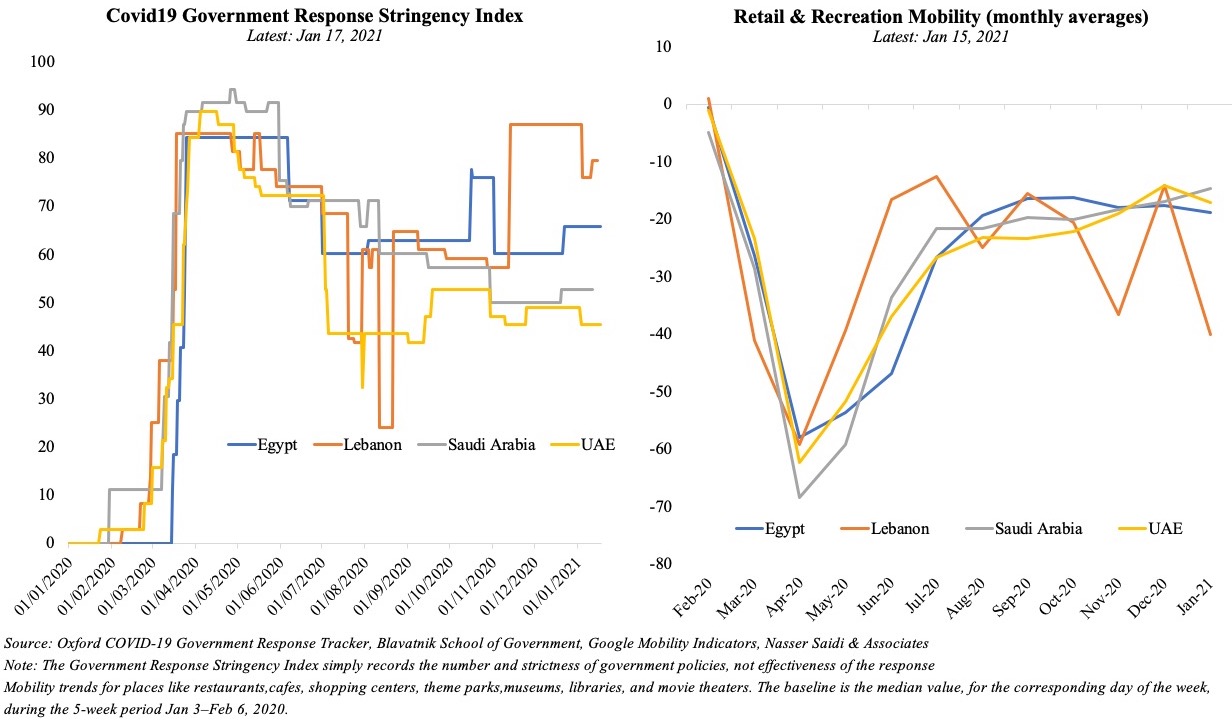
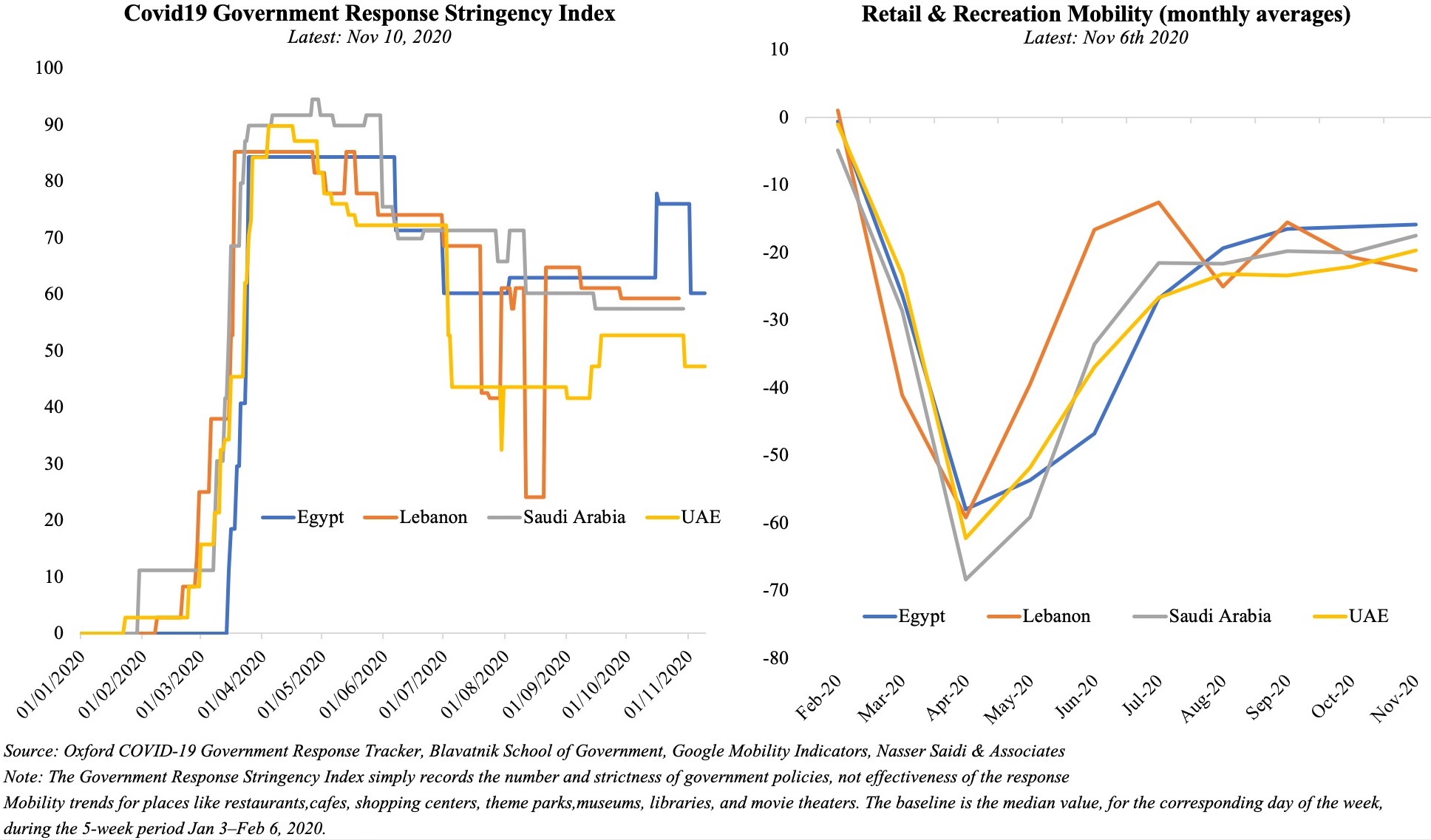
The UAE has seen a surge in Covid19 cases recently, touching a high of 3,977 new cases on Feb 3rd from just under 1,000 new cases on 27th of Dec and settling around a 7-day average of 331.55 new confirmed cases per million persons (latest available). As the cases ticked up, the UAE has re-introduced more stringent restrictions and an active crackdown on non-compliance. Mobility indicators indicate a strong negative relation with the Stringency Index: the tighter the government-imposed restrictions, the stronger is the observed reduction in mobility (Chart 1).
The Vaccination Drive
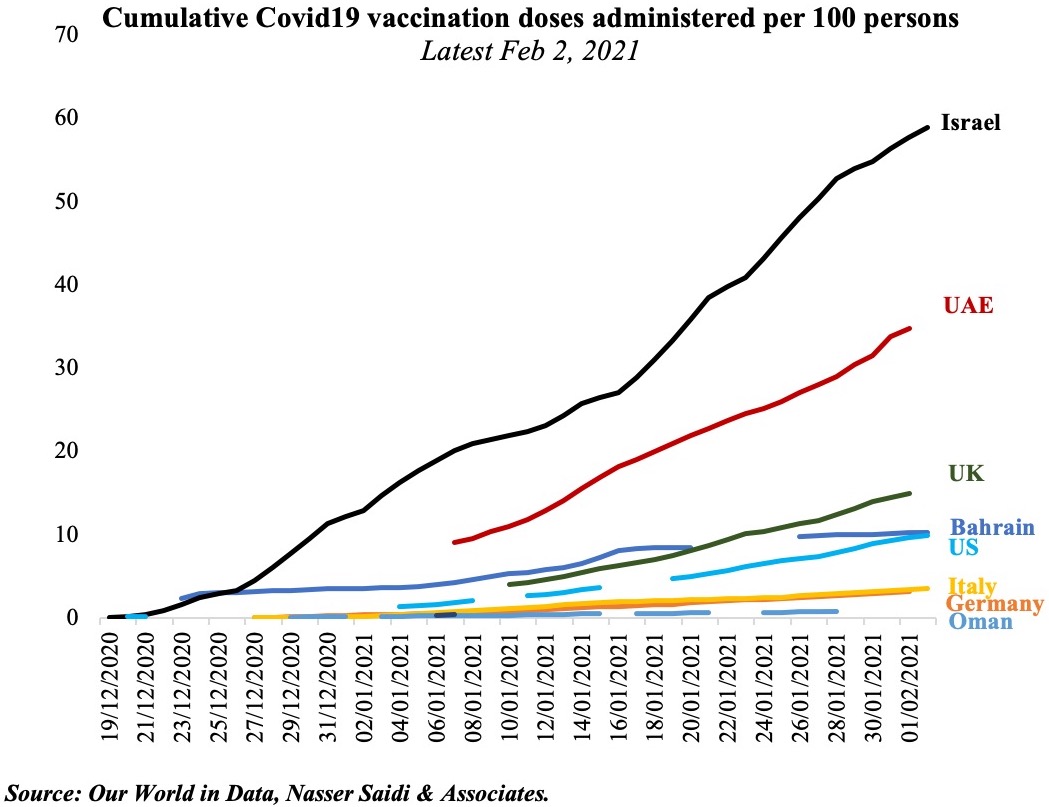
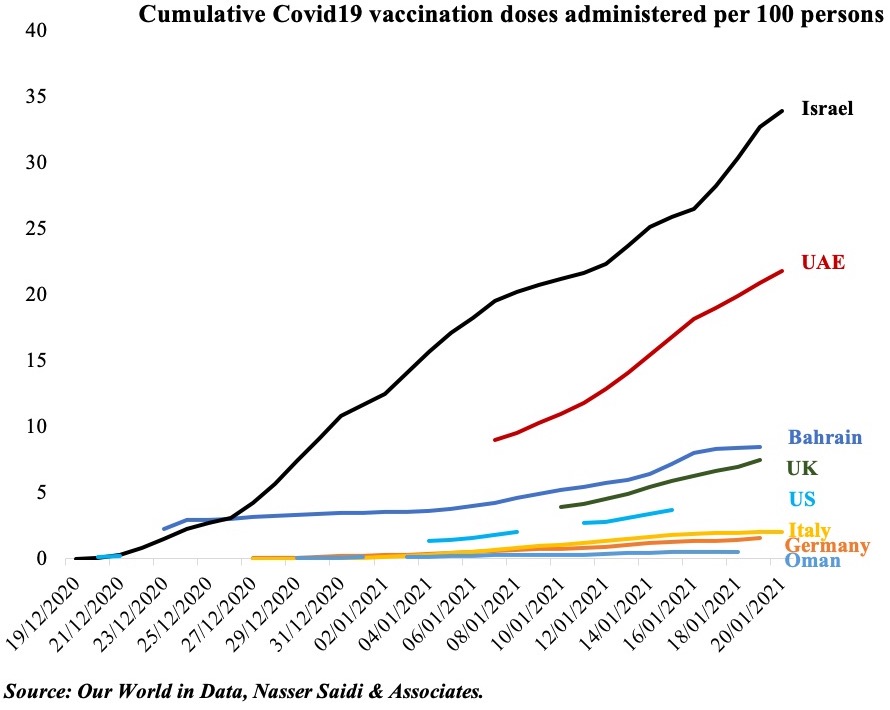
On the other hand, the UAE is also ramping up its vaccination drive since mid-Dec and is currently a global leader (second to Israel) having administered 45.77 vaccine doses per 100 people (as of 9th Feb, Chart 2). With 4 vaccines being expended currently – Sinopharm, Pfizer-BioNTech, AstraZeneca and Sputnik V – the government looks on track to vaccinate more than 50% of the population by end of Q1 of this year.
Is this sufficient to support economic recovery?
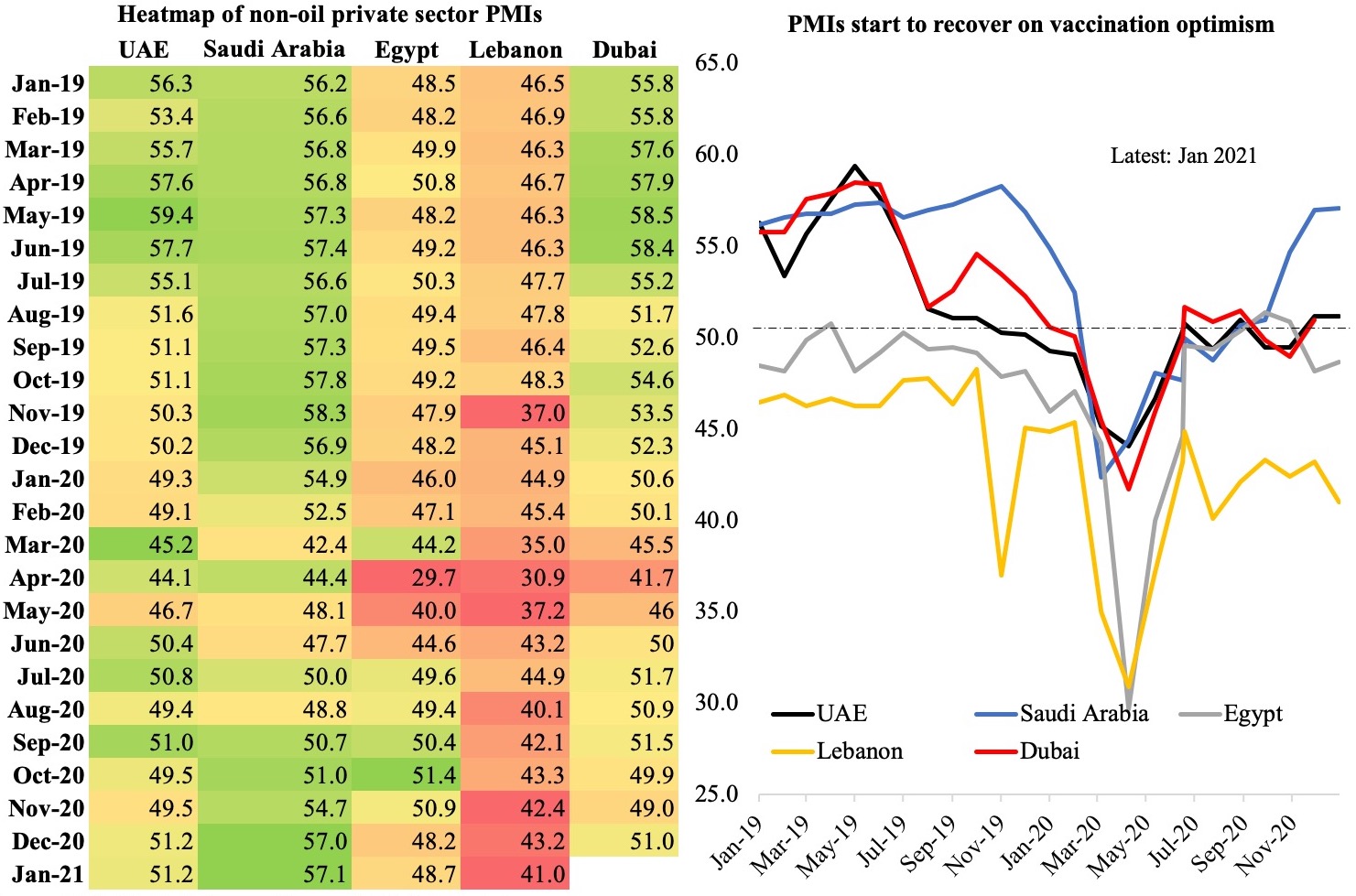
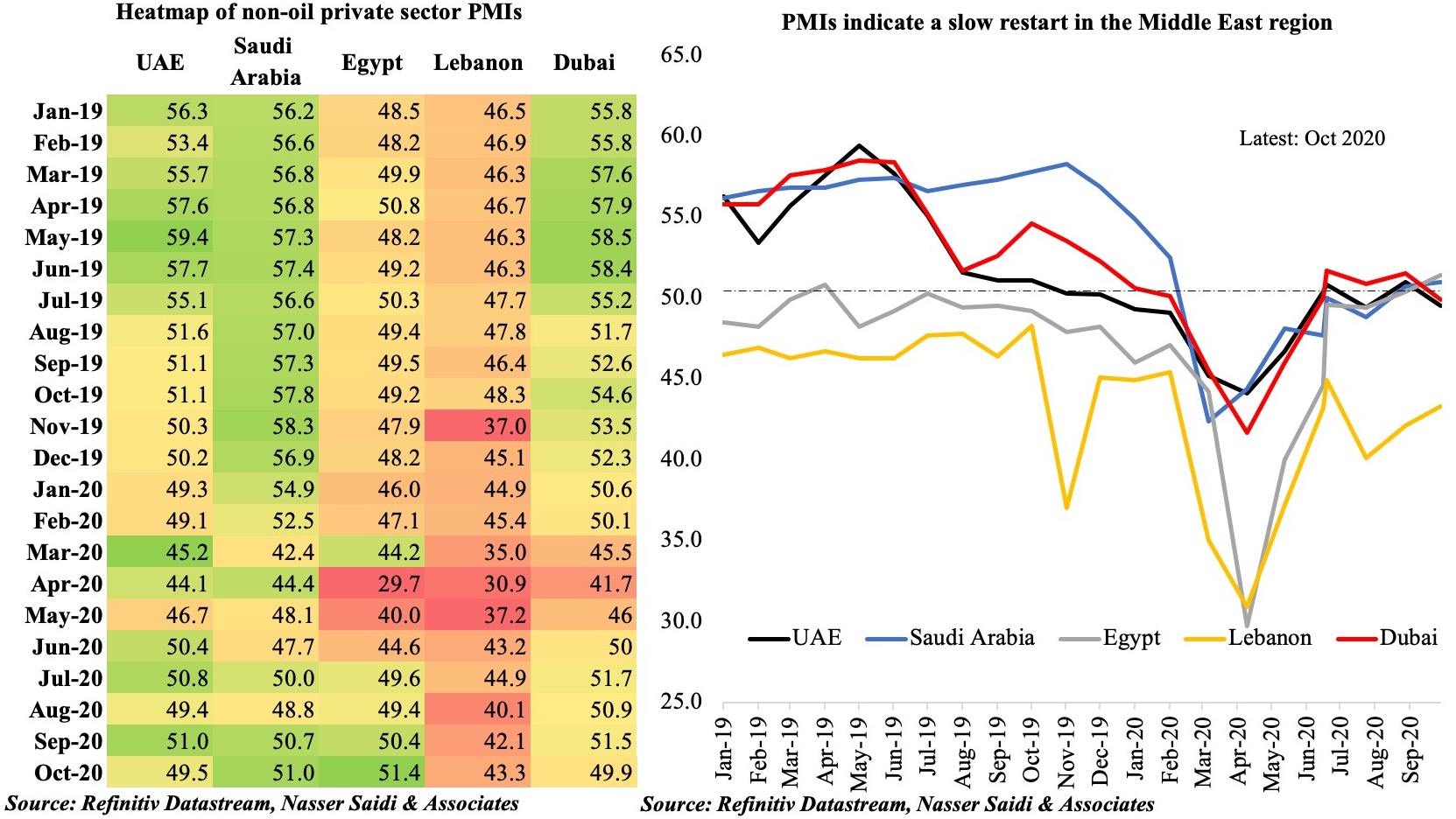
Given the paucity of monthly indicators/ data from official sources, we use the PMI numbers released by IHS Markit to gauge the level of business activity in the country and in the emirate of Dubai (Chart 3). Both PMIs have stayed quite close to the 50-mark (neutral) in Dec-Jan after two consecutive months of being in the contractionary territory. Job prospects seem to be improving in both UAE and Dubai, with increases in Jan (after nearly a year). Dubai’s tourism sector, after an uptick in Dec, has however returned to sub-50 levels – not unsurprising considering the outflow of foreign tourists after the New Year holidays (Dubai-London Heathrow travel corridor was the busiest international air route in the world in Jan, with more than 190k seats scheduled, according to OAG) and potential decline in domestic and international tourists as border/ quarantine restrictions were reinstated.
With the vaccination drive, it is evident that as the nation inches closer to herd immunity levels, domestic activity as well as business and consumer levels will gradually build up to pre-pandemic levels. However, domestic activity will not be sufficient to sustain long-term economic growth. It is pertinent to note that the UAE has in the past months passed a spate of investor and business friendly structural reforms including to attract skilled professionals to take up residence in the country. While the success of these reforms will not be seen immediately, steady and effective implementation is likely to support economic growth in the medium and longer-term.
How can the UAE step up its recovery? The UAE as a vaccination hub
It is in the best interests of the country, that is hosting the Expo later this year, to see high levels of vaccinated populations within the wider region (and globally). The longer countries remain unvaccinated, the greater the risk of the emergence of newer variants that could potentially result in another cycle of infections and lockdowns/ closures.
Two potential ways to support this:
- Increase the production of vaccines: a recent paper estimates that “increasing the total supply of vaccine capacity available in Jan 2021 from 2bn to 3bn courses per year generated USD 1.75trn in social value, while additional firm revenue was closer to USD 30bn”, far outweighing the investments required to do so. Vaccination is a public social good with multiple private benefits, just as Covid is a global public bad. So, the UAE’s plans to manufacture Sinopharm Covid19 vaccine later this year would act as a win-win: it would cater to both domestic and global demand (especially if the vaccine is to be administered on an annual basis) and boost the economy.
- The manufactured vaccines need to be distributed faster to reach those in need. In this backdrop, the UAE can put its position as a global logistics and transport hub to good use: vaccine delivery to smaller nations in the region as well as using its vast cargo network to transport vaccines across the globe. Dubai, with its Vaccine Logistics Alliance, will support WHO’s effort to deliver 2bn doses of vaccines this year; this is in addition to Abu Dhabi’s Hope Consortium which was set up for vaccine storage and distribution. This could be supported by vaccine aid – either in its contribution to global alliances like Covax (which plans to deliver 2.3bn doses this year) or via the free delivery of vaccines to smaller low-income nations (e.g. India’s free vaccines to Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh).
A global recovery is essential to the UAE’s overall growth prospects: as a country that relies on trade and tourism (together accounting for close to 15% of UAE’s GDP in 2019 and closer to 30% of Dubai’s GDP), the impact of Covid19 has been drastic (evident from UAE and Dubai GDP estimates). The oil sector, which constitutes 30% of UAE’s GDP, has been bogged down by the OPEC+ production cuts, alongside the subdued demand for oil. Even as the country promotes clean energy and energy efficient policies, signs of a recovery in oil demand (declining oil inventories thanks to turnaround in consumption in China and India) and higher oil prices (around USD 60 now) will be beneficial to trade and growth: UAE’s oil and related product exports are close to 40% of total exports and the main export destinations include India, China and Japan (which together garner more than 25% share of overall exports). A recovery in tourism is likely to take longer in comparison: virus containment, travel corridors, “vaccine passports” and “contactless” airport experiences seem to be some of the ways forward for future travel.
Lastly, no outlook is complete without risks: long-term diversification away from oil is a necessity, as is decarbonization efforts, and debt sustainability policies (especially in the context of another potential taper tantrum / faster-than-expected increase in interest rates, leading to tighter financing conditions).
Powered by: