Weekly Insights 13 Oct 2020: PMIs, Mobility & Economic Recovery
Download a PDF copy of this week’s economic commentary here.
1.Global PMIs, shipping & trade
PMIs across the globe were released last week. The headline JPMorgan global composite PMI fell for the first time in five months, dipping to 52.1 in Sep (Aug: 52.4). Most manufacturing surveys still indicated an expansion (a reading above 50) though the pace of recovery has slowed as a result of capacity constraints and supply chain delays. Sector-wise, the most significant beneficiary has been the automotive sector, where production capacity increased and new orders posted the most gain since Dec 2019. On the other extreme, tourism and recreation sector continues to be the worst hit – reflecting the glaring divergence between the manufacturing and services sector PMIs (Figure below). September’s PMI readings in the services sector have declined from Aug’s 7-month highs, as many countries witnessed a resurgence in Covid19 cases (and in some, new record daily cases!), leading to restricted lockdowns which added on to the restrictions due to social distancing policies. Employment posted a net increase for the first time since Jan: though jobs growth was faster in the services sector in Aug-Sep, remember that the sector had also seen the steepest job cuts earlier this year.
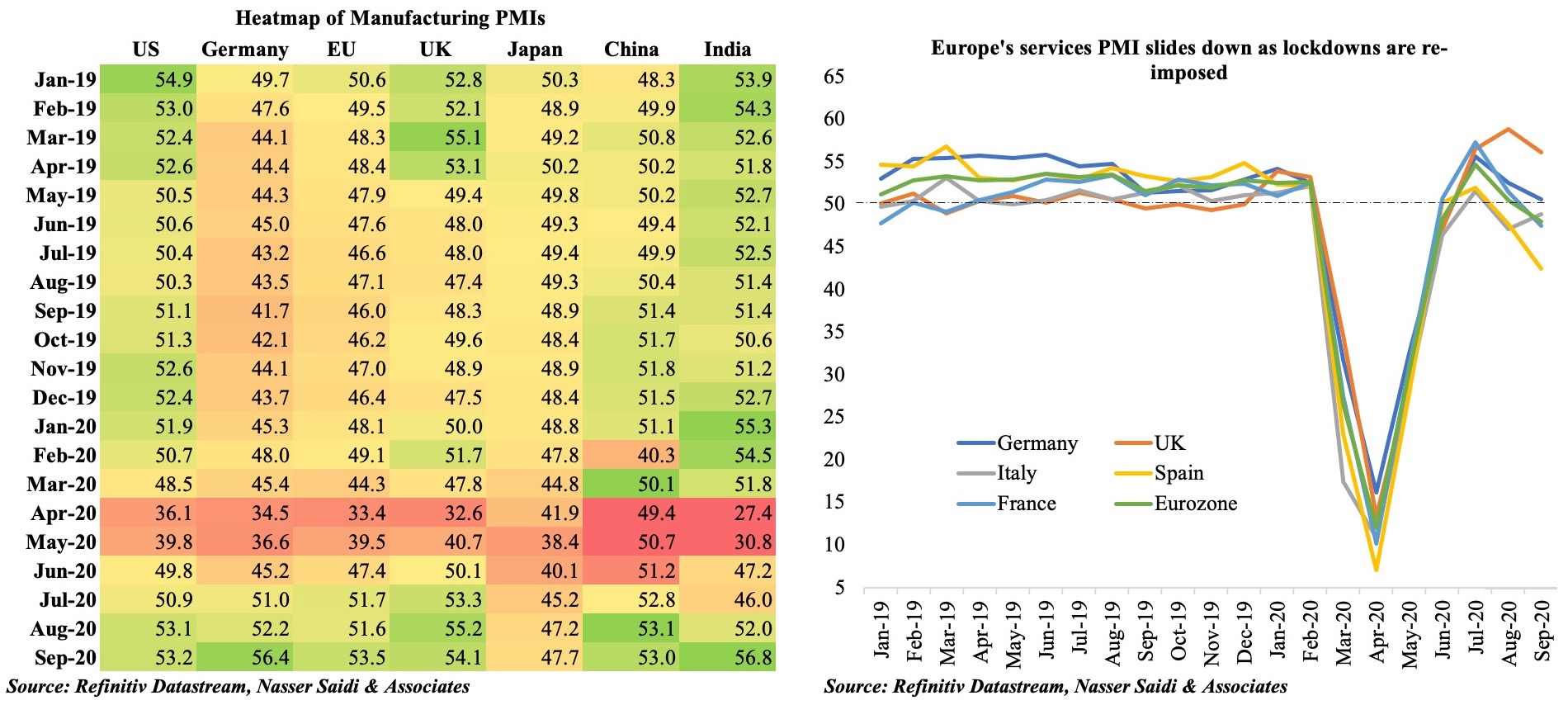
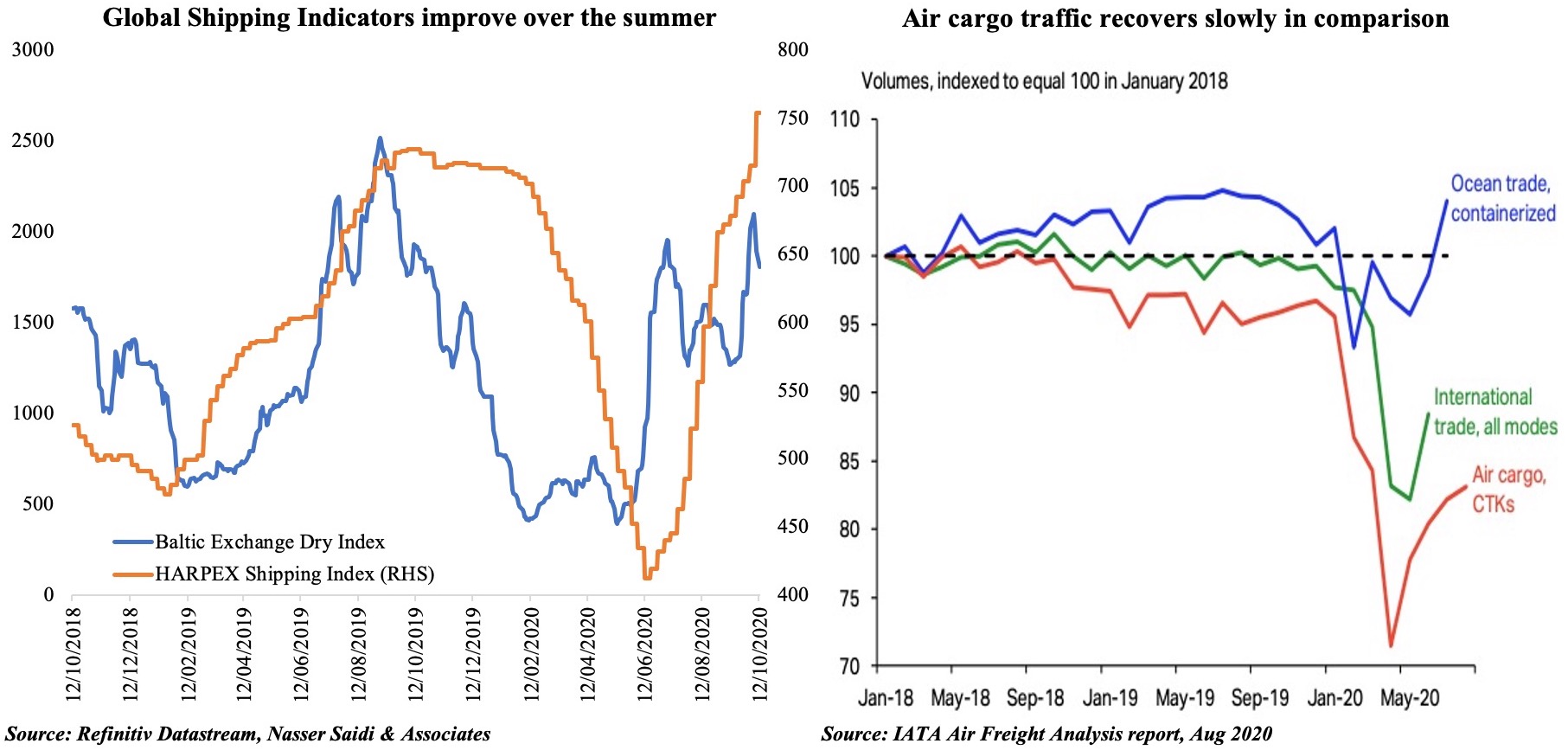
Recent manufacturing PMI readings have shown an increase in new export orders, supported by a pickup in demand. Global shipping indicators have improved during the summer, with both the Baltic Exchange Dry Index (tracks rates for ships carrying dry bulk commodities) and the Harpex shipping index (index created using container shipping rates across different classes of ship) picking up pace. Both indices rose to its highest in more than a year last week, after having touched 3-year highs in mid-2019 and declining sharply during the Feb-Jun period. However, the air freight sector has not recovered in tandem with shipping (Figure below), a result of cheaper ocean trade – a pattern visible during downturns – as well as insufficient air cargo capacity (according to IATA).
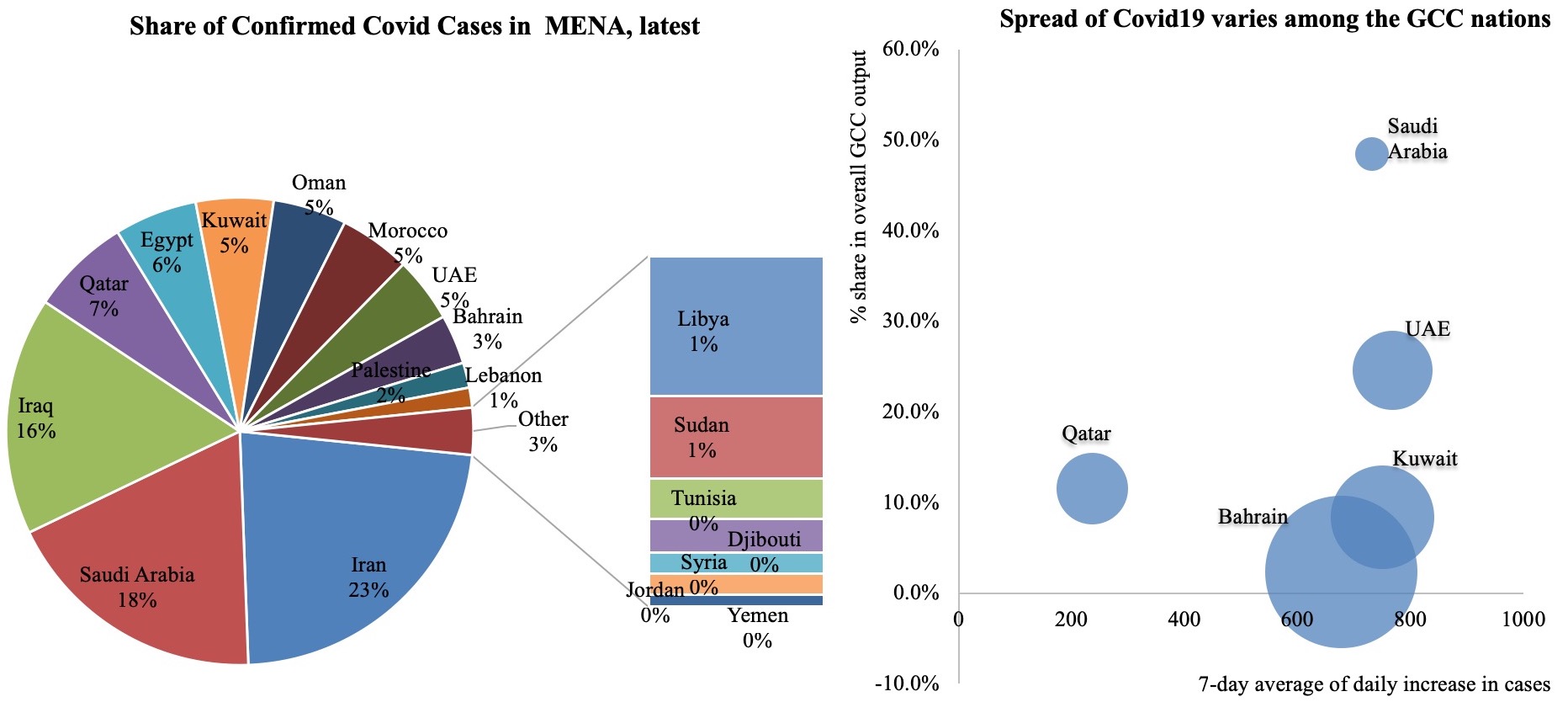
2. Regional PMIs
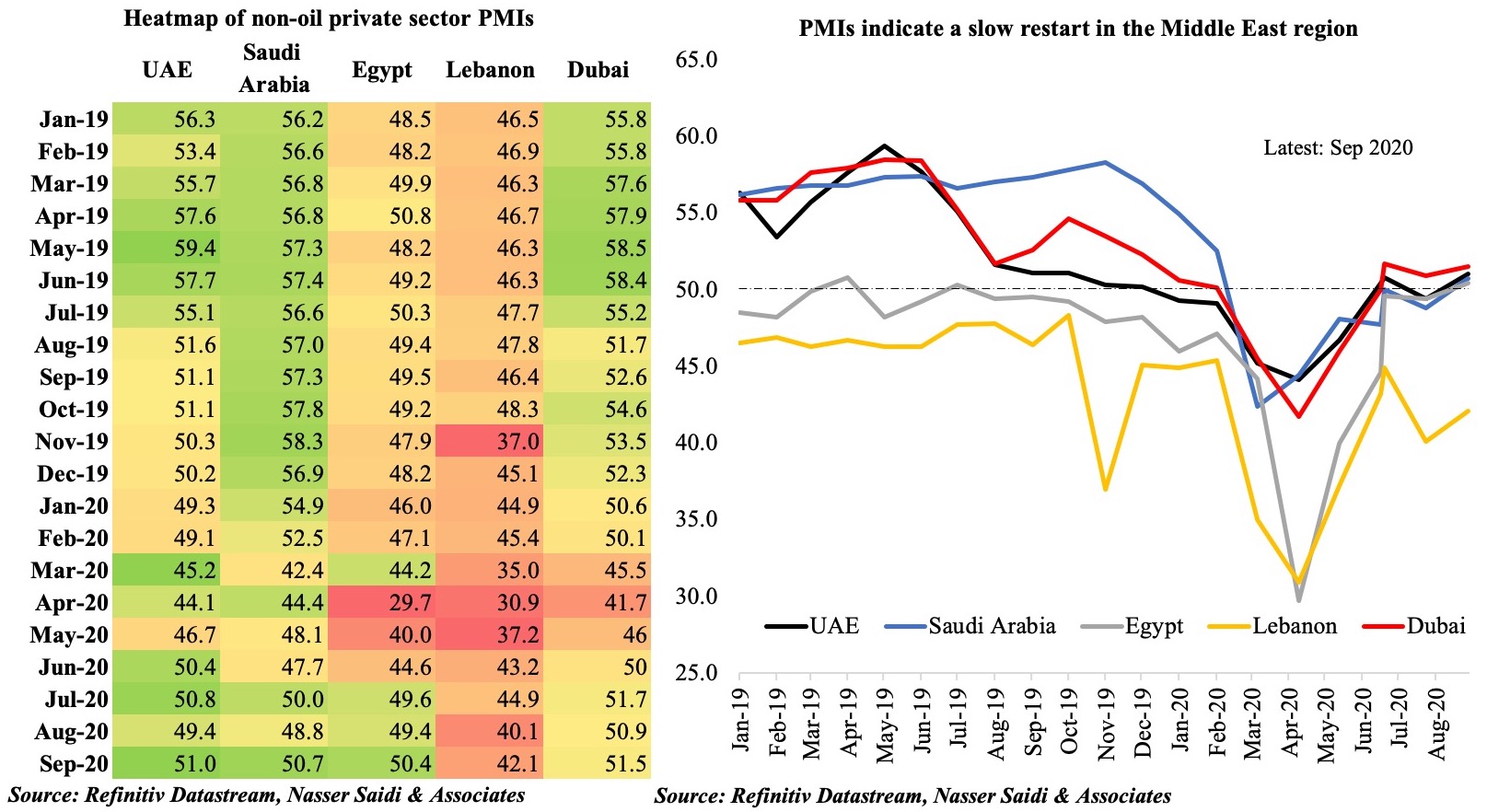
Regional non-oil private sector PMI’s indicate a slow restart: Sep’s modest improvement followed Aug when four of the countries moved into the contractionary territory (i.e. below the 50-mark). Significantly, demand growth has been picking up and the significant price discounting on offer has led to an increase in sales.
Job cuts are still occurring, as businesses adjust to reduce operating costs. The ILO estimates that Arab states witnessed a 2.3% drop in working hour losses in Q1 this year, followed by 16.9% and 12.4% respectively in Q2 and Q3. Job postings are slowly ticking up, though anecdotal evidence suggests that potential employees are willing to accept a significant pay cut to undertake similar work. This will lead to a wider disparity in public-private sector wages, not to mention the impact it would have on wider gender disparities (during Covid19, women are already more likely than men to witness a larger drop in mobility to lose jobs in the informal economy or see a reduction in working time).
Furthermore, with lack of access to finance/ liquidity, not all businesses will recover or survive in the next few months, should uncertainty remain. This could result in a structural change bought about due to Covid19 (e.g. the increase in number of online shopping platforms which are relatively less labour-intensive versus actual physical stores). Being faced with limited financial capabilities (due to job losses or salary cuts and depletion of savings), expatriates could also decide to return to their home countries (negatively affecting consumer spending in the region).
3. Stringency Index vs. Retail and Recreation sector activity
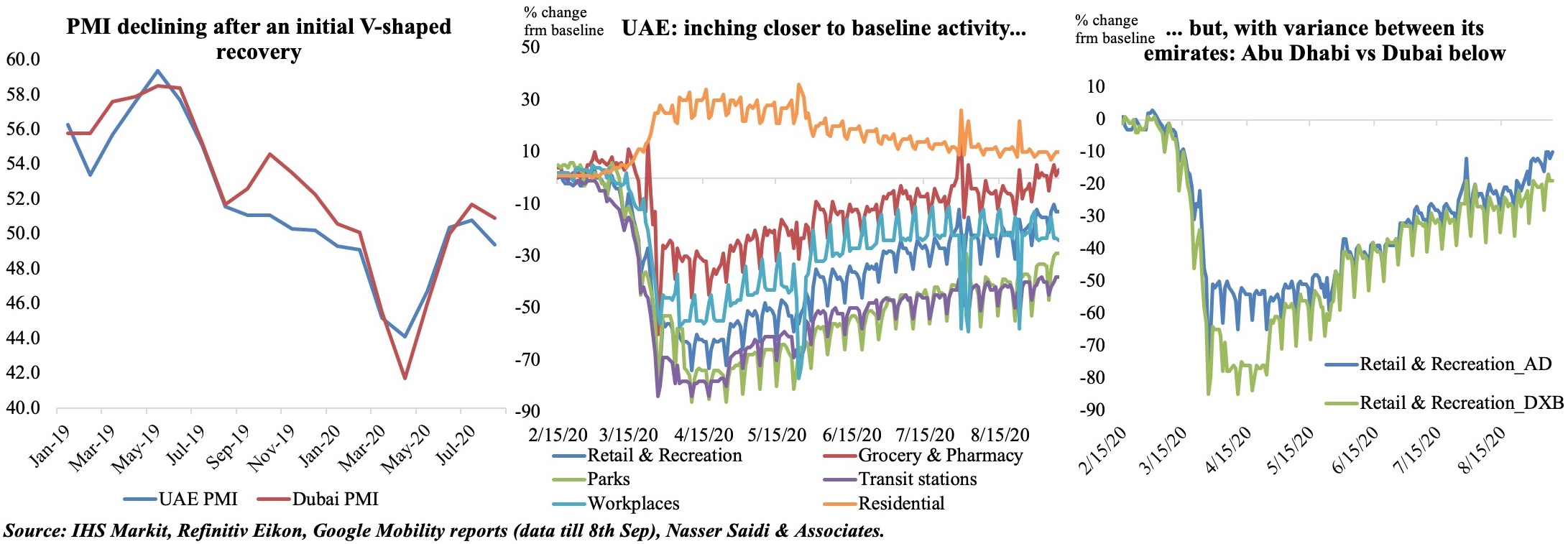
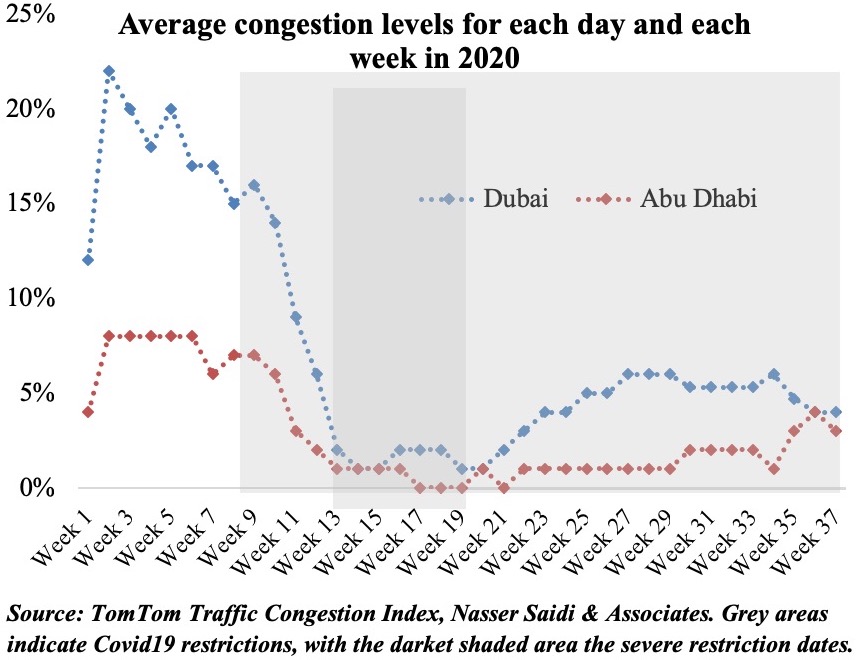
The Middle East has seen a resurgence in Covid19 cases in the recent weeks, and many nations are in the process of reimposing partial lockdowns or shorter nationwide lockdowns: the first panel in the figure below shows that the Government Response Stringency Index[1] has increased for the UAE in the past month (in line with the increase in cases). This is the best way forward, if we are to take into consideration the IMF’s recent World Economic Outlook analysis which found that early adoption of stringent and short-lived lockdowns curbed infections and could be preferable to mild and prolonged measures. The enforcement of lockdowns and social distancing policies was an important factor contributing to a recession: however, such short-term costs of lockdowns may lead to medium-term gains if the virus is contained.
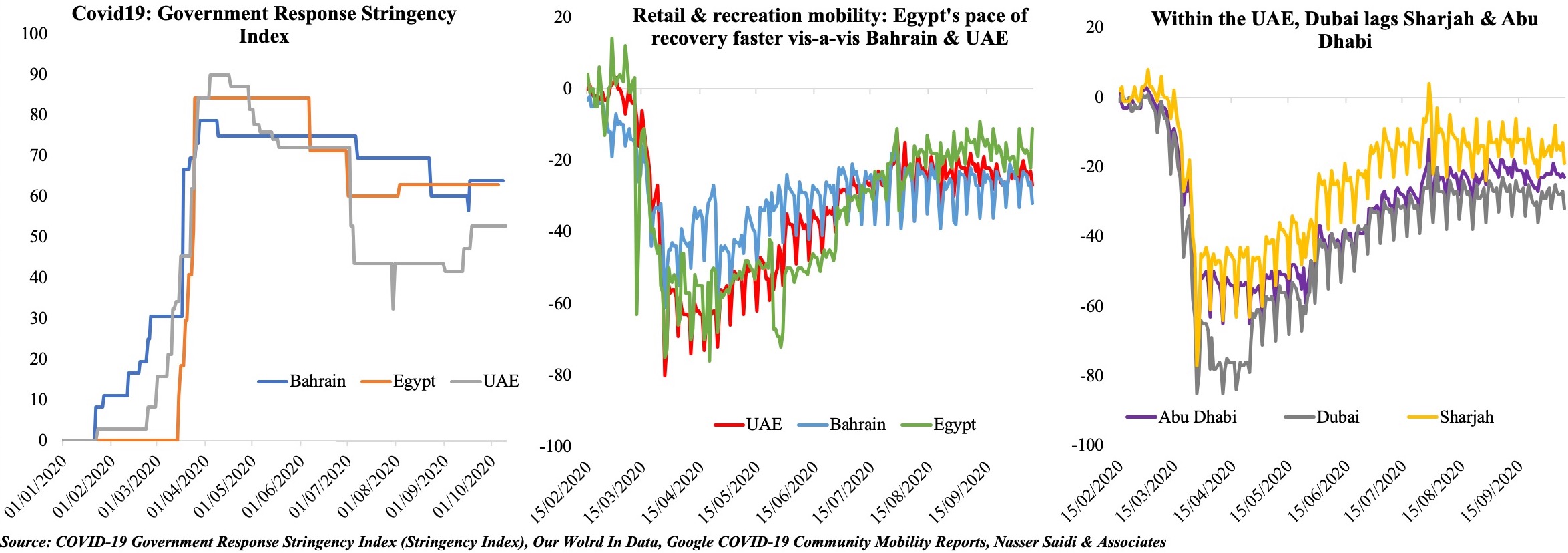
Google Mobility indicator for retail and recreation show that none of the three nations – Bahrain, Egypt, or UAE – have yet returned fully to the pre-Covid19 baseline. Among the three, Egypt, which had declined the most initially, recovered faster in comparison. More interestingly, within the UAE, recovery in retail sector mobility in Sharjah (-14% from baseline in Oct) and Abu Dhabi (-21% from baseline) has outpaced Dubai (-23%). This could potentially be due to higher confidence in these emirates – given mass testing in Sharjah, border controls in Abu Dhabi and a relatively longer lockdown period – compared to Dubai.
What next? Note that a second (or even third) wave of Covid19 is unfolding, as we enter the cold winter months: given the likelihood of resurgence of Covid19, partial recovery – as indicated by PMIs – may be temporary. If further virus containment measures are introduced, though it will dampen economic activity in the short-term, medium-term gains might be achieved. Initial restrictions will likely affect the customer-facing service sectors more than others, but risks to other sectors will increase if further restrictions are imposed. Overall, an air of uncertainty is unlikely to boost confidence among firms, negatively affecting investment decisions and economic activity. Governments need to signal willingness to continue stimulus measures if required and take decisions to introduce “circuit-breakers” if necessary.
[1] The Stringency Index is a composite measure based on nine response indicators that include school closures, workplace closures, and travel bans; the index ranges from 0 to 100 with 100 being the strictest. This index does not track the effectiveness of the response. More: https://www.bsg.ox.ac.uk/research/research-projects/coronavirus-government-response-tracker
Powered by: