Weekly Insights 6 May 2021: What do PMIs, Consumer Spending & Domestic Credit Tell us about Economic Activity?
Download a PDF copy of this week’s insight piece here.
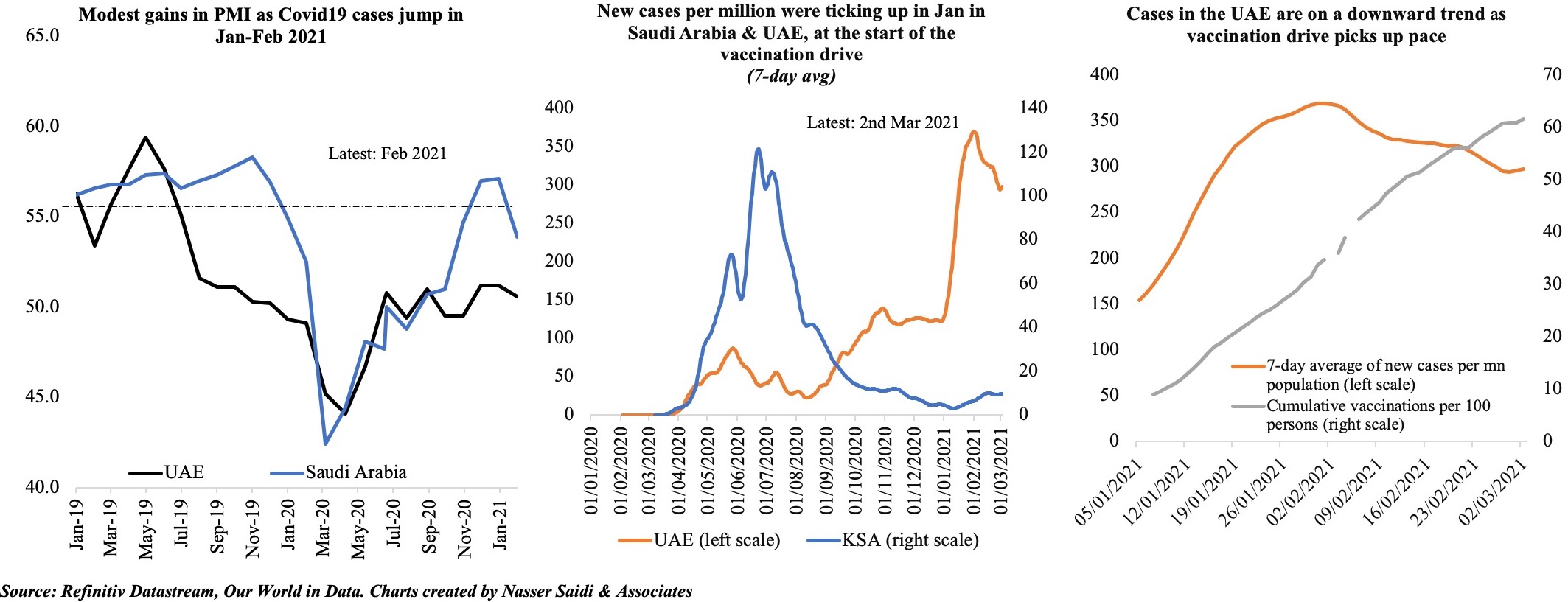
1. Manufacturing PMI rises globally; but, widespread vaccination required for confidence boost going forward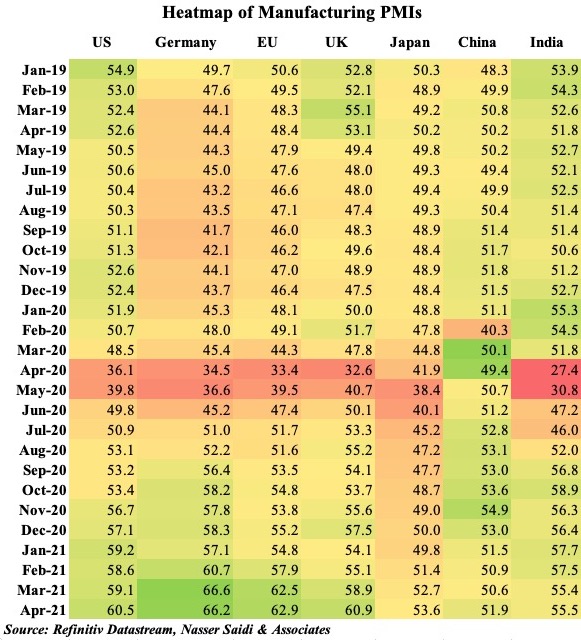
- The vaccination pace has been steadily increasing in many advanced nations including the US and UK – allowing the nations to reduce and/or remove severe restrictions. This has resulted in a return in confidence, evident in recent PMI data.
- However, the recent surge in Covid cases in India and Brazil could result in spillovers (Singapore reverted to Phase 2 restrictions); the only way out seems to be to vaccinating a vast majority of the global population.
- Unfortunately, poor countries are severely lagging behind in vaccination: in Africa, just 1% of the population has received at least one jab and 4.4% in Asia. This compares to 22% and 44% in Europe and America respectively. Vaccine shortages are still a problem (India’s Serum Institute is said to be severely behind on production)
- Another word of caution : while global manufacturing PMI hit a 11-year high, record supply chain delays are leading to production constraints; input costs rose at the fastest rate in a decade
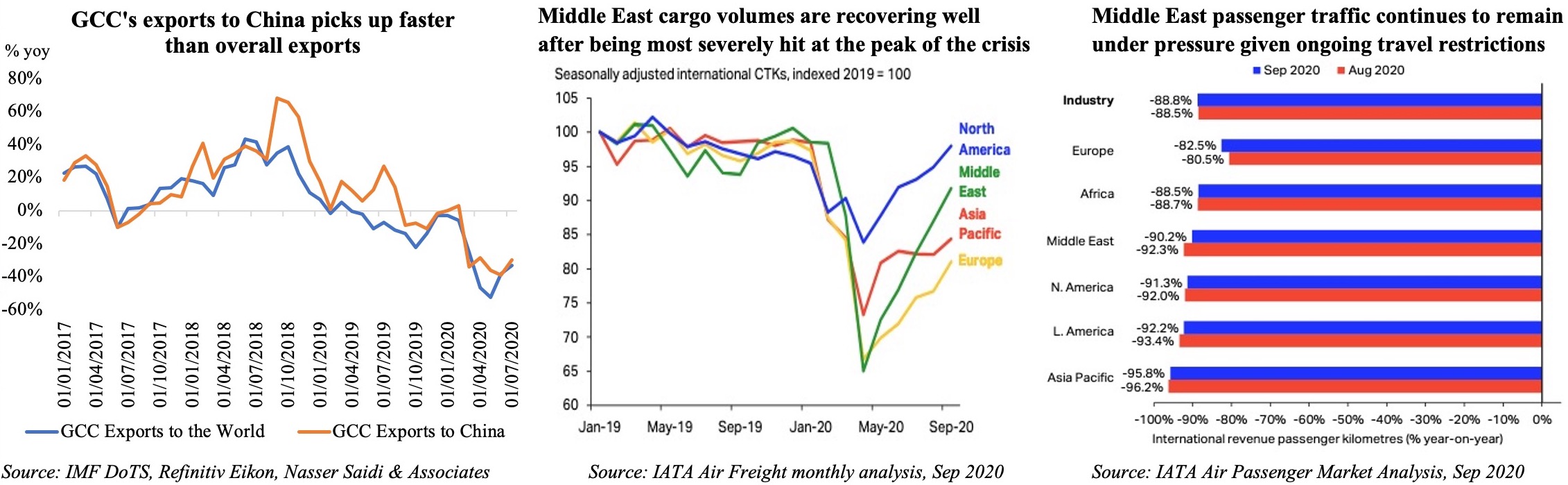
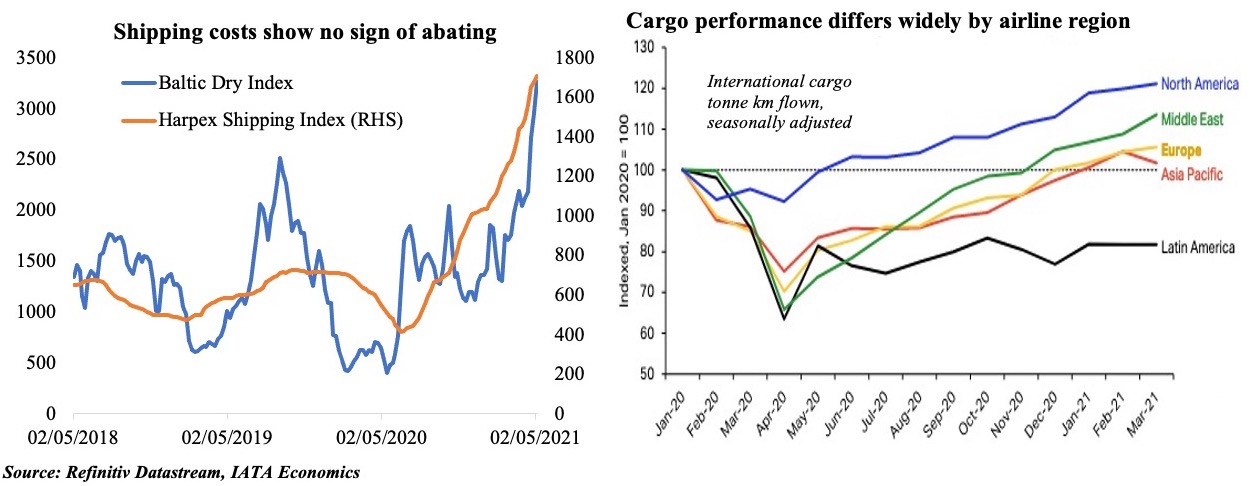
2. Shipping costs climb as demand increases, while air cargo struggles to keep up
- Container ship port calls are in many regions back to pre-pandemic numbers or higher (UNCTAD). But, high demand alongside shortage of containers has led to a surge in shipping costs (especially on long-distance routes). The recent Suez Canal blockage calls into question the vulnerability of trade chokepoints.
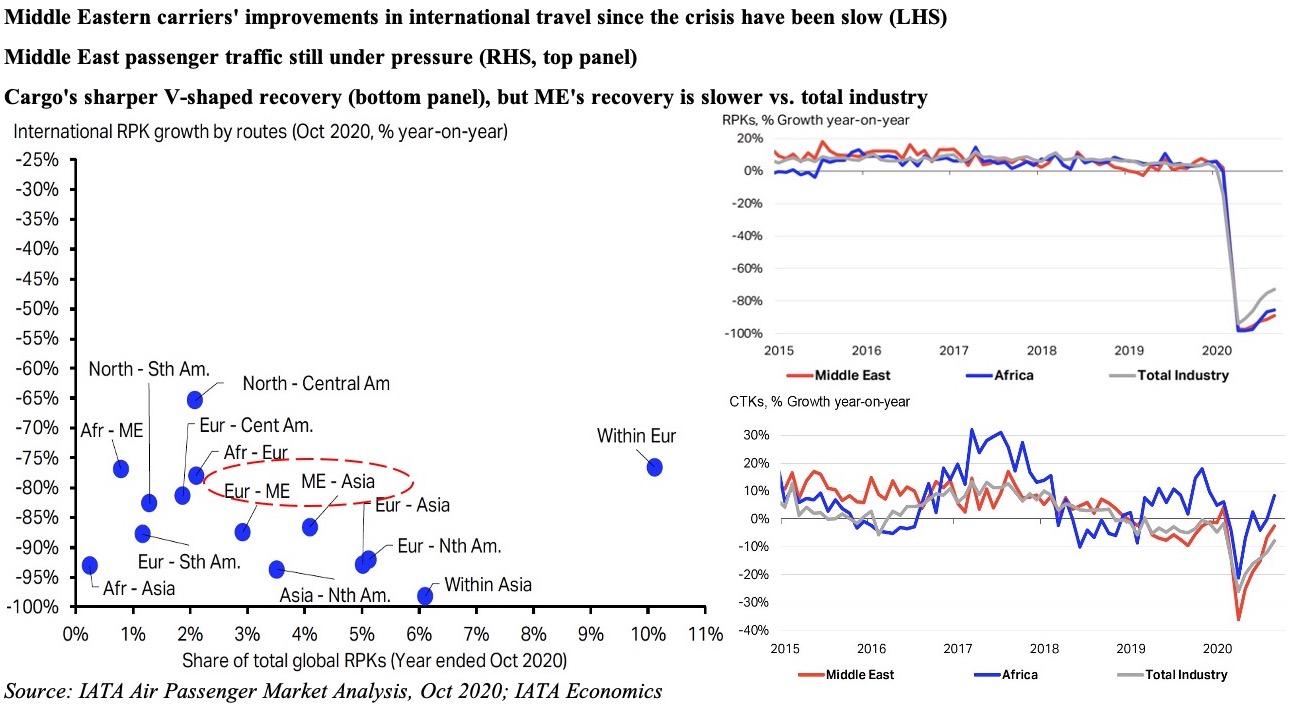
- Demand for commercial air traffic remains depressed: long-haul flights are still bearing most of the brunt as domestic travel is slowly picking up (as seen in China and the US). Travel bookings indicate strong domestic travel intentions and Europe could also witness a boost when it opens in summer for vaccinated tourists.
- Closure of long-haul routes continue to affect Middle Eastern airlines (revenue passenger kilometers were down by 81.7% yoy in Feb vs 74.7% globally); but, strong cargo growth was recorded (growing by 8.7% yoy in Feb 2021 vs the 9.5% drop in 2020; Middle East-Asia route grew the most – by 26.7% in Feb vs -7% in 2020)
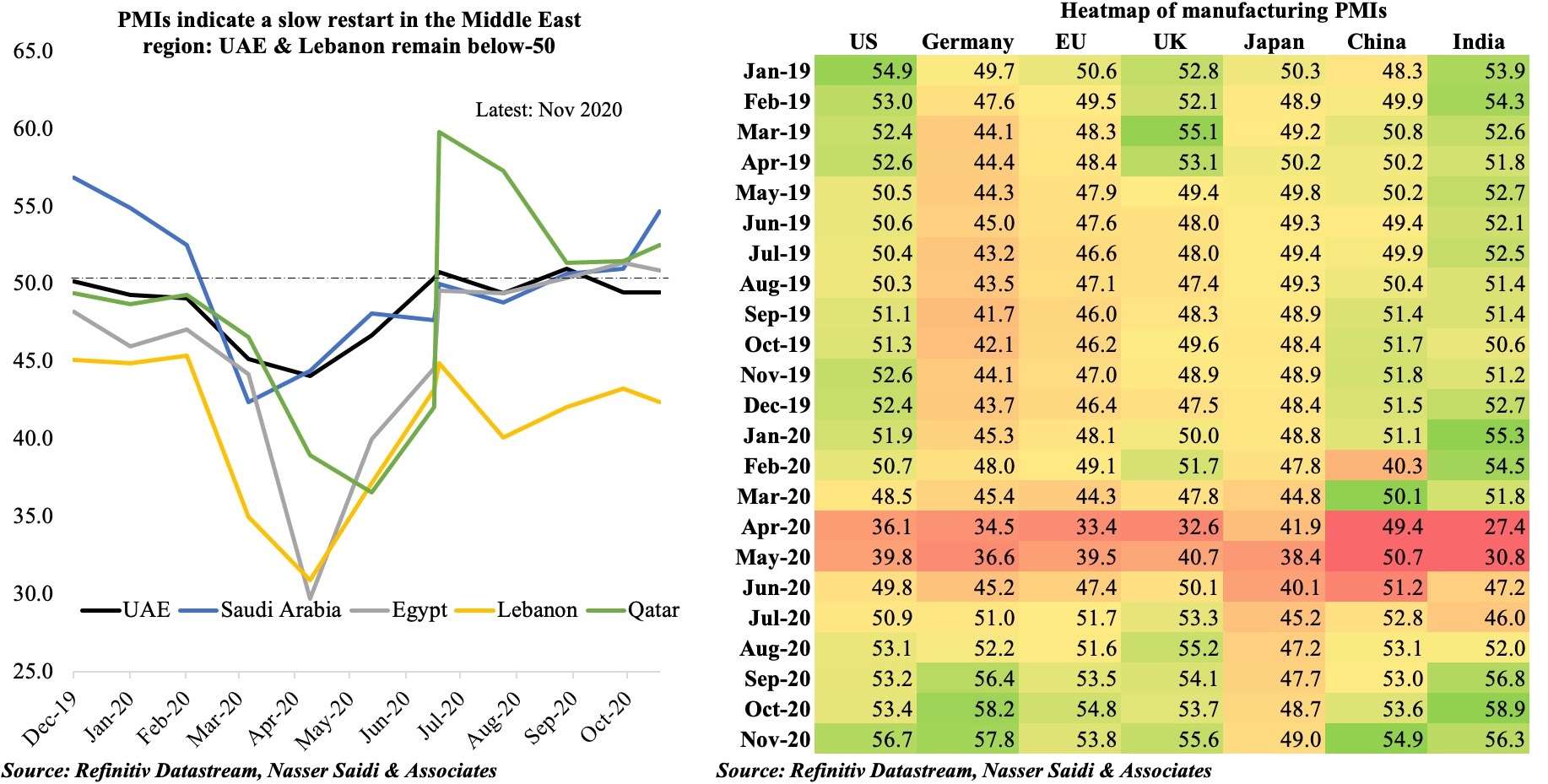
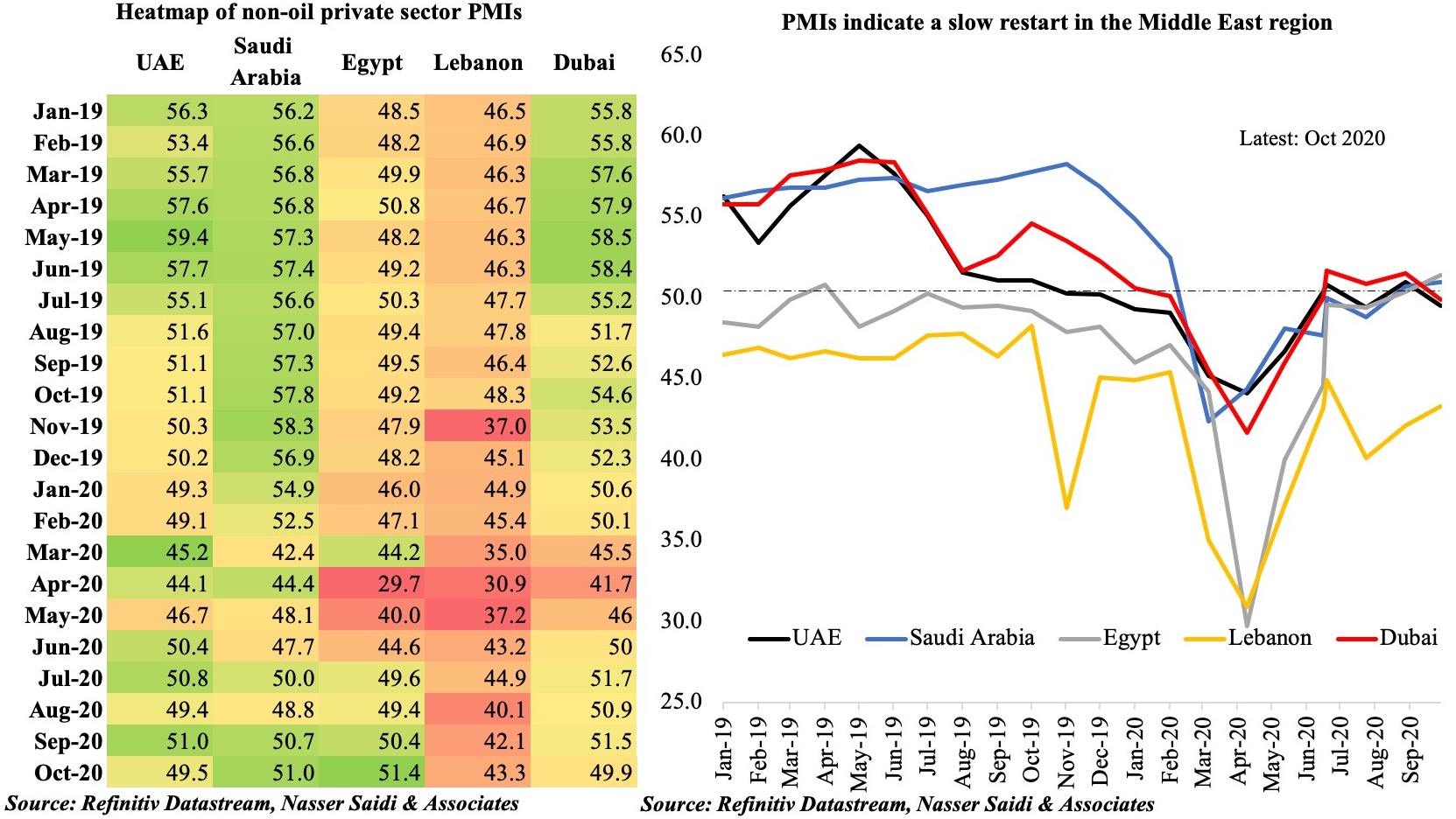
3. April PMIs edged up in UAE & Saudi Arabia: but employment sub-index diverges (as UAE stays below 50)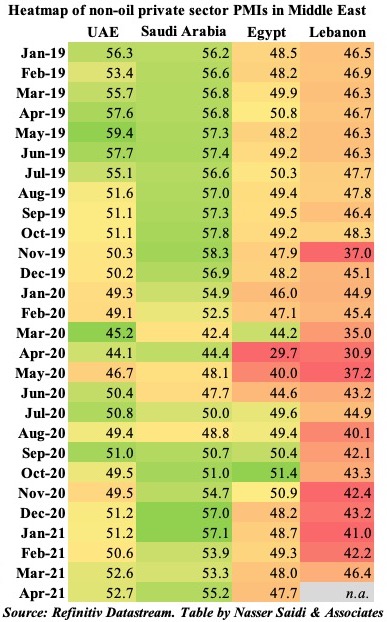
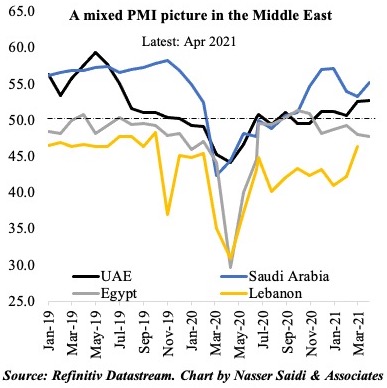
- In MENA, both Saudi Arabia and UAE posted higher PMI readings in Apr; Egypt declined further, falling below-50 for the 5th consecutive month.
- While vaccination pace is quite varied in the region, it seems to have a significant impact on business confidenc and the expectations of continued economic recovery. UAE has been the leader in vaccinating its residents, administering 108.99 doses per 100 persons, versus Saudi Arabia’s 28.2 and Egypt’s 0.64. This confidence has translated into the PMI readings.
- With UAE’s major export markets still rattled by Covid19, near-term outlook has risks; employment sub-index also fell for the 3rd month in a row. Though export orders rose, demand was largely domestic based.
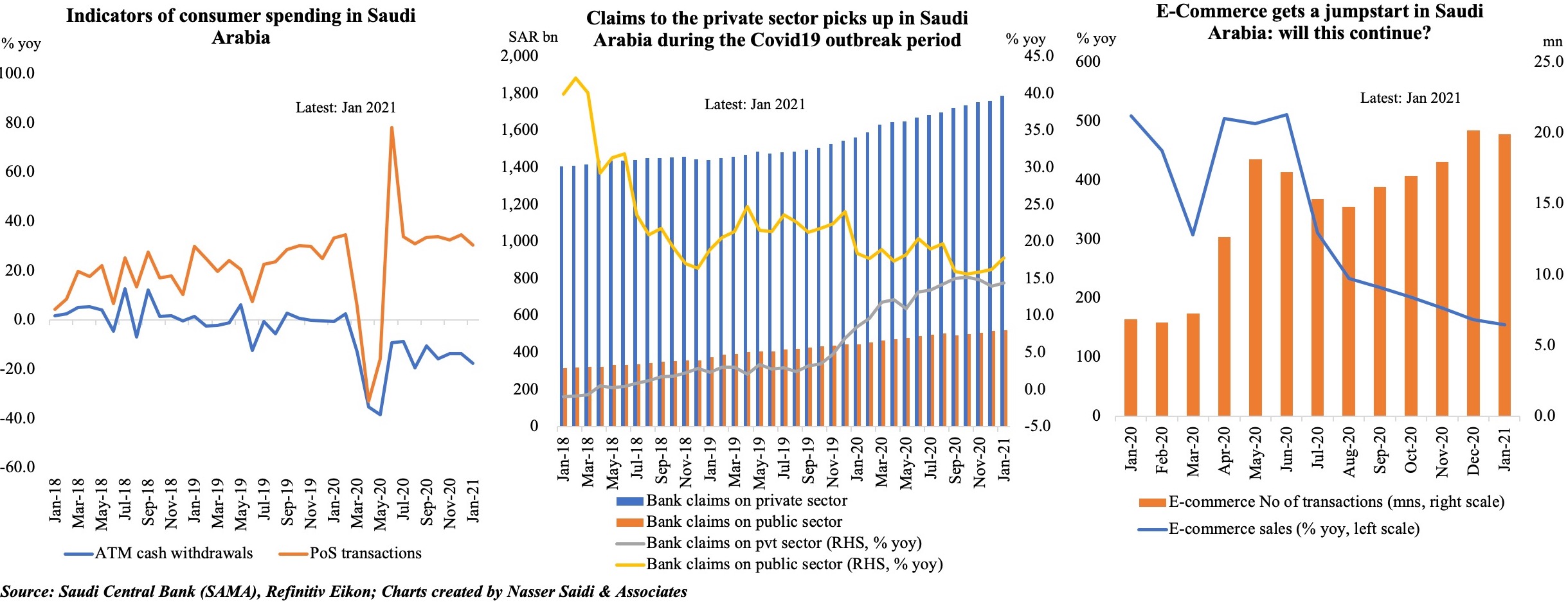
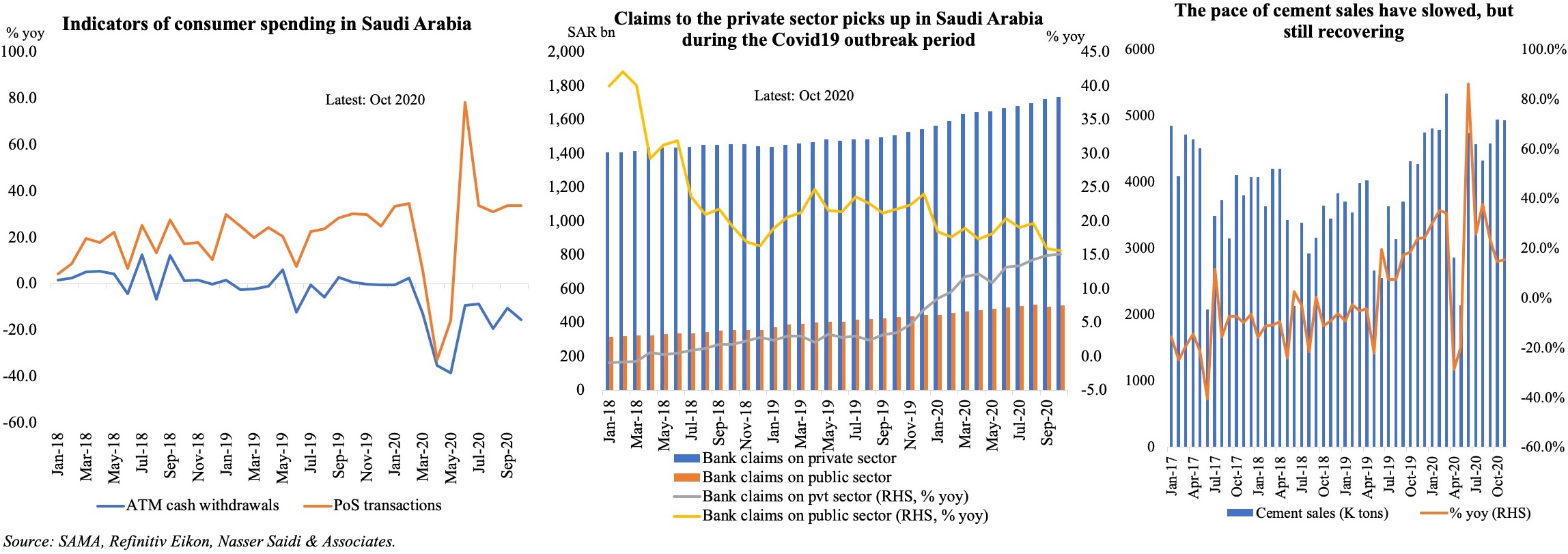
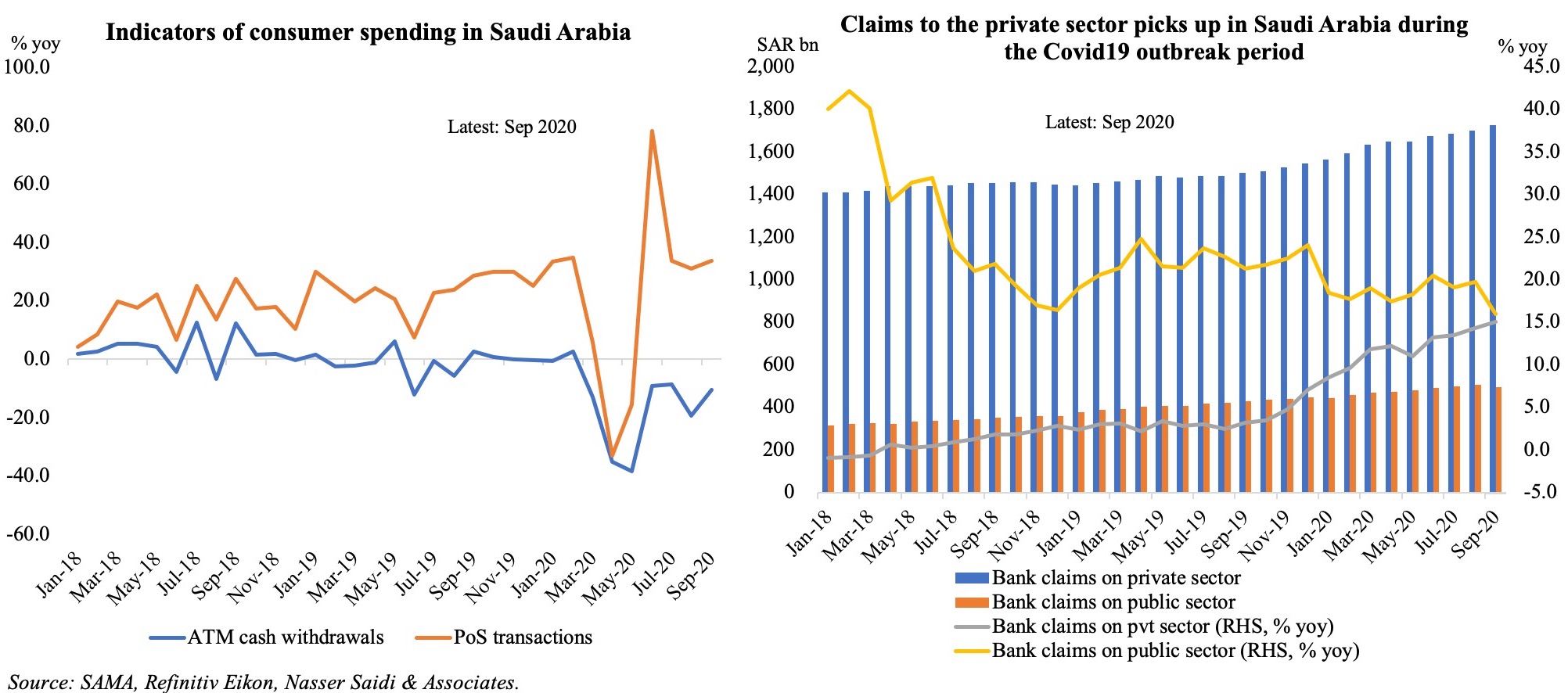
4. Consumer Spending Rebounds in Saudi Arabia
- The Saudi Central Bank’s monthly data on consumer spending showed a rebound in Mar, partly due to the low base in Mar 2020. PoS transactions continue to rise, accelerating by 64.7% yoy and 31.5% mom in Mar. ATM cash withdrawals fell by just 4% yoy, following 7 months of double-digit declines, and by 21% mom.
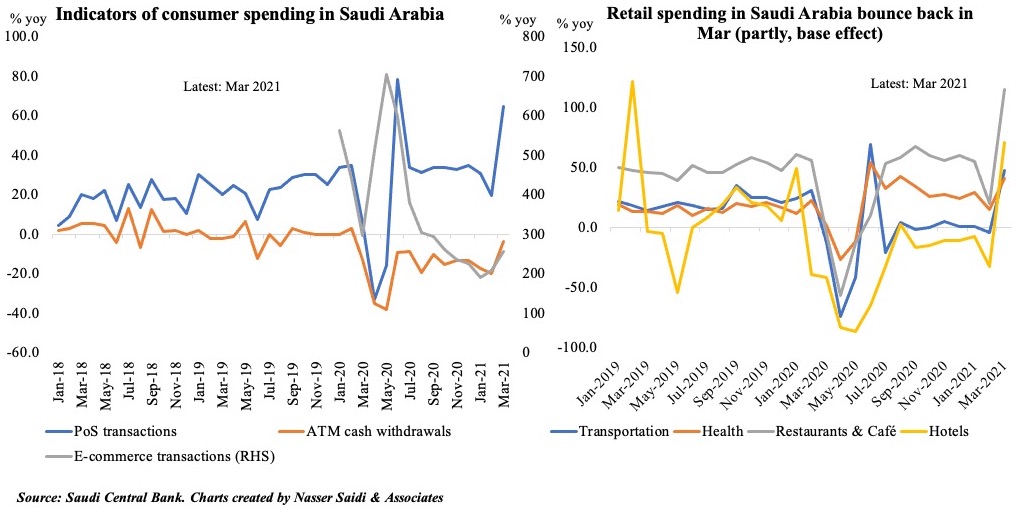
- Retail spending by sector showed a decline only in education (-2% mom and -18.3% yoy); clothing and footwear posted the highest pickup in mom terms (+68.2%). Spending has been slower in a few sectors ahead of the month of Ramadan (when many discount offers are available) like food and beverages, and electronics.
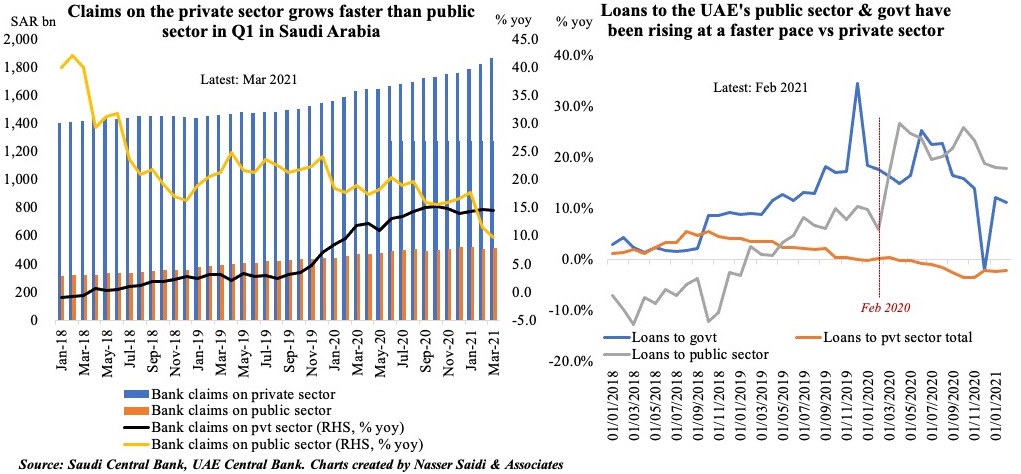
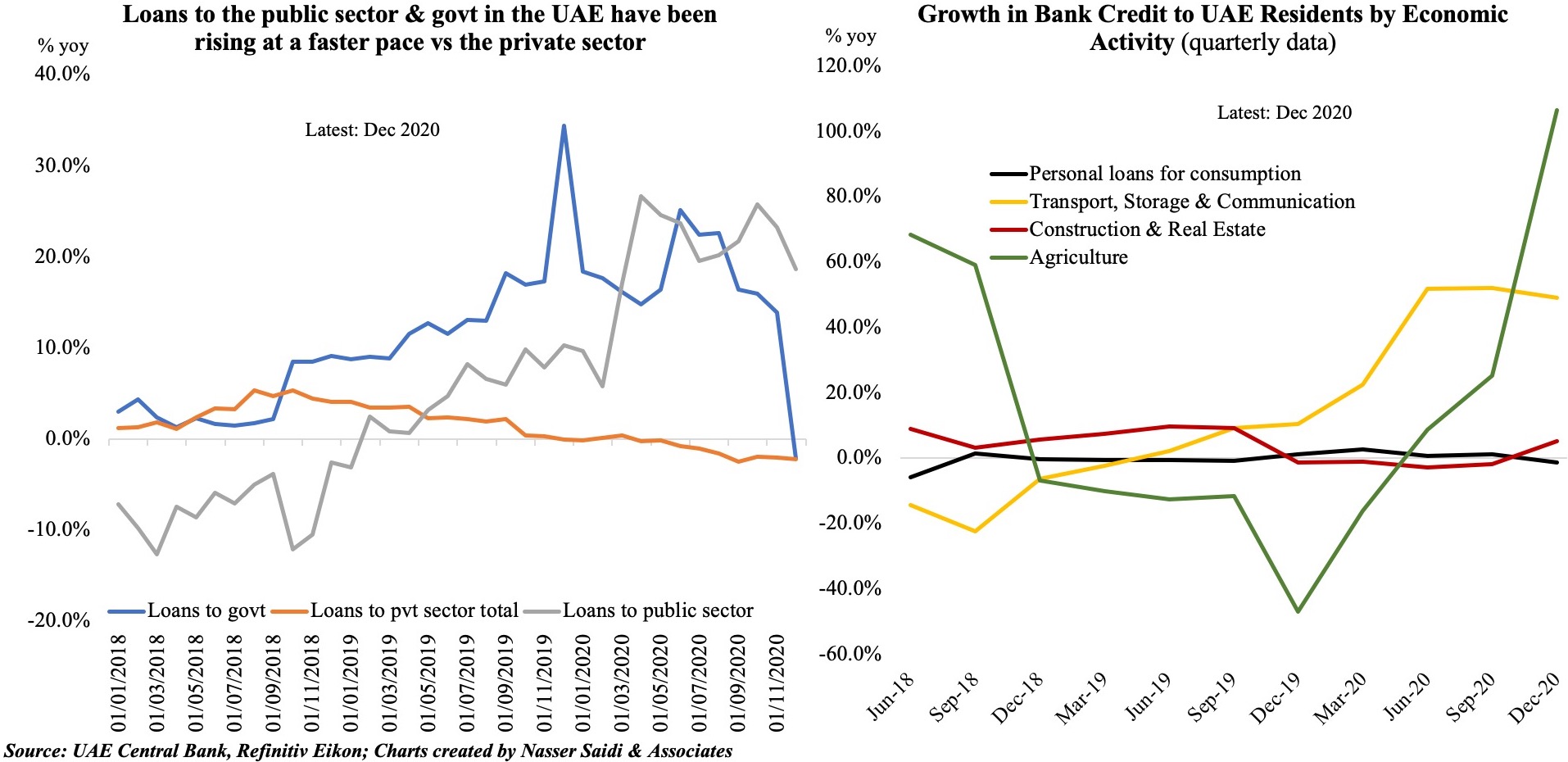
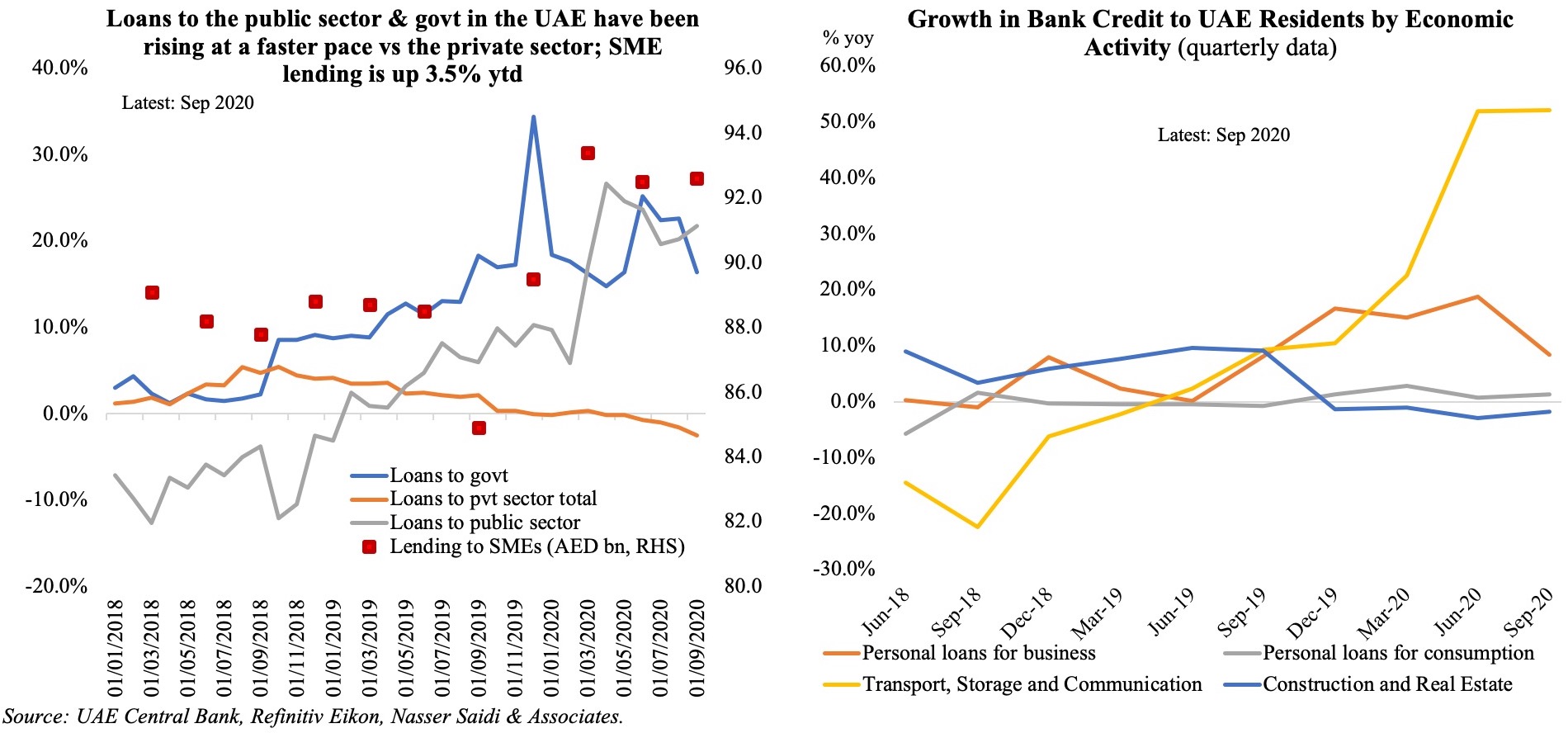
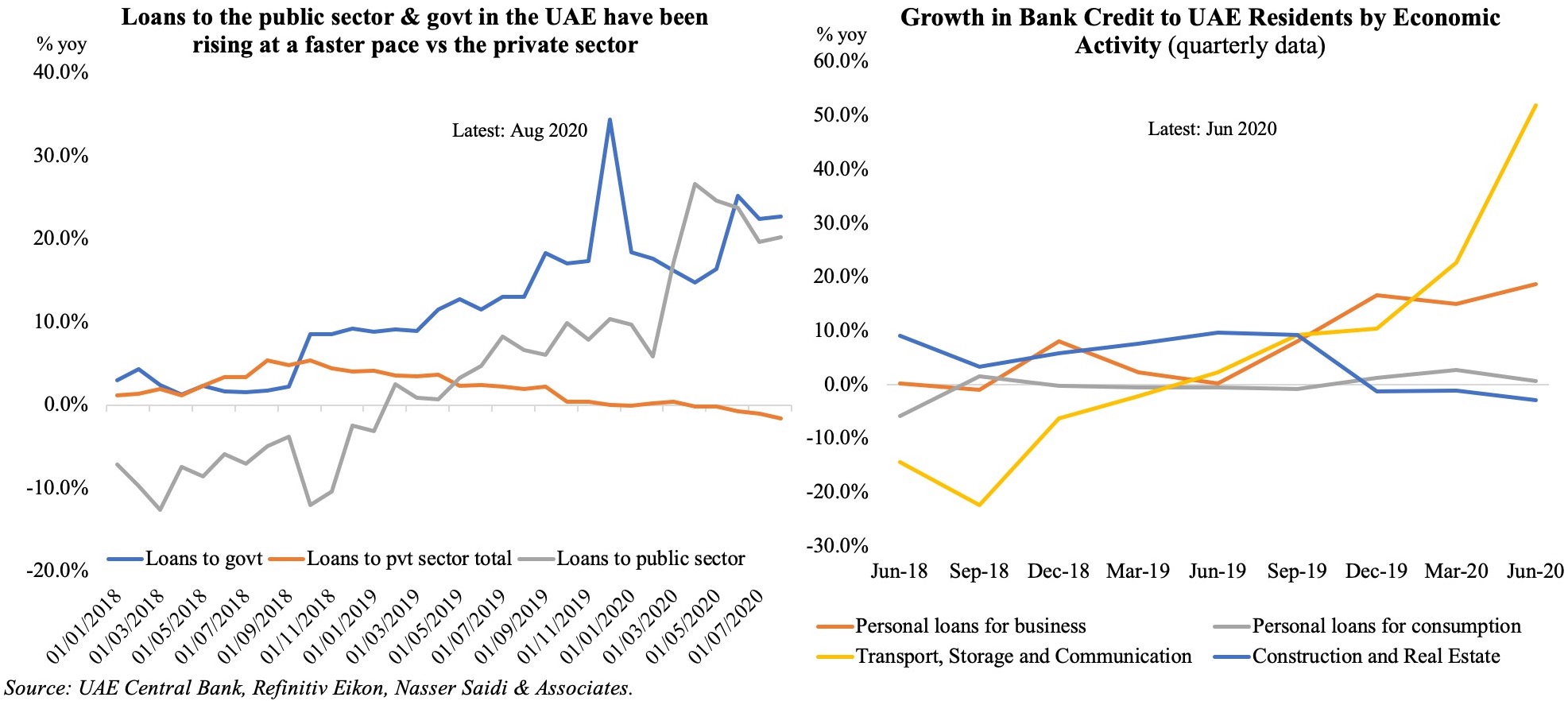
5. Varied patterns of domestic credit growth in Saudi Arabia & the UAE
- Loans disbursed in both Saudi Arabia and the UAE has been ticking up in 2021.
- Total domestic credit disbursed in UAE grew by 2.1% yoy in Jan-Feb 2021; the uptick has been in claims to the public sector (+17.9%), government (+11.6%) and private financial institutions (+8.8%) vs loans to the private sector (-2.3%). Together, loans to the government & public sector accounted for 30% of total in Feb 2021.
- In Saudi Arabia meanwhile, claims on the private sector grew by 14.6% yoy in Q1 2021 – faster than claims on the public sector (+13% yoy).