Markets
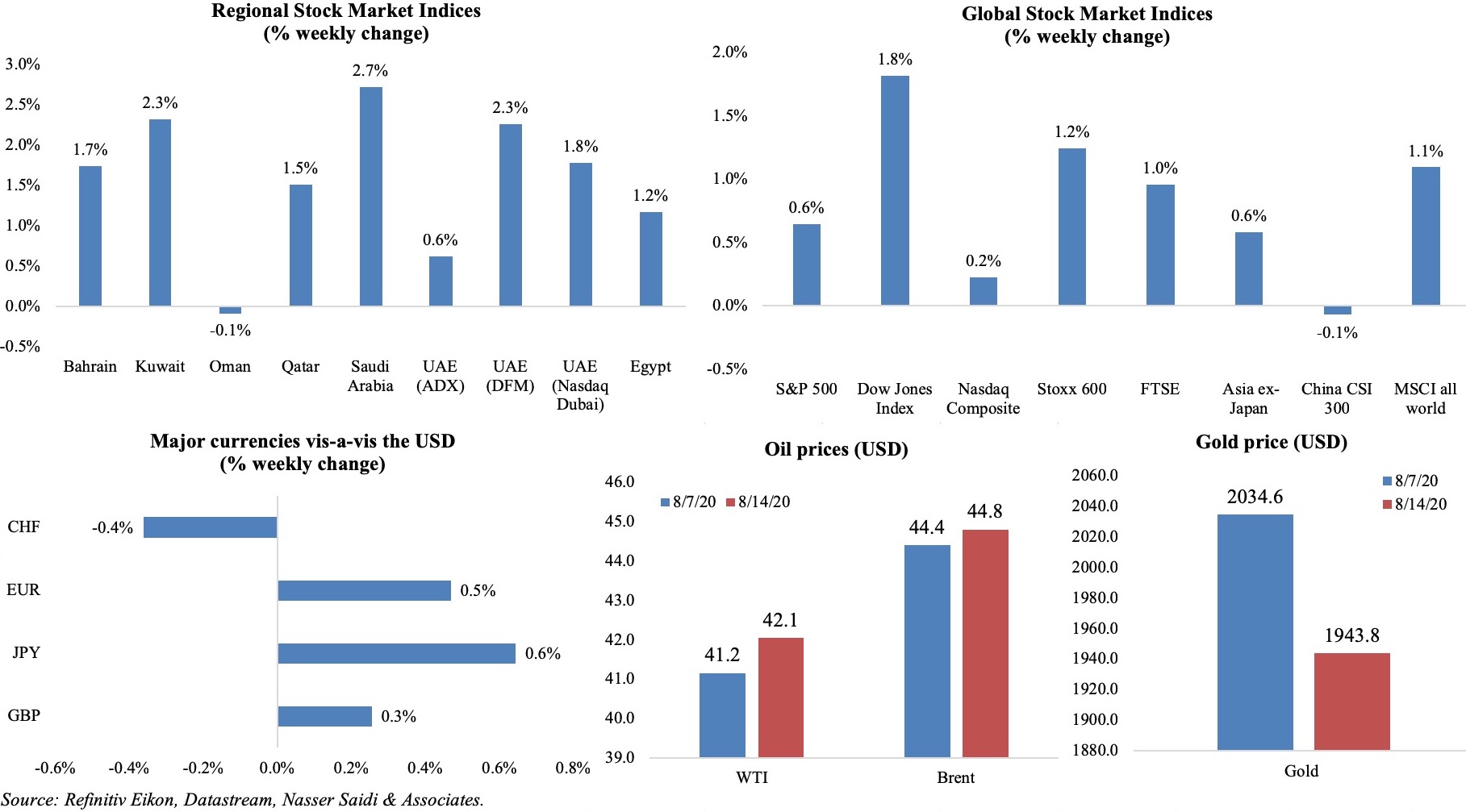
Global stock markets had another good week – though US stocks narrowly missed all-time highs, stocks linked to tourism/ airlines tumbled in Europe (surges in Covid19 cases are leading to quarantine requirements related to travel) and China’s stocks closed lower after weaker-than-expected data releases. Regional markets were mostly up during the week, with Dubai’s market hitting a 2-month high on Thur. The dollar index was into its 8th straight week of losses, while the euro, yen and pound sterling gained. Oil prices fell below USD 45 ahead of the OPEC+ meeting this week. Gold declined by 4.5% – biggest weekly fall since early Mar – following 9 weeks of gains.
Weekly % changes for last week (13-14 Aug) from 6th Aug (regional) and 7th Aug (international).
Global Developments
US/Americas:
- Inflation in the US rose by 1% yoy and 0.6% mom in Jul, thanks to an increase in costs of transport (2.9%), apparel (+1.1%), lodging away from home (1.2%) and car prices (0.8%). Excluding food and energy, prices were up 1.6% yoy and 0.6% mom.
- Producers price index in the US rebounded by 0.6% mom in Jul (Jun: -0.2%). This was the largest gain since Oct 2018 and was supported by rise in gasoline costs and portfolio management fees. Excluding food and energy, prices edged up by 0.3% mom.
- Industrial production increased in the US for a 3rd straight month, up by 3% mom in Jul (Jun: 5.7%); production is still 8.4% below Feb numbers. Factory output rose by 3.4%, given a 28.3% gain in the production of cars, trucks and auto parts. Capacity utilization also ticked up to 70.6% (Jun: 68.5%), though remaining below its long-term average of 79.8%.
- Non-farm productivity grew by 7.3% in Q2 from -0.3% in Q1 – the largest rise since Q2 2009. Hours worked tumbled by 43.0% in Q2, the largest since the series started in Q1 1947.
- US retail sales increased by 1.2% mom in Jul, following an 8.4% surge in Jun. Sales are higher than pre-Covid19 levels and up 2.7% yoy. Monthly sales picked up in electronics and appliances (22.9%), clothing (5.7%), bars and restaurants (5%) while motor vehicle parts and sales at dealers dropped by 1.2%. However, with the resurgence of Covid19 cases and expiry of federal unemployment benefit, sales are likely to remain mild going forward.
- Michigan consumer sentiment index for Aug edged up to 72.8 in Aug (Jul: 72.5).
- US budget deficit ballooned to a record USD 2.81trn for the period Oct 2019-Jul 2020. About USD 63bn was added to the deficit in Jul – the lowest monthly figure since the outbreak began.
- Initial jobless claims declined below the 1mn mark, totalling 963k in the week ended Aug 8, from 1.191mn the week before. Continuing claims decreased to 15.486mn in the week ended Aug 1, equaling 10.6% of the workforce.
- Mexico’s central bank lowered its benchmark interest rate by 50bps to 4.5%, after the country recorded its fifth consecutive quarter of contraction.
Europe:
- Eurozone GDP plunged by 12.1% qoq and -15% yoy in Q2 – the sharpest decline since the time series began in 1995. Quarterly GDP declined by more than 10% in Germany, Italy, France, Spain and the UK with the latter posting a fall of more than 20% during the quarter. Finland and Denmark fared relatively better, with drops of 3.2% and 7.4% respectively.
- The number of employed persons decreased by 2.6% qoq in the EU and by 2.8% in the euro area in Q2. The 5.5m job losses in the EU, which included 4.5m job losses in the eurozone, were “the sharpest declines” since the time series began in 1995, according to the Eurostat.
- Germany’s ZEW survey showed a deterioration in the assessment of the current situation (-81.3 in Aug from Jul’s -80.9) while economic sentiment improved (to 71.5 from 59.3). Economic sentiment index for the wider eurozone moved up to 64 from 59.6 in Jul.
- Wholesale prices in Germany slipped by 2.6% yoy in Jul (Jun: -3.3%), due to large declines in costs of used and residual materials (-18.4%), petroleum products (-17.9%) and live animals (-8.6%) among others. Consumer prices stayed flat at 0% yoy in Jul.
- Industrial production in the eurozone picked up by 9.1% mom in Jun, though the pace of recovery has slowed from May’s 12.3%; it still remains 11.6% below Feb levels. In yoy terms, production dipped by 12.3%, following the 20.4% plunge the month before.
- Preliminary estimates showed that UK GDP contracted by 20.4% qoq in Q2 – the worst quarterly slump on record – dropping the country in recession for the first time in 11 years. However, there is some positive news: in Jun alone, GDP bounced back by 8.7% mom (May: 1.8%) as restrictions were eased.
- Industrial production in the UK picked up by 9.3% mom in Jun (May: 6%), supported by manufacturing which gained by 11% (8.4%). In yoy terms, manufacturing was down 14.6%.
- Unemployment rate in the UK remained steady at 3.9% in the 3 months to Jun. A record decline in total weekly hours worked, with the average down by 203.3mn to 849.3mn in Q2.
Asia Pacific:
- China’s inflation increased by 0.6% mom and 2.7% yoy in Jul (Jun: -0.1% mom and 2.5% yoy), due to higher food prices (+13.2%). Core inflation (excluding food and fuel prices) fell to a 10-year low of 0.5%. Producer price index meanwhile declined by 2.4% in Jul following a 3% dip the month before.
- Money supply (M2) in China grew by 10.7% to CNY 212.55trn in Jul after posting an 11.1% gain the month before. New loans slowed to CNY 992.7bn from CNY 1810bn the month before, with corporate loans down to CNY 264.5bn (Jun: CNY 927.8bn). The annual growth of outstanding total social financing (TSF), a broad measure of credit and liquidity, quickened to 12.9% (Jun: 12.8%).
- Industrial production in China grew by 4.8% yoy in Jul, supported by new infrastructure projects leading to demand for commodities (including steel). Fixed asset investment declined by 1.6% yoy in the period Jan-Jul from the 3.1% drop in H1. FDI expanded by 15.8% yoy to CNY 63.47bn in Jul. Overall FDI inflow turned positive in Jan-Jul (+0.5% yoy) vs H1’s -1.3%.
- China’s retail sales edged down for the 7th straight month, down by 1.1% yoy in Jul, following the 1.8% dip in Jun. On a positive note, car sales rose 12% yoy in Jul.
- Japan’s current account balance narrowed to a five-year low of JPY 167.5bn in Jun (May: JPY 1176.8bn). Exports and imports fell by 25.7% and 14.4% respectively in Jun, causing trade deficit to widen to JPY 157.7bn; 99.9% drop in foreign tourists added to the travel account deficit.
- Industrial output in India declined for the 4th consecutive month by 16.6% yoy in Jun (May: -33.9%), with manufacturing reporting a 17.1% reduction (-38.4%). For the period Apr-Jun, overall IP fell by 35.9% yoy, while manufacturing plunged by 40.7%.
- WPI inflation in India fell by 0.58% yoy in Jun (May: -1.81%) in spite of costlier food prices. Inflation in food items touched a 4-month high of 4.08% in Jul, due to vegetable costs (+8.2%).
- Trade balance in India returned to a deficit of USD 4.83bn in Jul, after a month of trade surplus (USD 0.79bn in Jun). Merchandise exports fell for the fifth consecutive month by 10.2%, while imports dipped 28.4%.
- GDP in Hong Kong shrank by 0.1% qoq and 9% yoy in Q2 (Q1: -5.5% qoq and -9.1% yoy) – the 4th straight quarter of yoy declines. The resurgence of Covid19 cases weighed on consumer and tourism-related sectors, as visitor arrivals were down by 99.7% in Jun. The revised forecast is for a 6-8% drop in GDP this year.
- Singapore enters a technical recession as GDP plummets by 9% qoq and 13.2% yoy in Q2, worse than initial estimates, bringing the GDP contraction in H1 to 6.7% yoy. With the circuit break implemented in 7 Apr-1 Jun, activity dropped across the board: construction (-59.3% yoy), accommodation and food services (-41.4%), transportation and storage (-39.2%) and wholesale and retail trade (-8.2%) among others. For the full year, revised estimates expect an economic contraction of between 5-7%.
Bottom line: Q2 GDP data from the eurozone, Hong Kong, Singapore show massive plunges into recession (given restrictions during most of the quarter). More recent economic data (for Jun-Jul) across major markets are picking up in mom terms, but remain mostly lower than pre-pandemic readings: a second wave might put the brakes on this recovery. The rush to vaccines gain speed: Russia started its production of the Covid19 vaccine, as global confirmed cases crossed 21mn, while India – where both number of fresh cases and deaths touched record highs – stands ready to mass produce vaccines once they are ready. Watch out for key meetings this week – compliance to be a major discussion point at the OPEC+ ministers meeting (quota compliance fell to 96% in Jul, from 106% in Jun, with its collective output increasing by 1.1mn barrels per day, according to S&P Global Platts’ survey of production); Brexit discussions continue with formal negotiating sessions starting Aug 17 (can they reach a deal by the Oct 2 deadline?); central bank meetings this week (China, Indonesia, Philippines, Turkey) are likely to keep policy unchanged. A meeting to review the US-China Phase 1 trade deal (scheduled for Aug 15) has been delayed with no new date set as election fever picks up in US (with Biden’s choice of Senator Kamala Harris as the VP nominee and Trump’s comments on universal mail-in voting and the postal crisis).
Regional Developments
- Declines across oil and non-oil revenues – by 35% yoy and 13% respectively in H1 – resulted in a drop in Bahrain’s revenues by 29% to BHD 910mn. Expenditure during the period stood at BHD 1.708bn, resulting in a deficit of BHD 798mn – up 98% compared to the biannual deficit for the fiscal year 2019.
- The Bahrain Bourse listed the new Government Development Bonds: the bonds will mature in 5 years on Jul 30th There are now 14 conventional bonds and sukuk listed on the exchange with an approximate value of USD 7.11bn.
- The IMF approved a 12-month stand-by arrangement for Egypt at a total value of USD 5.2bn, to support the economy and mitigate the impact of the Covid19 outbreak.
- Egypt’s central bank held interest rates steady – lending rate at 10.25% and the deposit rate at 9.25% – at the latest meeting. This is the lowest since early 2016.
- Urban consumer price inflation in Egypt eased to 4.2% yoy in Jul (Jun: 5.6%); food prices were down by 1.5% yoy alongside an increase in electricity and energy prices. Core inflation declined to 0.7% in Jul (Jun: 1%).
- Unemployment among Egypt’s university graduates touched 36.1% in 2019: among these, male unemployment was 25.1% while among females, a staggering 53.2%.
- Iraq has started 10 rebuilding projects in Northern Mosul, which were part of the post-war reconstruction plan approved two years ago.
- Jordan closed the main Jaber border crossing with Syria for a week, after a spike in Covid19 cases from across the border. Other land crossings with Saudi Arabia, Israel and the Palestinian territories are only open for commercial goods.
- Foreign assistance to Jordan by donor countries and international financing institutions touched USD 465.4mn in H1 2020. This includes USD 107.6mn offered to support Syrian refugees and USD 222.2mn as soft loans.
- Auditing tax returns and a crackdown on tax evasion enabled Jordan to recover JOD 445mn in Jan-Jul this year.
- Kuwait moves into the 4th stage of gradual easing after the Covid19 outbreak from Aug 18: in this stage, more activities like gyms, sports clubs, salons and tailor shops will open.
- Kuwait’s fiscal deficit widened by 69% yoy to KWD 5.64bn (USD 18.44bn) in the 2019-2020 fiscal year, after revenues fell by over 16% alongside a 3.2% drop in expenditure (to KWD 21.14bn). If the public debt law (submitted in Jul) is passed by the Parliament, the government plans to issue KWD 4-5bn in public debt by the end of 2020-21 fiscal year.
- Kuwait’s finance minister stated that proposal to amend the Future Generation Law changes “the way of deduction” i.e. a deduction is made for the Future Generation Fund only when there is a surplus.
- Foreign reserves in Kuwait inched up by 2.99% yoy and 1.83% mom to KWD 13.92bn (USD 45.65bn) in Jun. The book value for gold reserves stood at KWD 31.7mn.
- A new residency law will come into effect in Kuwait, enabling an expat to stamp residence up to 5 years and for an expat businessman for 10 years.
- PMI in Lebanon ticked up to 44.9 in Jul (Jun: 43.2); output continued to drop, as did new orders while sales declined every month since Jun 2013 – all weighed down by lira’s depreciation, inflation surge, a liquidity crisis and lack of reforms.
- Lebanon approved a 2-week state of emergency in Beirut, giving the army powers to prohibit gatherings and close down assembly points.
- The IMF called on Lebanon to restore a solvent financial system and introduce temporary safeguards to avoid capital outflows (including formalizing capital controls and unifying the exchange rate) while also asking for comprehensive audits of key institutions, including the Central Bank. More: https://www.imf.org/en/News/Articles/2020/08/09/pr20278-statement-by-imf-md-kristalina-georgieva-int-conference-support-beirut-lebanese-people
- The IIF forecasts Lebanon’s economy to shrink by 24% this year, from an estimated 15% drop earlier. External financing needs for the next 4 years have increased to over USD 30bn.
- Lebanon’s economy minister clarified that the country has flour to last 4 months after reports emerged of a potential shortage. In addition, the World Food Programme is sending 17,000 tonnes of flour as a first batch of a 50,000-tonne supply plan.
- Oman secured a USD 2bn bridge loan with a group of international and regional banks, reported Reuters. The pricing was “relatively cheaper than the market” and the loan is likely to be repaid with money raised from an international bond issuance in 6 months’ time.
- About 79k expats have left Oman between Mar-Jun this year, on repatriation flights arranged by their respective countries, according to the National Centre for Statistics and Information.
- Total number of passengers travelling through Oman’s airports reached 3.59mn as of end-May 2020. Passengers through the Muscat International Airport fell by 51% yoy to 3.22mn.
- Oman’s largest solar power plant, Ibri II, is set to start operations by the mid-2021. The plant, being built at a cost of USD 400mn, is expected to power up to 33,000 homes and remove 340,000 tonnes of CO2 emissions from the country’s footprint per annum.
- Electricity production in Oman declined by 3.1% yoy to 13,254.8 GW per hour at end-May while water production increased by 5.5% to 147.26mn cubic metres.
- Industrial production index in Saudi Arabia slipped by 22.4% yoy, largely due to a decline in mining and quarrying production activity (-23.2%).
- Tadawul plans to launch an ESG index in cooperation with MSCI by end-2020 or Q1 2021. This will include at least 70 Saudi listed companies, according to the bourse’s chief executive.
- Foreigners net purchases on Saudi Tadawul surged to SAR 224.94mn in the week ended Aug 6th, compared with net sales of SAR 50.84mn and SAR 174.1mn by Saudi and GCC nationals respectively.
- FT reported that Aramco is planning to slash its capital spending to USD 20-25bn this year, to pay a USD 75bn dividend promised to investors during its IPO. Payouts to minority shareholders as pledged are protected for five years. Aramco’s Q2 profits plummeted by 73%.
- Private firms in Saudi Arabia applying for financial compensation under the unemployment insurance scheme (SANED) have been asked to reduce the percentage of beneficiaries to 50% of total Saudi employees (for those operating outside the “most affected business activities).
- Hotel occupancy rates in Jeddah improved to 32.1% in Jul, vs Apr’s low of 21.9%, according to STR data. Average daily rate touched SAR 769.35 in Jul, the highest since Oct 2019, and the revenue per available room averaged SAR 247.17 – the highest since Feb.
- In a bid to attract investors, Saudi Arabia updated regulations for municipal real estate transactions allowing the extension of the maximum contract period to 50 years from 25 years and reducing the bank guarantees amount.
- Saudi Arabia launched a platform for electronic notarization of employment contracts.
- The aviation and related industries in the Middle East are likely to lose about 1.5mn jobs during the pandemic, according to IATA. This is more than half the region’s 2.4mn aviation-related employment. GDP supported by the industry will fall by up to USD 85bn this year.
UAE Focus
- The UAE agreed to establish and pursue diplomatic relations with Israel including bilateral travel and trade (including technology and goods) as well as cooperation on food security, climate change and energy. In exchange Israel will suspend “temporarily” its plan to annex parts of occupied Palestinian territory in the West Bank. Bahrain, Egypt and Oman endorsed the move.
- Dubai non-oil PMI improved to 51.7 in Jul (Jun: 50), thanks to strong expansions in activity and new orders. Travel and tourism posted the first rise in activity since Feb on government’s effort to restart tourism. However, job growth remained weak, falling for a 5th straight month and outlook among businesses weakened for the first time since Apr (on expectations of a protracted recovery).
- Industrial production index in Abu Dhabi grew by 9.2% yoy in Q1 2020, supported by a pickup in “manufacture of machinery and equipment”.
- Weekly CPI inched up by 0.2% in week 4 of Jul 2020, using Feb as a reference month. Inflation for food and non-food consumer goods increased by 0.6% and 8.8% respectively.
- Abu Dhabi formed an economic collaboration committee, comprising representatives from 4 public sector entities and 22 private sector firms, to form working groups on 7 key sectors: construction & real estate; banking & financial services; retail, hospitality & tourism; education & technology; healthcare; industry & manufacturing and one specialized on SMEs.
- According to the latest Q2 2020 Credit Sentiment Survey by the UAE Central Bank, about 53% of respondents (senior credit officers of all banks and financial institutions extending credit within the UAE) stated that the demand for loans has declined either substantially or moderately, as per while 37.6% stated that credit standards had tightened moderately.
- Emirates District Cooling, a subsidiary of Dubai Investments, announced a 7% discount on customers’ “declared load” bill for the 3 months (Aug-Oct) across all sectors.
- Property transactions in Dubai touched 2361 in Jun, worth a total of AED 4.9bn and the secondary market had higher sales transactions than off-plan transactions. Overall, 5605 transactions were recorded in Q2 this year, worth AED 11.05bn.
Media Review
Media Review
Priorities for Saving the Private Sector
https://www.project-syndicate.org/commentary/supporting-the-private-sector-in-developing-countries-by-philippe-le-houerou-2020-08
How six companies are using technology and data to transform themselves
https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/how-six-companies-are-using-technology-and-data-to-transform-themselves
Americans rush to be their own bosses as Covid19 hits the job market
https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2020-08-12/americans-rush-to-be-their-own-bosses-as-covid-hits-job-market
Indian Billionaires Bet Big on Head Start in Coronavirus Vaccine Race
https://www.nytimes.com/2020/08/01/world/asia/coronavirus-vaccine-india.html
UAE-Israel establish formal diplomatic relations: viewpoints
https://www.economist.com/middle-east-and-africa/2020/08/13/israel-and-the-uae-make-their-quiet-affair-public
https://foreignpolicy.com/2020/08/15/uae-israel-business-technology-peace/
https://www.aei.org/foreign-and-defense-policy/israeli-emirati-normalization-be-careful-what-you-wish-for/
https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2020-08-14/dubai-is-poised-to-gain-from-travel-opening-with-israel
https://www.ft.com/content/cd0a594f-008b-413d-9cd5-3d9b71cc8d6e
Saudi Arabia’s PIF moves billions from blue chips to ETFs
https://www.wsj.com/articles/saudi-wealth-fund-moves-billions-from-blue-chips-to-etfs-11597513874
Offshore companies linked to Lebanon central bank governor have assets worth nearly USD 100mn
https://www.occrp.org/en/investigations/lebanons-offshore-governor
https://www.reuters.com/article/lebanon-crisis-governor/offshore-companies-linked-to-lebanon-c-bank-governor-have-assets-worth-nearly-100-mln-report-idUSL8N2FE39N
How powerful was the Beirut blast?
https://graphics.reuters.com/LEBANON-SECURITY/BLAST/yzdpxnmqbpx/
Powered by: