Markets
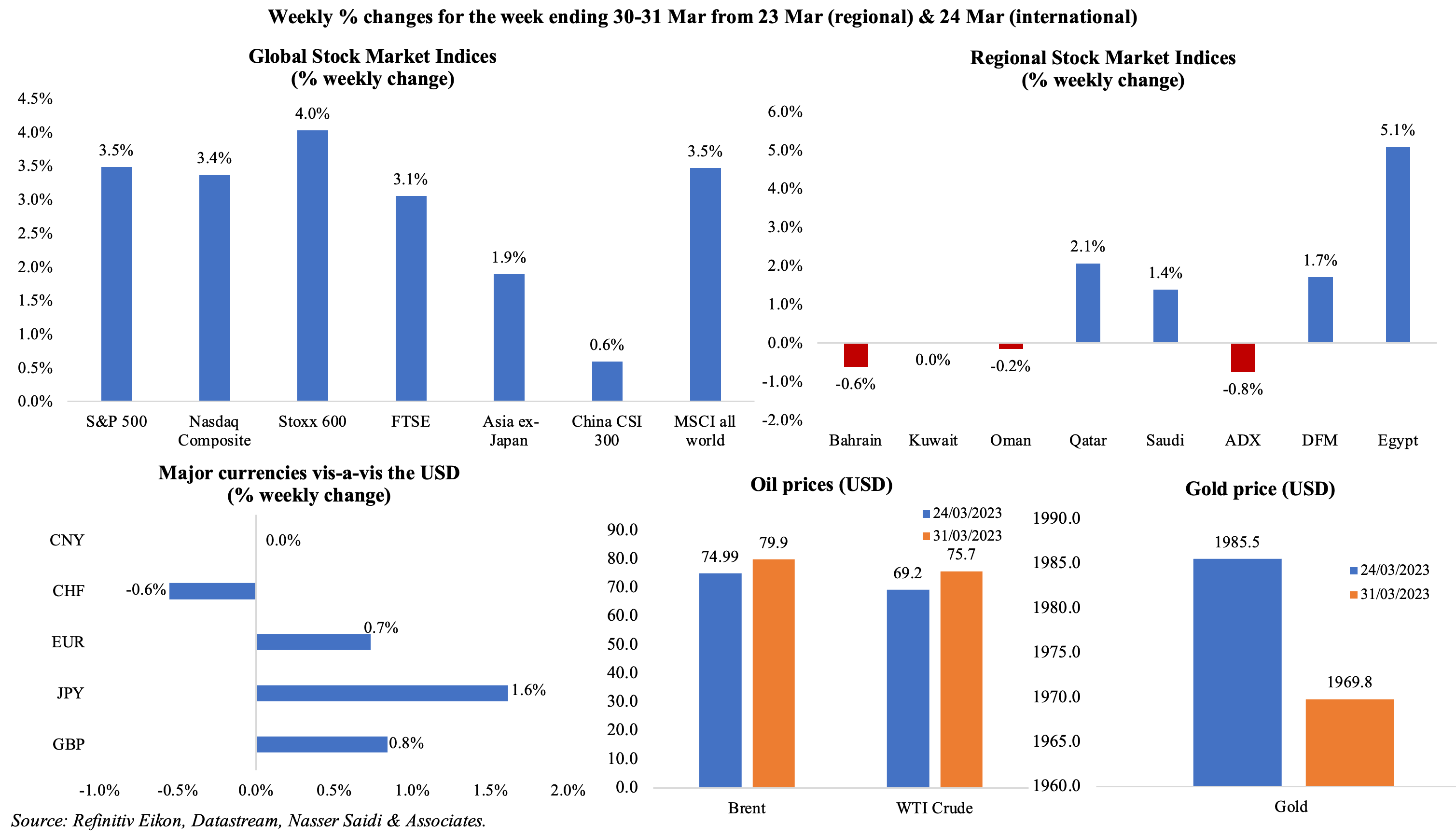
Global equity markets gained last week: in the US, tech stocks more than offset the losses in the financial sector and Nasdaq Composite reported the best quarter since Q2 2020; in Europe, Stoxx600 touched the highest level in 2 weeks; Asian equities were boosted by strong data from China (especially non-manufacturing PMI data); MSCI all world index posted its largest weekly gain since mid-Nov. Regional markets were mixed, with Saudi Tadawul clocking in a gain of 1.4%; Qatar and Egypt posted a 2.1% and 5.1% weekly rise, though both recorded a decline of 3.4% compared to Feb. The dollar posted its worst Q1 performance since 2018, dropping by 1.3% despite of the safe-haven demand. Oil prices increased compared to a week before for the 2nd consecutive time (while posting declines of 5% and 2% monthly for Brent and WTI respectively) while gold price edged lower. OPEC production cuts were announced after markets closed last week (prices are up sharply by some 8% in early trading today).
Global Developments
US/Americas:
- US GDP grew at a 2.6% annualised rate in Q4 (Q3: 3.2%), a shade lower than the previous estimate of 2.7%, thanks to downward revisions in consumer spending (to 1% from previous estimate of 1.4%) and exports.
- Personal income & spending in the US slowed in Feb: income rose by 0.3% mom (Jan: 0.6%) while spending rose at a slower pace of 0.2% mom (sharply down from Jan’s 2% gain). Core PCE index softened in Feb, rising by 4.6% yoy.
- Goods trade deficit in the US widened to USD 91.6 bn in Feb (Jan: USD 90.1bn), as exports dropped by 3.8% (to USD 167.8bn) while imports also fell (by 2.3% to USD 259.5bn). There was a 11.9% plunge in shipments of motor vehicles and parts while imports of motor vehicles and parts fell by 7.1%.
- S&P Case Shiller home prices inched up by 2.5% in Jan (Dec: 4.6%, as higher mortgage rates remained well above year-ago levels.
- Pending home sales inched up for the 3rd straight month in Feb, up by 0.8% mom (Jan: 8.1%) to the highest level since Aug. In yoy terms, pending home sales fell by 21.1% in Feb (Jan: 24.1%), the 21st month in a row of declines.
- Dallas Fed manufacturing business index declined further to -15.7 in Mar (Feb: -13.5), with new orders remaining negative for the 10th month running while the production index rose to 2.5 (from -2.8).
- Richmond Fed manufacturing index improved to -5 in Mar (Feb: -16), with shipments component moving into positive territory (to 2 from Feb’s -15) while employment and new orders improved to -5 and -11 respectively (from -7 and -24). Chicago PMI inched up to 43.8 in Mar (Feb: 43.6) but remained below-50 for the 7th straight month.
- The University of Michigan consumer sentiment index was revised down to 62 in Mar (prelim & Feb: 67), the first decline in 4 months. Year-ahead inflation expectations eased to 3.6% in Mar, the lowest reading since Apr 2021, and from 4.1% in Feb.
- Initial jobless claims ticked up by 7k to 198k in the week ended Mar 25th with the 4-week average rose slightly to 198.25k, remaining under 200k since mid-Jan. Continuing jobless claims also moved up by 4k to 1.689mn in the week ended Mar 18th.
Europe:
- Inflation in the EU eased to 6.9% in Mar (Feb: 8.5%), posting the biggest drop on record. Core inflation however accelerated to a new record-high of 7.5% (Feb: 7.4%).
- Unemployment rate in the eurozone stood at 6.6% in Feb while youth unemployment was at 14.4%. Spain and Greece posted the highest levels of unemployment rates, at 12.8% and 11.4% while Slovenia was the lowest at 3.2%.
- Economic sentiment indicator in the euro area slipped to 99.3 in Mar (Feb: 99.6), falling for the second month in a row. Separately, consumer confidence in the EU also declined, to -20.7 in Mar (Feb: -20.6).
- German HICP showed that prices eased to 7.8% in Mar (Feb: 9.3%), the lowest rate since Apr 2022.
- Germany retail sales unexpectedly fell by 1.3% mom in Feb (Jan: -0.3%): non-food sales were down by 0.3% while food sales inched up by 0.2%. In yoy terms, sales dropped by 7.1%, declining for the 10th straight month.
- Germany’s seasonally adjusted jobless rate inched up by 0.1ppts to 5.6% in Mar. The number of people out of work increased by 16k in seasonally adjusted terms to 2.54mn.
- The German Ifo business climate index rose to 93.3 in Mar (Feb: 91.1), the fifth consecutive uptick, driven mainly by business expectations. Both current assessment and expectations showed an increase, up by 1.5 and 2.8 points to 95.4 and 91.2 respectively.
- Germany’s GfK consumer confidence survey improved to -29.5 in Apr (Mar: -30.6), the highest reading since Jul.
- UK GDP edged up by 0.1% qoq in Q4 (Q3: -0.1%), versus a previous estimate of unchanged; UK output was 0.6% below its level in Q4 2019. Business investment dropped by 0.2% in Q4 (2.2% below pre-pandemic levels) while households disposable income rose by 1.3% and household spending was up to 0.2%.
Asia Pacific:
- China’s NBS manufacturing PMI declined to 51.9 in Mar (Feb: 52.6), with output, new orders and export sales expansionary (though rising at a slower pace) while employment slipped to 49.7 (from 50.2). Non-manufacturing PMI rose to a 12-year high of 58.2 in Mar (Feb: 56.3), with both services and construction sub-indices also touching record highs.
- Caixin manufacturing PMI inched lower to the neutral level of 50 in Mar (from Feb’s 8-month high of 51.6), given softer increases in production and new orders. New export orders however moved back into contraction, the 7th time of below-50 readings in the past 8 months.
- Core inflation in Tokyo slowed to 3.2% yoy in Mar (Feb: 3.3%), largely a result of government subsidies to lower utility bills. Excluding fresh food, CPI jumped by 2.9%, the biggest increase since the 1989 fiscal year. Excluding food and energy, prices rose to 3.4% (Feb: 3.1%).
- Industrial production in Japan rebounded in Feb, rising by 4.5% mom (Jan: -5.3%), supported by output of motor vehicles (15.4% from Jan’s 10.1% drop). In yoy terms, IP fell by 0.6%, the fourth straight month of declines.
- The Bank of Japan’s Tankan survey showed that big manufacturers’ sentiment fell to +1 in Mar (Dec: +7), the 5th straight quarter of decline and the lowest reading since Dec 2020.
- Japan’s unemployment rate unexpectedly increased in Feb to 2.6% (Jan: 2.4%), the highest reading since Oct 2022, while the jobs-to-applications ratio dropped 0.01 point to 1.34.
- Retail sales in Japan grew by 1.4% mom (the fastest pace in over 2 years) and 6.6% yoy in Feb, thanks to increased sales at auto dealers and department stores.
- Japan’s leading economic index was revised up to 96.6 in Jan from a prelim reading of 96.5 (Dec: 97.2), the lowest reading since Nov 2020. The coincident index also inched up to 96.4 (prelim: 96.1), but it was the lowest figure since May 2022 and lower than Dec’s 99.4.
- Manufacturing PMI in Japan improved to 49.2 in Mar (Feb: 47.7), the lowest reading since Sep 2020 and staying below-50 for the 5th consecutive month. Output and new orders shrank, but at a slower pace while input cost inflation slowed to the lowest since Aug 2021.
- India current account deficit shrank to USD 18.2bn or 2.2% of GDP in Oct-Dec (Jul-Sep: USD 30.9 or 3.7% of GDP), thanks to a narrowing goods trade deficit (USD 72.7bn from USD 78.3bn) and strong readings of services exports (+24.5% yoy) and private transfer receipts (+31.7% to USD 30.8bn). As a result, balance of payments surplus widened to USD 11.1bn vs a surplus of USD 0.5bn in Oct-Dec 2021.
- Fiscal deficit in India stood at INR 14.54trn (USD 177.02bn) in Apr-Feb, accounting for 83% of the annual estimate. Net tax receipts grew by 17% to INR 17.32trn (or 83% of annual estimate) while spending during the period was higher by 13% to INR 34.93trn.
- South Korea’s industrial output fell by 3.2% mom in Feb (Jan: +2.4%), with the production of semiconductors and automobiles declining by 17.1% and 4.8% respectively. Separately, retail sales rebounded by 5.3% mom in Feb, following Jan’s 1.1% dip.
Bottom line: The main concern for investors continues to be the direction of monetary policy in the aftermath of the banking worries. Though inflation has eased, it is quite worrisome that the rate hikes so far has done little to ease prices, excluding the more volatile energy and food prices. Core inflation rates remain stubbornly high. The PMI readings will be watched – flash indicators had shown a better performance across services PMI than manufacturing; in the US, new orders had declined for six consecutive months.
Regional Developments
- OPEC+ announced surprise voluntary production cuts on Sunday, a precautionary measure to support “stability” of the market: cuts will start from May till end-2023. Saudi Arabia, Iraq and UAE will reduce output by 500k, 211k and 144k barrels per day respectively.
- Reuters reported that Saudi Arabia is planning to invite the Syrian President to attend the Arab League Summit being hosted in Riyadh this May. Earlier in the week, Egypt resumed contacts with Syria, with the latter’s foreign minister visiting Cairo (1st time in over a decade).
- GDP in Bahrain grew by 4.9% yoy in 2022, the fastest pace since 2013, and compared to 2021’s 2.7% growth pace, largely driven by an expansion of the non-oil sector (+6.2%) while the oil sector posted a decline (-1.4%). The Ministry of Finance and National Economy forecasts growth at 2.9% and 3.1% in 2023 and 2024. Sector-wise, growth accelerated in sectors most affected during Covid: hotels and restaurants (+13.9%), real estate (5.5%), trade (5.4%) and transport and communication (4.5%).
- The central bank of Bahrain made amendments to its Crypto-assets module, to include “Digital Token Offerings” under the framework for regulated crypto-assets. More: https://cbben.thomsonreuters.com/sites/default/files/net_file_store/Vol_6_CRA_2023.pdf
- Egypt’s central bank hiked overnight interest rates by 200bps: the lending and deposit rates now stand at 19.25% and 18.25% respectively. The apex bank cited monetary policy tightening as a “necessary condition” to achieve inflation targets (7% (± 2 percentage points) on average by 2024 Q4 and 5% (± 2 percentage points) on average by 2026 Q4).
- A draft 2023-24 budget approved by Egypt’s cabinet raised spending on food and petroleum products subsidies by 20% and 24% respectively. The budget forecasts a primary surplus of 2.5% alongside a 38% uptick in overall revenues; GDP growth is projected at 4.1% during the fiscal year and inflation is pencilled in at an average of 16%.
- Egypt signed a USD 335.5mn development financing agreement with Japan International Cooperation Agency, for support in achieving comprehensive health coverage.
- Egypt will soon allow visa on arrival in the south of its Sinai Peninsula for Iranians travelling with tour groups; it could be extended to other parts of the nation after evaluation. Egypt had recently given Turkish nationals similar access to visas on arrival, after the countries re-established ties.
- Iraq’s oil ministry disclosed that oil revenues touched USD 7.4bn in Mar, with an average price per barrel of USD 73.37. Exports during the month averaged 3.255mn barrels per day (Feb: 3.295mn bpd), according to the ministry.
- Kuwait Investment Authority is planning to reduce its stake in Mercedes Benz through the sale of 20mn shares; this would reduce its stake to less than 5% from 6.84% (it was the 3rd largest stakeholder).
- Lebanon’s central bank will allow banks to purchase an unlimited amount of USD on its Sayrafa platform until end-Apr in an expensive effort to limit the sharp depreciation of the LBP exchange rate.
- Reuters reported that Oman’s OQ Gas Network is preparing for a public share sale for as early as June this year. OQ’s oil drilling business raised USD 244mn from a 49% stake sale in Mar 2023.
- Qatar announced a new regulatory framework for listed derivatives after a 3-month consultation period. A new derivatives market be launched, allowing for the trading of options and future contracts on local stocks and the main equity index, according to the financial centre regulatory authority. The exchange also plans to set up an entity to provide clearing and settlement services for trades in options and derivative contracts.
- Exports from Qatar fell by 2.2% yoy and 8.7% mom to QAR 31bn in Feb while imports fell at a faster pace (-14.3% yoy and -16.4% mom), resulting in a surplus of QAR 22.9bn. Its top import trade partners were China (15.6% of total imports), US (13.1%) and India (6.9%).
- Qatar Energy signed a deal to acquire stakes in two Canadian offshore exploration blocks from ExxonMobil.
- Japan crude oil imports from Arab nations rose to more than 98% of its total imports in Feb: Saudi Arabia and UAE together accounted for 77.8% of the total. Interestingly, in Feb, there were no oil imports from Russia.
Saudi Arabia Focus

- Unemployment rate of Saudi Arabia’s citizens fell to an all-time low of 8% in Q4 2022 while inclusive of expats unemployment slipped to 4.8% in Q4 (Q3: 5.8%). Female unemployment among Saudis fell to 15.4% in Q4(less than half of 33.7% in Q2 2016), with the decline seen across all age groups.
- Saudi Arabia’s merchandise exports slipped by 3% yoy in Jan 2023, after posting 23 months of gain. This was a result of the 2% yoy drop in oil exports (to SAR 82.1bn) alongside the 3rd consecutive month of fall in non-oil exports (-13% to SAR 17.8bn). The share of oil exports meanwhile remained around 80% of total exports. China was the top export destination for Saudi Arabia in Jan 2023: valued at SAR 15.6bn, it accounted for 14.8% of total Saudi exports.
- Banks in Saudi Arabia reported a 7.5% yoy rise in net profits to SAR 5.18bn (USD 1.38bn) in Feb. Loans disbursed to the private sector grew by 11.05% yoy to SAR 2.32trn while deposits were up by 8.2% to SAR 2.3trn. Consumer spending rose by 10% yoy to SAR 97.9bn in Feb, thanks to rising point-of-sales transactions. Additionally, total assets held by SAMA increased by SAR 830mn month-on-month to SAR 1.92trn in Feb 2023.
- Four new IPO applications have been approved by the Saudi Capital Market Authority, with approval valid for 6 months. The firms include First Milling Co., Lumi Rental Co., Saudi Call Trading and Abdul Aziz Al-Tuwaijri Trading Co., with the latter 2 approved for listing on the parallel market Nomu.
- Saudi Aramco raised its investment in China, by finalising a planned joint venture in northeast China (the Liaoning project, in the city of Panjin) and acquiring a 10% stake in privately controlled Rongsheng Petrochemical Corp.
- The Real Estate General Authority chief disclosed that Saudi Arabia is planning to relax its property ownership laws for foreigners, with the law “in its final stages” and to be “made public in a short period”.
- More than 6000 government services have been digitalised in Saudi Arabia, representing 97% of all government services. Saudi Arabia was ranked first regionally and third globally in the World Bank’s GovTech Maturity Index 2022.
- Saudi Arabia’s cabinet approved a decision to join the Shanghai Cooperation Organization as a dialogue partner. Dialogue partner status is usually a first step within the organisation before a full membership is granted in the medium-term.
- Saudi Ports Authority plans to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 1046 tons by end of this year. The aim is to reduce the average movement of yard cranes per incoming container required for manual inspection by 33%.
UAE Focus![]()
- The UAE central bank forecasts growth of 4.3% in 2024, while keeping its 2023 growth prediction unchanged at 3.9% (2022 estimate of 7.6%). The apex bank expects non-oil GDP to have grown by 6.6% in 2022, while inflation clocked in at 4.8% for the full year (projected to decelerate to 3.2% this year).
- Inflation in the UAE averaged 4.8% in 2022, with quarterly reading the highest in Q3 2022 (6.5%), as per data in the Central Bank’s latest Quarterly Economic Review report. Transport costs were up by 23.2% in 2022, while recreation & culture and restaurants & hotels posted significant increases of 13.8% and 7.2% respectively in 2022.
- The UAE government plans to double the re-exports over the next 7 years: the 24 initiatives announced towards this end also includes the creation of a national re-export committee. UAE re-exports crossed AED 600bn in 2022 for the first time, up 14% yoy. Saudi Arabia, Iraq, India, Oman, Kuwait, China, US, Hong Kong and Belgium were the 10 biggest re-export markets.
- UAE and Israel signed a customs cooperation agreement, in effect from Apr 1st, ensuring the proper application of customs laws and also permitting Israeli companies to compete in government tenders in the UAE. Bilateral trade between the two nations more than doubled to USD 2.5bn+ in 2022.
- The IPO of Presight AI, owned by Abu Dhabi’s G42 Group, raised AED 1.822bn (USD 496mn) after being oversubscribed by 136 times (excluding commitment from IHC, its cornerstone investor). Separately, Al Ansari Financial Services raised AED 773mn (USD 210.5mn) in IPO; firm had increased the size of its retail offering to 7.5% of the share capital.
- ADNOC initiated work on a pilot project in Fujairah to convert atmospheric carbon dioxide into rock formations – the first carbon negative project of its kind in the region. This technology will support the company’s efforts to raise its carbon capture and storage capacity to 5mn tons per year by 2030.
- A new EY report estimates that Expo Dubai will add AED 154.9bn to the UAE economy between 2013-2042, with 62% of the economic benefits occurring in the legacy phase to 2042. The report also finds that the Expo will support about 35k jobs annually over the period.
- DP World has invested more than USD 10bn in the global logistics sector since 2012, and USD 320mn in 2022, according to FDI data. This makes it one of the top 5 overseas investors in the logistics sector in the past decade: Amazon and Denmark’s AP Moller Maersk are others.
- UAE will cancel the licence granted to Russia’s MTS bank last year, after the bank was placed under British and U.S. sanctions in Feb 2023. Its operations will be wound down within 6 months.
Media Review
Middle East on ‘radar’ of global investors as it enjoys IPO boom
https://www.ft.com/content/a156c6d4-6597-4395-b581-65daa8976381
https://www.reuters.com/markets/deals/global-ipos-marred-by-banks-recession-enjoy-few-bright-spots-2023-03-31/
Pressure builds on Egypt to devalue currency further
https://www.reuters.com/markets/currencies/pressure-builds-egypt-devalue-currency-further-2023-03-28/
Yearly investments in renewable energy must more than quadruple to over USD 5 trillion: IRENA’s World Energy Transitions Outlook 2023
https://www.irena.org/Publications/2023/Mar/World-Energy-Transitions-Outlook-2023
The Fed’s Role in the Bank Failures
https://www.project-syndicate.org/commentary/federal-reserve-qe-role-in-svb-signature-bank-failures-by-raghuram-rajan-and-viral-acharya-2023-03
Powered by: