Markets
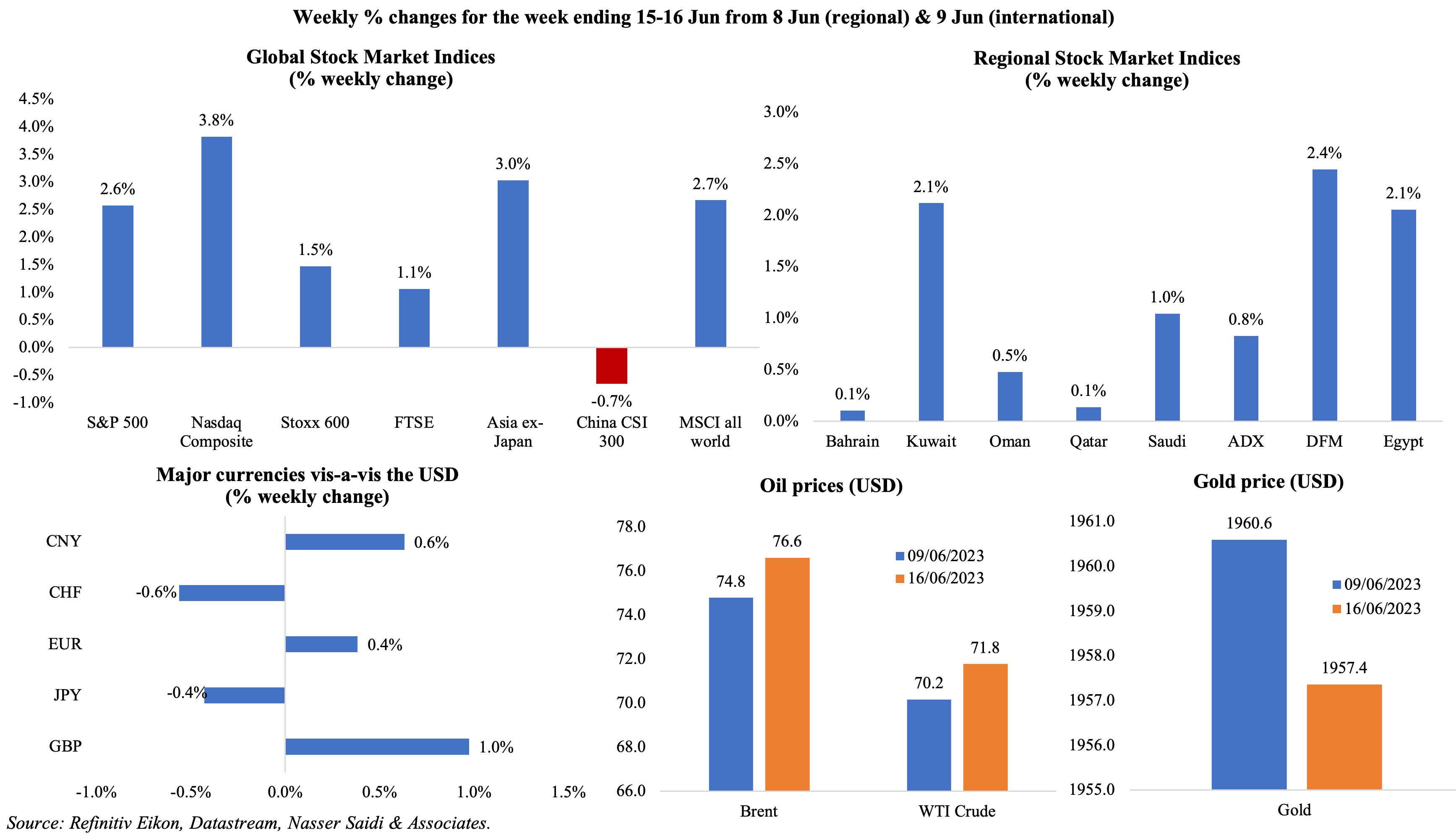
Equities markets had a strong week, with most markets reporting gains including in Asia (which benefitted from the rate cuts from China) and the MSCI all world index closing near its highest level since mid-Apr last year. Regional markets ended the week on a positive note as well, with the Abu Dhabi index back in the green after 7 consecutive weeks of declines. In the backdrop of a central-bank-meetings heavy week, currencies put up a good show: the yen fell to its lowest vis-à-vis the euro in 15 years and a 7-month low against the greenback after the BoJ meeting; the yuan hit a fresh six-month low after the rate cut in China; the dollar posted its biggest weekly drop since mid-Jan. Both Brent and WTI oil prices posted a weekly gain (2.4% and 2.1% respectively) while gold price nudged a tad lower (-0.2%).
Global Developments
US/Americas:
- The Fed paused the rate hike cycle after 15 consecutive months of hikes, though Powell stated that “the process of getting inflation back down to 2% has a long way to go”.
- Inflation in the US eased to 4% in May (Apr: 4.9%), the slowest increase since Mar 2021 and down from the peak of 9.1% in Jun 2022. In mom terms, energy prices dropped by 3.6%, food prices inched up by 0.2% while the shelter index rose by 0.6% (the largest driver of core price increase). Core inflation eased to 5.3% (Apr: 5.5%).
- US producer price index declined by 0.3% mom in May (Apr: 0.2%), dragged down by declines in the cost of food (-1.3%) and gasoline (-13.8%). It was up by 1.1% yoy, the slowest yoy gain since Dec 2020, and up from Apr’s 2.3% rise; core PPI eased to 2.8% yoy (Apr: 3.1%), the smallest rise since Feb 2021.
- Industrial production in the US inched lower by 0.2% mom in May (Apr: 0.5%) while manufacturing output inched up by 0.1% mom (Apr: 0.9%). Overall output fell by 0.3% in yoy terms, with auto production slowing (0.2% following Apr’s 9.8% rise) alongside a 0.3% rise in durable manufacturing output.
- Retail sales in the US surprisingly gained for a second month in a row in May, up by 0.3% mom from Apr’s 0.4% uptick. The increase was driven by sales at auto dealers (1.4%) and sales at building materials and garden equipment (2.2%) while sales at food services and drinking places nudged up by 0.4%. Core retail sales grew by 0.2% mom, slower than Apr’s 0.6% rise.
- Budget balance in the US widened to USD 240bn in May (Apr: USD 176bn), quadrupling from a year ago as government spending increased (20% yoy to USD 548bn) and taxes collected fell (by 21% to USD 307.5bn). The rising US budget deficit will likely lead to rising borrowing needs and debt issuance putting pressure on market liquidity.
- NY Empire State manufacturing index unexpectedly increased to 6.6 in Jun (May: -31.8), as new orders and shipments indices climbed up by 31 and 28 points respectively to 3.1 and 22. Separately, Philadelphia Fed manufacturing index worsened to -13.7 in Jun (May: -10.4): new orders remained negative while the index for shipments turned positive and employment stayed steady.
- Michigan consumer sentiment index improved in Jun, to 63.9 from 59.2 the previous month. Sentiment is now 28% higher than the historic low touched last year. The year-ahead inflation expectation slipped to 3.3% (May: 4.2%), the lowest since Mar 2021, while inflation expectations for the next 5 years edged lower to 3% (May: 3.1%).
- Initial jobless claims remained unchanged at 262k in the week ended Jun 9th, staying close to the near-highest reading since Oct 2021, and the 4-week average ticked up by 9250 to 246.75k (the highest level since Nov 2021). Continuing jobless claims inched up by 20k to 1.775mn in the week ended Jun 2nd.
Europe:
- The ECB raised interest rate by 25bps to 3.5%, the highest level in 22 years, also recording the eighth straight increase since Jul 2022. ECB President Lagarde suggested that more hikes were on the cards, given that controlling inflation will take longer than previously expected.
- Industrial production in the eurozone rebounded by 1% mom in Apr (Mar: -3.8%). However, capital goods output surged by 14.7% mom (Mar: -15.2%) while both durable consumer and non-durable goods fell by 2.6% and 3% respectively.
- The German ZEW economic sentiment index improved to -8.5 in Jun (May: -10.7) while the current situation in contrast fell further to -56.5 (May: -34.8). In the eurozone, economic sentiment slipped to -10 in Jun (May: -9.4), alongside the situation indicator dropping by 14.4 points to -41.9 points.
- Wholesale price index fell in Germany by 1.1% mom in May (Apr: -0.4%), largely due to the decline in energy prices. In yoy terms, it fell by 2.6%, the softest since Jul 2020.
- UK GDP grew by 0.2% mom in Apr (prev: -0.3%): services output rose by 0.3% (thanks to wholesale and retail trade, alongside information and communications) while manufacturing and construction contracted by 0.3% and 0.6% respectively.
- Unemployment rate in the UK dropped to 3.8% in the 3 months to Apr (Mar: 3.9%). According to a senior ONS official, the number of employed people had crossed its pre-pandemic level for the first time, setting a new high. Average earnings excluding bonus increased by 7.2% yoy in the 3 months to Apr (Mar: 6.8%), but lags inflation.
Asia Pacific:
- The People’s Bank of China cut reverse repo rate last week, by 10bps to 1.9%, signalling further easing for longer-term rates, thereby injecting CNY 2bn through its 7-day repos. On Thursday, it cut the borrowing costs of its one-year medium lending facility by 10bps, the first easing in 10 months.
- In addition to lowering rates, China announced a list of 22 measures to stimulate the economy including lower business costs, reducing VAT for small firms as well as guiding financial institutions to increase their medium- and long-term loan issuance for the manufacturing sector.
- Money supply in China grew by 11.6% yoy in May (Apr: 12.4%). New loans surged to CNY 1.36bn in May (Apr: CNY 718.8bn), lower than expected, and growth of outstanding total social financing grew at a slower 9.5% pace (Apr: 10%).
- More signs of weakness in China. Industrial production grew by 3.5% yoy in May, slowing from Apr’s 5.6% expansion. Retail sales were up by 12.7% yoy, much slower than Apr’s 18.4% hike. Fixed asset investment increased by 4% in Jan -May (Jan-Apr: 4.7%): a breakdown indicated that private fixed asset investment shrank by 0.1% while investment by state entities surged by 8.4%.
- Youth unemployment in China surged to a record high 20.8% in May 2023 while overall unemployment rate remained at 5.2% in May.
- FDI into China grew by 0.1% yoy in Jan-May (Jan-Apr: 2.2%): FDI into the high-tech manufacturing expanded by 30.8% and that in the high-tech service sector was up 1.5%.
- The Bank of Japan held the short-term interest rate target at -0.1% while also making no changes to its yield curve control policy (in line with expectations).
- Exports from Japan unexpectedly increased by 0.6% yoy in May thanks to car exports (+66%) while the semiconductor sector remained weak. Exports to China fell for the 6th month, down by 3.4%, a result of lower shipments of steel and auto parts. Imports fell by 9.9%, down for the 2nd straight month, leading to a narrow trade deficit to JPY 1.3725trn.
- Japan machine tool orders plunged by 22.2% in May (Apr: -14.4%), with domestic and foreign orders declining by 24% and 21.3% respectively. Separately, core machinery orders rose by 5.5% mom in Apr, the first rise in 2 months.
- India’s inflation inched lower to 4.25% in May (Apr: 4.7%), the lowest reading since Apr 2021, as food inflation fell sharply (2.91% from 3.84%). Wholesale price inflation fell by 3.84% yoy in May (Apr: -0.92%), recording the steepest pace of decline since Nov 2015.
- Industrial output in India increased by 4.2% yoy in Apr (Mar: 1.7%) with manufacturing up by 4.9% and mining output by 5.1%. Consumer durables fell by 3.5% yoy, following a 8.4% drop in Mar.
Bottom line: Last week saw the no-surprises central bank meetings from the Fed, ECB and Bank of Japan while the PBoC shook markets with its multiple rate cuts, as data (on industrial output, retail sales, new loans etc) underscored the slow pace of economic recovery in China. This week expect another rate cut in China’s benchmark loan prime rate hike alongside an uptick from the Bank of England, taking UK rates to a 15-year high.
Regional Developments
- Bahrain issued “golden licenses” to five firms that have made large-scale investment projects valued at more than USD 1.4bn including Citi and Saudi Telecommunication Company. This would enable these firms to receive fast tracked approvals in addition to priority in allocation of land, infrastructure, and access to government services among others.
- A US diplomat indicated that Bahrain is likely to restore diplomatic ties with Iran “sometime soon”.
- Egypt allocated EGP 127.7bn (USD 4.14bn) for food subsidies in the Parliament-approved EGP 3trn budget for the financial year 2023-24 (starting July 1st), reported Reuters. The budget estimates revenues of EGP 2.142trn and a deficit of EGP 824.44bn (or 6.96% of GDP).
- Reuters reported that India is considering a barter trade proposal with Egypt, potentially to be announced during the visit by the Indian PM to Egypt. Egypt wants to get wheat supplies (though India currently has a wheat export ban) among others while India wants gas & fertiliser. The agreement will allow Egypt to potentially make purchases in rupees. Earlier in the week, Bloomberg reported that Egypt had opened a credit line with India, only for the supply minister to refute the statement.
- Egypt officially applied to join the BRICS bloc, disclosed the Russian ambassador to Cairo. This comes in the backdrop of the BRICS studying new payment mechanisms for trade transactions and Egypt supply minister’s statement that the nation was exploring the possibility to pay for imports from India, China and Russia in their local currencies.
- Qatar’s sovereign wealth fund is planning to invest in 7 hotels in Egypt, acquiring stakes of up to 30% in the hotels. Some of the hotels also come with a historic premium, dating back to the 1800s.
- Iran’s oil exports touched a 5-year high of more than 1.5mn barrels per day (bpd) in May, according to Kpler. This stood at around 2.5mn bpd in 2018, prior to US’s withdrawal from the nuclear deal. Oil production had been increased to more than 3mn bpd in May: this is about 3% of global supply and the highest since 2018.
- Iraq’s Parliament approved its IQD 198.9trn (USD 153bn) budget for 2023, based on an oil price of USD 70 a barrel and oil exports at 3.5mn barrels per day. The deficit, at a record high IQD 64.36trn is double the deficit registered in 2021. The record spending is driven by a much higher public wage bill (more than 600k employees are to be hired) and costs of development projects (including infrastructure).
- While on an official visit, Qatar’s Emir revealed plans to invest USD 5bn in Iraq across multiple sectors in the coming years. He also signed various MoU’s relating to energy, electricity and construction. Energy cooperation agreements relate to crude oil, liquefied gas supply to Iraq, establishment of a joint oil company and construction of an oil refinery.
- Kuwait signed a contract worth USD 367mn with Turkey’s defence firm Baykar to buy TB2 drones. Neither the number of drones nor when those would be delivered were disclosed.
- Lebanon’s Parliament failed to elect a President for a 12th time after neither candidate came close to winning the 86 votes needed to win in a first round; Hezbollah and allies withdrawing from the session denied a quorum needed to continue into a second round (where 65 votes are enough for victory). IMF official and ex-finance minister Azour had 59 votes in the first round.
- Inflation in Oman edged down to 0.91% yoy in May, with the increases led by restaurants & hotels (3.69%) and furniture & household equipment (3.14%) while food & beverages were up by 2.73%.
- Credit disbursed by Oman’s banking sector grew by 6.3% yoy to OMR 30bn at end-Apr, with credit to the private sector up 6.8% to OMR 25.2bn. Deposits meanwhile increased by 5.5% to OMR 27.2bn (of which private sector deposits stood at OMR 17.9bn).
- Inflation in Qatar eased to 2.61% in May (Apr: 3.68%), though recreation & culture posted the highest increase (+9%) while housing & utilities and education followed closely at 6.7% and 4.06% respectively.
- Bilateral trade between Qatar and China grew by 45% yoy to QAR 95.7bn in 2022. Qatar exports oil and hydrocarbon gases, copper and polyethylene to China while its major imports are mobile phones, cars, and self-processing digital devices.
- International donors pledged EUR 5.6bn (USD 6.13bn) to support Syria and nations hosting Syrian refugees at an EU-hosted conference in Brussels. The pledges include EUR 4.6bn for this year and EUR 1 bn for 2024. The EU pledged EUR 3.8bn in grants.
- Saudi air connectivity leapt to 13th place from 27th in 2019, according to IATA. Furthermore, Saudi maritime connectivity has also increased, allowing it to rise to 16th across 187 nations in Q2 2023 according to UNCTAD’s Liner Shipping Connectivity Index.
- China’s Xi, in talks with his Palestinian counterpart, expressed willingness to mediate peace talks between Palestine and Israel. Peace talks mediated by the US broke down in 2014.
Saudi Arabia Focus
- Inflation in Saudi Arabia inched up to 2.8% yoy in May (Apr: 2.7%), thanks to higher housing costs (8.4%).Overall housing rents surged (9.9% yoy) alongside apartments rents (23.7%), given higher demand for expatriate accommodation versus limited supply.
- Wholesale prices in Saudi Arabia dropped in May, declining 1.1% yoy, for the first time since Jun 2020,with declines seen in 3 of the five categories. WPI plunged to 1.1% during the period Jan-May 2023 from a double-digit 11.4% surge a year ago.
- Day one of the 10th Arab-China Business Conference in Saudi Arabia saw the signing of 30 investment agreements worth USD 10bn across various sectors including technology, tourism, healthcare and renewables among others. This included a USD 5.6bn deal signed with Chinese electric car maker Human Horizons on the development, manufacture, and sale of its vehicles.
- The Bank of China will start operations in Riyadh later this year, by opening its first branch by either end-Oct or early-Nov.
- Money supply in Saudi Arabia grew by 5.59% yoy and 0.83% week-on-week to SAR 2.63trn (USD 700bn) in the week ending June 8th.
- Aramco’s Industrial Investments Program, Namaat, is helping to launch 31 local and international firms worth SAR 92bn (USD 24.53bn). Of these, 13 have launched operations while another 5 are still in the implementation phase. Firms include a cloud storage company, an iron sheet manufacturer, and a logistics management center among others.
- Moody’s upgraded Saudi Arabia’s banking system to positive from stable, citing high demand for credit and improved loan performance supported by robust oil prices, an increase in non-oil GDP growth and the ambitious reform agenda.
- Occupancy rate in Jeddah hotels was near 80% in May, the highest monthly rate since 2016, according to STR. The bookings jump was driven by the Arab League Summit held on May 19th. The average daily rate touched SAR 924.32 in May and revenue per available room reaching SAR 738.80.
- About 16 companies from Saudi Arabia (including Aramco and Saudi Electricity Company) bought more than 2.2mn tonnes of carbon credits at an auction organised by the Regional Voluntary Carbon Market Company in Kenya.
UAE Focus![]()
- India and the UAE plan to raise non-oil bilateral trade to USD 100bn by 2030, according to the former’s trade minister. Non-oil trade between the two nations grew by 5.8% yoy to USD 50.5bn during the period May 2022 to Apr 2023. He also disclosed that a rupee-dirham trade mechanism was being discussed “very active[ly]” by the central banks and progressing at a “very fast pace”.
- UAE became the 4th largest investor in India in 2022-23, with FDI increasing over three-times to USD 3.35bn (roughly 2.5% total FDI received by India). The top investors were Singapore (USD 17.2bn), Mauritius (USD 6.1bn) and the US (USD 6bn).
- Abu Dhabi signed a deal for its first car factory that uses recyclable materials, reported WAM. The e-commerce platform Sinaha have agreed with international partners to build this facility. The vehicles will use local raw materials and will feature an economical petrol engine and an all-electric motor.
- Brent crude’s premium to Middle East benchmark Dubai fell to just under USD 1 a barrel on Friday, its lowest level since Jan 2021, largely due to the weakness in Brent prices.
- DMCC announced a 24% yoy increase in Chinese businesses in the free zone to over 700.
- Taking into consideration the Eid holidays (in the 4th week of June), UAE Ministry of Human Resources and Emiratisation extended the deadline for companies to meet semi-annual Emiratisation targets to 7th Jul (from 30th June).
- OKX crypto exchange is seeking regulatory approval to operate in Dubai, according to an OKX executive. The firm has already received a preparatory license and opened an office in Dubai with plans to hire 30 staff.
- UAE is expected to attract 4500 millionaires by end-2023, the second-most globally, according to a report by Henley & Partners. Australia tops the list attracting 5200 millionaires (up from 3800 in 2022) while Singapore ranks third attracting a record high 3200 millionaires (from 2900 last year).
Media Review
The rise of the Persian Gulf is reshaping the world
https://www.washingtonpost.com/opinions/2023/06/16/saudi-arabia-gulf-reshaping-world/
Analysis: Iraq enjoys respite from turmoil but risks remain
https://www.reuters.com/world/middle-east/iraqs-enjoys-respite-turmoil-risks-remain-2023-06-16/
China’s economy is on course for a “double dip”
https://www.economist.com/finance-and-economics/2023/06/18/chinas-economy-is-on-course-for-a-double-dip
Electric Vehicle Fleet Set to Hit 100 Million by 2026: BNEF
https://about.bnef.com/blog/electric-vehicle-fleet-set-to-hit-100-million-by-2026-but-stronger-push-needed-to-stay-on-track-for-net-zero/
FT’s climate graphic of the week: first days of June bring record heat
https://www.ft.com/content/0341c2d0-b982-47c0-af8f-b415d09c520a
Powered by:







