Markets
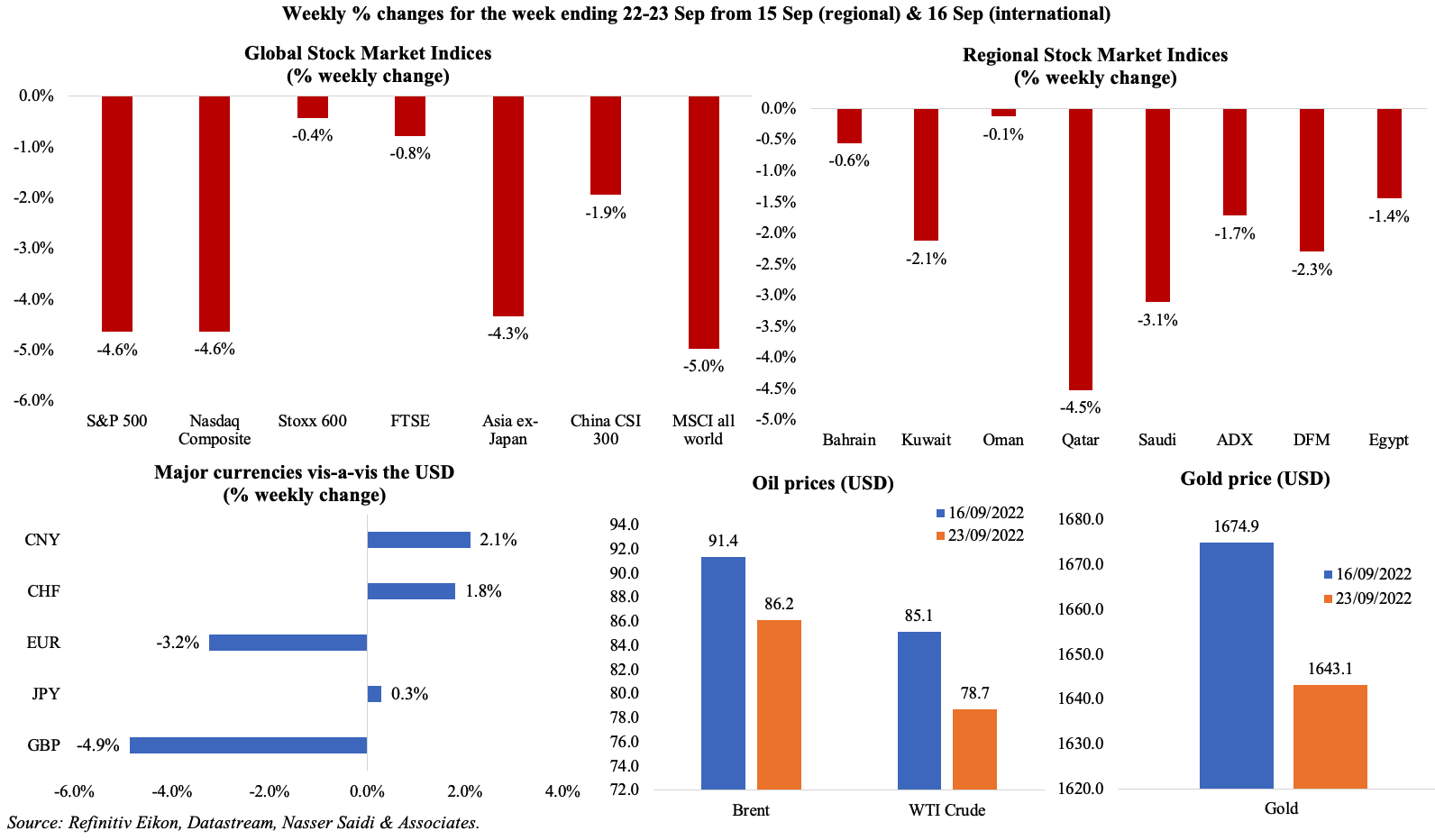
Most equity markets tumbled last week on recession worries, after several central banks raised rates (including the US, UK, Indonesia, Norway and Switzerland) in a bid to supress inflation; the MSCI World index fell to a 2-year low. Regional markets also mirrored global patterns, ending in the red. The US dollar index hit a 20-year high on Wednesday following the hawkish Fed statement, while the British Pound continues to tumble after the announcement of debt-financed tax cuts: the pound sterling is at a 37-year low, and the euro dropped to a 20-year low. Oil prices fell to an 8-month low on the strong dollar and fears of recession, while and gold price declined to the lowest since Apr 2020.
Global Developments
US/Americas:
- The Fed hiked its benchmark federal funds rate for a 3rd consecutive time by 75bps to a target of 3-3.25%. The Fed expects rates to rise to 4.4% by end-2022 and peak at 4.6% in 2023, before coming down to 3.9% and 2.9% in 2024 and 2025 respectively. During the press conference, Powell emphasised that “the historical record cautions strongly against prematurely loosening policy”.
- Housing starts unexpectedly grew by 12.2% mom to 1.575mn in Aug, with the multi-family housing segment rising to the highest level in more than 36 years. Building permits in the US fell by 10% mom to 1.517mn in Aug, the lowest level since Aug 2020. Existing home sales slipped by 0.4% mom and 19.9% yoy to 4.8mn in Aug. The median price of an existing home sold in Aug was USD 389,500, up 7.7% yoy.Rising mortgage rates and high prices are increasingly weighing on the housing market.
- Kansas Fed manufacturing activity improved to 2 in Sep (Aug: -9): the report stated that regional factory activity was sluggish overall, but firms were moderately optimistic about growth in future months.
- Preliminary manufacturing PMI in the US edged up to 51.8 in Sep (Aug: 51.5), with new orders growing for the first time since Sep. Services PMI inched up to 49.2 in Sep (Aug: 43.7), while reporting an easing in input prices.
- Initial jobless claims increased slightly by 5k to 213k in the week ended Sep 16th, still near the lowest reading since late-May, with the 4-week average down by 6k to 216.75k. Continuing jobless claims declined by 22k to 1.379mn in the week ending Sep 9th in line with a hot labour market.
Europe:
- Germany’s Producer Price Index surged by 7.9% mom and 45.8% yoy in Aug, the highest increases on record, driven by higher energy prices (+139% yoy). Excluding energy, PPI was up 14% yoy.
- Consumer confidence in the eurozone slipped to a record low of -28.8 in Sep (Aug: -25). Confidence in the wider EU also fell to a record low, down by 3.5 points to -29.9. Surging inflation and rising financing costs are likely to push Europe into a recession later this year.
- Preliminary manufacturing PMI in Germany slipped to 48.3 in Sep (Aug: 49.1), the worst reading since Jun 2020. Services PMI edged down to 45.4 from 47.2 in Aug, posting the steepest decline in 28 months.
- Eurozone’s preliminary manufacturing PMI inched lower to 48.5 in Sep (Aug: 49.6), with the output sub-index inching down to 46.2. Services PMI slowed to 48.9, the lowest since Feb 2021 and from Aug’s 49.8 heralding recession.
- The Bank of England raised rates by 50bps to 2.25% (3 members of the monetary policy committee favoured a 75bps rise and one a 25bps rise), the highest rate since the global financial crisis in 2008. The Bank called for “further, forceful” monetary tightening to lower inflation though gave no indication of the direction of future policy rates.
- The UK’s mini-budget was a debt-financed tax-cutting package: it cut the basic rate of income tax to 19% from Apr 2023, cancelled the scheduled rise in corporate tax (to 25% from Apr 2023, from 19% currently) and also abolished the 45% higher rate of income tax; some EU-directives/ regulations are set to be scrapped later this year. The proposed tax cuts would increase Britain’s public-debt-to-GDP ratio from a little over 80% in 2021-22 to nearly 95% in 2026-7, according to the Institute of Fiscal Studies and Citi.
- Preliminary services PMI in the UK fell below-50 in Sep, down to 49.2 (the weakest since Jan 2021) from 50.9 in Aug. Manufacturing PMI inched up to 48.5 (still in contractionary territory) from 47.3 the month before.
- GfK consumer confidence index in the UK tumbled to -49 in Sep (Aug: -44), the lowest since records began in 1974. Households continue to face a “cost of living crisis” thanks to “rapidly rising food prices, domestic fuel bills and mortgage payments”.
Asia Pacific:
- The PBoC left its benchmark lending rates unchanged. Earlier last week, the PBoC lowered the borrowing cost of 14-day reverse repo rate by 10bps to 2.15% (it was the first use of 14-day reverse repos since Jan 30th). It injected CNY 2bn (USD 286.54mn) through 7-day reverse repos and another CNY 10bn through the 14-day tenor.
- FDI into China grew by 16.4% yoy to CNY 892.74bn (USD 138.41bn) in Jan-Aug, with inflows into high-tech firms rising by 33.6%. EU FDI inflows surged by 123.7% in Jan-Aug.
- The Bank of Japan left interest rates unchanged, pledging to maintain its ultra-loose policy, leaving it as the only country in the world to retain negative interest rates. Japan however intervened in the currency market, selling dollars for the first time since 1998, after the yen tumbled to a 24-year low.
- Japan’s inflation rose to 3% yoy in Aug (Jul: 2.6%) while core inflation exceeded the BoJ target for the 5th consecutive month – at 2.8%, it was the fastest pace in nearly 8 years. Excluding food and energy, prices increased to 1.6% (Jul: 1.2%), the fastest rise since 2015.
- Singapore inflation grew to 7.5% yoy in Aug while core inflation rose to 5.1%, inching closer to a 14-year high. The central bank is largely expected to tighten policy at next month’s scheduled meeting (it has already tightened policy 3 times this year, two were surprise moves).
Bottom line: Preliminary manufacturing PMI readings did not paint a pretty picture last week, amid central banks continuing to raise interest rates and Japan’s currency market intervention (after staying pat on interest rates). On the political front, the UK’s mini-budget has shocked markets, while Italy looks set to swear in a right-wing government. All readings point to the onset of recession in the coming quarter. Meanwhile, Germany and UAE’s energy agreement signals the start of new alliances on the global energy front.
Regional Developments
- Bahrain’s GDP grew by 6.9% yoy in Q2, tweeted the Crown Prince: this is the highest since 2011 and compares to the 5.5% growth reported in Q1.
- Bahrain and Israel have initiated free trade talks, after two years of normalization of diplomatic ties. Bilateral trade between the two nations touched just USD 7.5mn in 2021.
- Contactless payments in Bahrain surged by 75% in Aug while e-commerce transactions increased by 13%. The highest number of transactions took place at restaurants (more than 1/3-rd of the total) while in terms of value government services topped the list (~30% of total).
- Egypt’s central bank left interest rates unchanged at the latest meeting, and raised the reserve ratio to 18% from 14%, stating that the current policy stance was consistent with “achieving price stability over the medium term”.
- The Chairman of the Egyptian Exchange revealed that discussions were at an advanced stage with 5 or 6 firms that want to list on the exchange. He also cited lack of liquidity as a key challenge for the exchange.
- The sovereign wealth fund of Egypt signed agreements for 10 projects worth EGP 25.5bn during 2021, to be implemented across varied sectors including utilities and infrastructure, tourism, real estate as well as financial services and education among others. The fund is also considering about 44 projects with investments of EGP 140bn over the coming 5 years.
- Egypt has a target of investments worth USD 7.7-8bn in the oil and gas sector, according to the minister of petroleum and mineral resources.
- Japanese investments in Egypt surged by 52% yoy in 2021, while bilateral trade increased by 13% yoy to USD 1.5bn, according to the finance minister. He also disclosed that Egypt is considering the issuance of green Samurai bonds following the previous successful offering.
- Lebanon’s investments in Egypt are worth around USD 1.2bn, according to Egypt’s minister of trade and industry, and reflects continuing capital flight from the crisis riden country. The country ranks 14th largest in terms of investing in Egypt.
- The IMF, at the end of the delegation visit to Lebanon, called out the “slow” “progress in implementing reforms” agreed in Apr. The IMF statement called for full protection of the nation’s small depositors while explicitly mentioning that “the hierarchy of claims” should be respected. The bottom line was that the IMF Board would consider request for new financing only after reform actions (that were agreed in Apr) are completed. More: https://www.imf.org/en/News/Articles/2022/09/21/pr22314-lebanon-imf-staff-concludes-visit-to-lebanon
- Oman’s nominal GDP grew by 32.4% yoy to OMR 20.261bn in H1 2022, the fastest expansion in over a decade, with non-oil nominal GDP growing by 14.9% to OMR 13.106bn.
- Oman foresees no delay in its income tax implementation target of 2024, with the government currently evaluating the structure and thresholds for high income, according to the minister of economy.
- Oman has successfully managed to reduce its public debt down by 11.5% to OMR 18.4bn at end-Aug 2022; external public debt accounts for 3/4th of the public debt portfolio.
- Bilateral trade between Oman and Saudi Arabia more than doubled to over OMR 1.249bn in H1 2022. Saudi Arabia was Oman’s fourth largest trade partner in 2021, following China, UAE and India, with OMR 1.3bn in merchandise trade.
- Gulf central banks raised key interest rates following the Fed’s 75bps hike: Kuwait raised the key discount rate by 25bps to 3% while Bahrain raised the rate on its 1-week deposit facility by 75bps to 4%. Other GCC apex banks also lifted rates last week. The rate hike will result in higher borrowing rates and could reduce domestic demand.
- IMF’s discussions with Egypt and Tunisia are approaching an end soon, and will be executed alongside reforms and economic programs, reported Asharq Business, citing the Director of the Middle East and Central Asia department.
- According to S&P Global Ratings, the GCC banks had a strong H1 2022, with Saudi and Kuwaiti banks’ earnings already reaching close to pre-pandemic levels while Qatar and UAE are taking slightly longer in terms of recovery.
- Alpen Capital’s GCC Hospitality Report shows that travel and tourism spending in the UAE was highest in the GCC region, at USD 27.4bn, followed by Saudi Arabia (USD 22.2bn) and Qatar (USD 16.5bn).
Saudi Arabia Focus
- Saudi Arabia’s non-oil exports surged by 26.4% to USD 7bn in Jul, while oil exports stayed above the SAR 100bn mark for the fifth consecutive month (accounting for 81% of total exports). Among non-oil exports, chemical and allied industries took the lion’s share (35.9%). China topped both export and import partner lists while other major export destinations were South Korea and India.
- JODI data revealed that Saudi Arabia’s crude oil exports rose by 2.5% mom to 7.38mn barrels per day (bpd) in Jul: this was the highest since Apr 2020. Production rose to the highest in more than 2 years, at 10.815mn bpd.
- The spot of top crude oil supplier to China was taken back by Saudi Arabia in Aug, after 4 months: crude oil imports from Saudi grew by 5% yoy to 475mn tons, or 1.99mn bpd in Aug (vs Russia: +28% yoy to 8.342mn tons). Saudi topped the list in the period Jan-Aug, supplying 58.31mn tons of oil (-0.3% yoy) versus Russia’s 55.79mn tons (+7.3%).
- India and Saudi Arabia discussed the feasibility of rupee-riyal trade and also reaffirmed cooperation in joint energy related projects (like refineries, petroleum storage facilities etc).
- The Saudi Fund for Development extended the USD 3bn deposit placed with Pakistan’s central bank for one year (was set to mature on 5th Dec 2022).
- Saudi PIF has created 500k jobs through its 54 companies spanning 10 different sectors, revealed its governor. The aim for PIF is to create 1.8mn “quality” jobs.
- The value of point of sales transactions in Saudi Arabia fell by 3.3% (from a week ago) in the week ended Sep 17, with education sector posting the biggest drop (-53.3%).
- The Saudi central bank governor stated at a conference that digital currencies will not be an absolute alternative to cash but will play an important role beside other payment systems.
- Total assets of Saudi Arabia’s banking sector amounted to SAR 3.5trn until end-Q2 2022, disclosed the minister of finance. The aim is to raise this to more than 4.5trn by 2030.
- Saudi Arabi’s holdings of US Treasury bonds grew by 2% mom to USD 121.6bn in Jul, posting the highest mom increase since Sep 2021.
- Saudi Aramco’s CEO called attention to the underinvestment in oil and gas while stating that taxing oil companies and capping energy bills were only short-term solutions to the ongoing energy crisis.
- The Al Jouf region in Saudi Arabia signed investment contracts for 26 projects worth over SAR 194mn (USD 51.5mn) last week.
- Saudi Arabia announced the launch of an astronaut programme, planning to send the nation’s first female astronaut into space next year.
- Saudi Power Procurement Co. launched five projects – 3 wind and 2 solar – to produce electricity using renewable energy, with a total capacity of 3,300 megawatts.
UAE Focus![]()
- UAE real GDP grew by 3.9% yoy to AED 1.499bn in 2021, with non-oil sector growing at a faster pace of 5.8%.
- UAE and Germany signed a “landmark” energy agreement that spans joint efforts to boost energy security, decarbonisation and combat climate change. ADNOC and German utility RWE signed a deal for the former to deliver 137k cubic metres of LNG by end-Dec.
- Bilateral non-oil foreign trade between the UAE and Saudi Arabia grew by 92.5% in the past decade to AED 124.69bn by end-2021, according to the FCSC. Gold topped the list of commodities exported to Saudi Arabia in 2021, with a value of AED 9bn.
- The value of exports and re-exports of firms registered with the Dubai Chamber increased by 20% yoy to AED 177bn in Jan-Aug 2022. The number of registered firms expanded by 69% to 314k during the period.
- The UAE Ministry of Economy launched the “Thabat Venture Builder” enabling family-owned businesses to develop viable business projects by adopting emerging technologies; batches of 10-20 businesses will be taken by the program. The aim is to double the contribution of family-owned businesses to AED 1.17trn by 2032.
- Binance received an approval to join the ‘Minimal Viable Product’ program from the Virtual Asset Regulatory Authority (Vara): this allows them to offer a range of Vara-approved virtual assets-related services to qualified retail and institutional investors in Dubai.
- The Salik IPO raised AED 3.73bn (USD 1.017bn) and was oversubscribed 49 times across all tranches; the government sold more than 1.86 bn shares or 24.9%.
- Burjeel Holdings announced plans for a 11% stake sale IPO, after Abu Dhabi’s IHC took a 15% stake in the firm for an undisclosed amount. The IPO will launch on Sep 30th and close on Oct 4th, with listing on ADX expected to happen on Oct 10th.
- Abu Dhabi Securities Exchange disclosed that the value of shares owned by Saudi investors totalled AED 5.627bn in the beginning of Sep: this amounts to 25% of shares owned by Arab and GCC investors. There were 145,647 Saudi investors, representing 42% of total Arab and GCC investors.
- Dubai sports sector’s contribution to the economy exceeded AED 9bn (USD 2.45bn) in 2021, accounting for 2.3% of GDP. With 105k new job opportunities to be created, the sector is expected to account for 3.8% of total employment in Dubai.
- Arthur D Little’s Global Electric Mobility Readiness Index places UAE 8th globally in terms of readiness of the market for electric mobility. The UAE EV market is estimated to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate of 30% between 2022 and 2028.
Media Review
UAE agrees LNG deal with Germany
The pound’s decline
https://www.economist.com/britain/2022/09/26/the-pound-is-plumbing-near-historical-depths-why
Dr. Nasser Saidi’s interview on Al Arabiya about the demise of the GBP
https://twitter.com/AlArabiya_Bn/status/1574369596815167488
In dollar we trust
Economics may take us to net zero all on its own
https://www.ft.com/content/967e1d77-8d3c-4256-9339-6ea7025cd5d3
Powered by:







