Markets
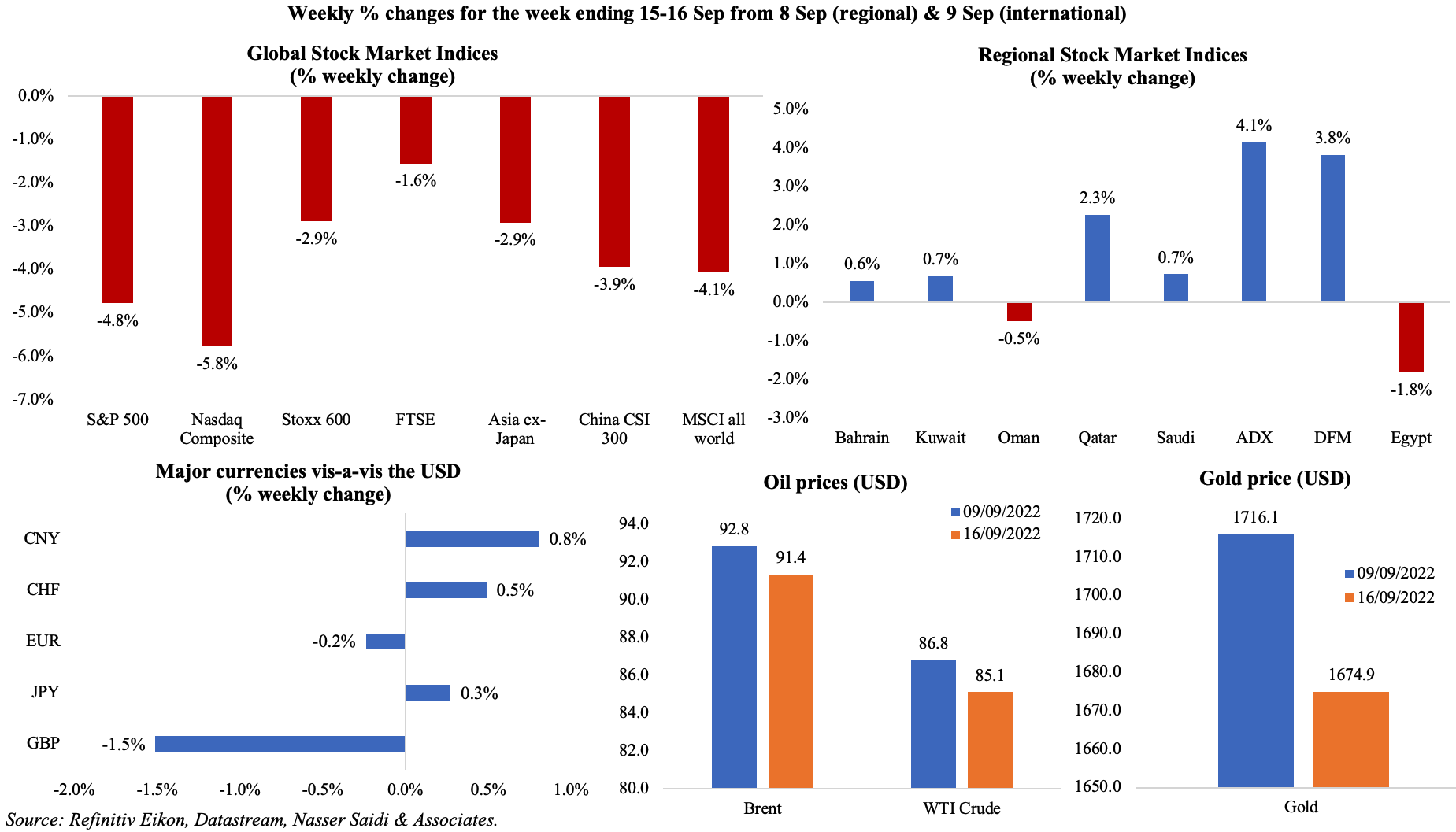
Most equity markets closed lower last week on investors’ expectations of a looming global recession and a high Fed interest rate hike (some expecting a 100bps rise), potentially leading to a global demand slowdown. The Cboe Volatility Index (VIX) currently stands at around 27.6 (above-30 readings point to acute fear, often resulting in steep losses in equities). Most regional markets posted gains, on predictions of global oil demand growth (OPEC and IEA see it rising between 2% and 3% this year and next). The GBP fell to the lowest level since 1985 after disappointing retail sales data, while the JPY strengthened. Oil prices edged lower on fears of lower fuel demand if global growth is restrained. Gold prices slipped to below USD 1700 – its weakest in four weeks.
Global Developments
US/Americas:
- Consumer price inflation in the US increased by 0.1% mom in Aug, with the drop in energy prices offset by increases across other categories (new vehicles, shelter and household furnishing among others). A more worrisome reading was that of core inflation, which grew to 6.3% from July’s reading of 5.9%. Markets expect a 75bps interest rate increase at this week’s meetings.
- Producer price index in the US eased to 7.3% yoy in Aug (Jul: 7.7%), the smallest yoy gain since Aug 2021. In mom terms, PPI dipped by 0.1%, the second consecutive monthly decline. The Aug easing was largely due to a drop in prices for goods (mostly cost of gasoline) while the cost of services gained (0.4% mom vs Jul’s 0.2%).
- Industrial production in Aug edged down by 0.2% mom in Aug (Jul: 0.5%) while manufacturing managed a second straight month of gains (0.1% in Aug, following Jul’s 0.6% rise). Auto production dropped by 1.4% while production of non-durable manufactured goods rose by 0.2%. Overall capacity utilisation fell 0.2 ppts to 80 in Aug.
- NY Empire State manufacturing index improved to -1.5 in Sep (Aug: -31.3), as new orders increased and shipments accelerated. Philadelphia Fed manufacturing survey fell to -9.9 in Sep from Aug’s 6.2, after new orders index remained negative amid increases in employment.
- Michigan consumer sentiment index inched up to a 5-month high of 59.5 in Sep (Aug: 58.2), as both current conditions and expectations improved to 58.9 and 59.9 respectively (from 58.6 and 58 in Aug).
- Retail sales in the US unexpectedly rebounded by 0.3% mom in Aug (Jul: -0.4%), with more purchases of motor vehicles and uptick in school shopping amid falling gasoline prices allowing. Excluding autos, retail sales declined by 0.3% mom after a flat reading in Jul.
- Initial jobless claims declined for the 5th consecutive week: it was down by 5k to 213k in the week ended Sep 9th, the lowest since late-May, with the 4-week average down by 8k to 224k. Continuing jobless claims rose by 2k to 1.403mn in the week ending Sep 2nd.
Europe:
- Inflation in the eurozone was confirmed at 9.1% yoy in Aug, given the rise in energy and food prices.
- Industrial production in the eurozone slipped by 2.3% mom (the biggest fall since Apr 2020) and 2.4% yoy in Jul. Production declined across the board, by 4.2% mom for capital goods, durable consumer goods (-1.6%) and intermediate goods (-0.8%).
- The ZEW Economic Sentiment Index for Germany plunged to -61.9 in Sep (Aug: -55.3), with the index of the current situation also falling to -60.5 from -47.6 the month before. Eurozone’s ZEW Economic sentiment index declined by 5.8 points to -60.7 in Aug.
- Current account surplus in Germany narrowed to EUR 5bn in Jul (Jun: EUR 16.2bn and Jul 2021: EUR 20.7bn), as the goods surplus shrank (to EUR 8.3bn from EUR 18.6bn a year ago) while services deficit widened (to EUR 7.4bn).
- UK GDP grew slightly by 0.2% mom in Jul (Jun: -0.6%), as the higher cost of living affected household demand and spending patterns. Industrial production slipped by 0.3% mom while manufacturing inched up by 0.1%; services expanded by 0.4% amid two consecutive contractions in construction.
- Inflation in the UK eased slightly to 9.9% yoy in Aug (Jul: 10.1%), the first fall since Sep 2021, after a decline in petrol prices amid higher food prices (14-year high of 13.1%). Producer price index eased in Aug, with the input prices down by 1.2% mom (the first drop in two years) and output price by 0.1%.
- UK unemployment rate unexpectedly eased to 3.6% in the 3-months to Jul (Jun: 3.8%), the lowest since 1974. Average earnings excluding bonus rose to 5.2% yoy in the 3 months to Jul (Jun: 4.7%). Claimant count increased by 6.3k in Aug, following a drop of 14.5k in Jul.
- Retail sales in the UK plunged by 1.6% mom and 5.4% yoy in Aug (Jul: 0.4% mom and -3.2% yoy). This was the biggest monthly decline since Dec 2021, with all retail sectors affected by the decline. Excluding fuel sales, retail spending was down by 5%, faster than the 3.1% dip in Jul.
Asia Pacific:
- Industrial production in China grew by 4.2% yoy in Aug (Jul: 3.8%), with passenger car production surging by 33% amid yoy declines in cement and steel production.
- Fixed asset investment in China grew by 5.8% yoy in Jan-Aug (Jan-Jul: 5.7%), in spite of a drag from real estate investment (-7.4%). Separately, retail sales rose by 5.4% yoy in Aug (Jul: 2.7%), supported by increase in passenger car and food sales.
- China’s aluminium imports fell by 19% yoy to 200,440 tonnes in Aug, according to customs data; this brings total this year to 1.48mn tonnes, down by 27%. This reflects the increase in domestic output – the nation made a record 3.51 million tonnes of aluminium in Aug, following a prior record set in Jul.
- Industrial production in Japan declined for the 5th straight month, by 2% yoy in Jul (Jun: -2.8%). In mom terms, however, IP inched up by 0.8% mom, with increases across motor vehicles (12%), general-purpose and production machinery (8.6% and 6% respectively).
- Exports from Japan increased by 22.1% yoy in Aug, while imports surged by 49.9%, causing the trade deficit to widen to JPY 2.82trn (its largest trade deficit on record). The weak yen has added to higher import costs.
- India’s consumer price inflation increased to 7% yoy in Aug (Jul: 6.71%), driven by food prices (7.6% from Jul’s 6.75%). Separately, wholesale price inflation slowed to 12.4% in Aug (Jul: 13.93%) thanks to a fall in commodity prices.
- Industrial output in India grew by 2.4% yoy in Jul (Jun: 12.3%), the lowest since Apr, with capital goods production posted the highest growth among use-based categories (+5.8%). Manufacturing output increased at a faster pace of 3.2%, though slower than Jun’s 12.5% gain. Cumulative industrial output expanded by 10% in Apr-Jun.
- Singapore’s central bank released an “Industry Transformation Map 2025” that includes plans to create 3-4k net finance jobs on average each year, a SGD 400mn (USD 285mn) investment in local talent, a SGD 100mn fund to support sustainability in the finance sector (green fintech, sustainable financing solutions etc) and streamlining corporate structures used by investment funds and family offices among others.
Bottom line: FT research states that since June, the world’s 20 major central banks have together raised interest rates by 860 basis points. Central bank hikes will once again be watched this week, with the Fed, BoE, central banks of Sweden, Norway all expected to hike while the Swiss National Bank’s hike could turn Swiss rates positive for the first time in 8 years. Though there is pressure on the BoJ to hike (given the widening rate gap with the US), it seems unlikely that such a move will happen this week. The UK’s case is one to watch carefully – with the BoE planning hikes amid the government’s fiscal plans to reverse the rise in social security contributions and corporate taxes.
Regional Developments
- Bahrain-origin exports increased by 8% yoy to BHD 416mn (USD 1.09bn) in Aug, with the top 10 trading partners accounting for 81% of the total – a list topped by Saudi Arabia (BHD 88mn), US (BHD 57mn) and the Netherlands (BHD 43mn). Imports grew by 5%, with China, Australia and Brazil the top three origin nations.
- The head of Aluminium Bahrain disclosed that European customers were “hesitating to order” given chances of recession and a subsequent fall in demand. He also stated that profitability was “not there anymore”, with lower prices amid a 30% rise in costs since 2020.
- Egypt’s President visited Qatar on a 2-day trip, with bilateral and regional issues on the discussion table and an underlying intent to reinforce financial ties. This was the first trip to Qatar since relations were restored after a diplomatic row. Bilateral trade between Egypt and Qatar grew by 76.4% yoy to USD 44.8mn in 2021. Remittances from Qatar to Egypt jumped by 14.3% to USD 1.5bn in the 2020-21 fiscal year.
- Remittances into Egypt declined by 14.7% yoy to USD 2.38bn in Jul, according to the central bank. In the period Jan-Jul, remittances inched up by 0.16% yoy to USD 18.72bn.
- Egypt’s Suez Canal Authority plans to raise transit fees by 15% for vessels (including those carrying oil and petroleum products) in 2023; fees for dry bulk carriers and tourist ships will be hiked by 10%.
- US administration decided to withhold military aid to Egypt, the tune of USD 130mn, over human rights failure. This accounts for 10% of the USD 1.3bn allocated annually for Egypt.
- Kuwait imports grew by 12% yoy to KWD 9.6bn at end-2021, with China and UAE the top nations exporting to Kuwait (amounting to KWD 1.7bn and KWD 1.1bn respectively).
- Kuwaiti citizens working in both public and private sectors increased in H1 2022: in the public sector, the number of Kuwaitis grew by 5.2% (from end-2020) to 372,942 while the private sector number grew by 20% to 75,921.
- Lebanon’s parliament suspended budget talks given the absence of a quorum thereby delaying efforts to undertake reform required to access funds from the IMF. The IMF at a news briefing highlighted “slow progress in implementing some of the critical actions” and stated that an IMF staff mission will visit this week to discuss ways and means to “speed up” reforms.
- Lebanon’s central bank stopped providing dollars for gasoline imports, possibly leading to higher and more volatile prices, and gas station owners will be forced to price fuel at the parallel market rate.
- Crude oil and condensate production in Oman grew by 10.1% yoy to 223.2mn barrels in Jul. Overall oil exports increased by 16.7% yoy at end-Jul, while exports to Japan and South Korea surged by 206% yoy (to 7.3mn barrels) and 68.7% respectively.
- Oman energy company OQ is planning an IPO of its gas pipeline unit, with Bloomberg reporting that the IPO could raise as much as USD 800mn. Listing is likely to be in the Muscat exchange and Saudi Tadawul, according to the sources.
- French oil and gas company TotalEnergies signed a natural gas exploration and production sharing agreement with Oman‘s energy ministry.
- Reuters reported Qatar’s Ooredoo is considering the sale of its tower network. Sales of similar tower assets have happened in the Gulf region recently as firms aim to reduce high costs on infrastructure and shift focus to the technology.
- GCC mergers and acquisitions transactions grew by 25% yoy to 105 in H1 2022, according to Markaz. GCC acquirers accounted for 69% of the transactions that closed during H1 2022.
Saudi Arabia Focus
- Inflation in Saudi Arabia increased to a 14-month high of 3% yoy in Aug, largely driven by food prices (4.31%) and multiple services-related activities like recreation (5.05%) and restaurants & hotels (7.35%). Transport prices inched up to 4% in Aug, after 2.5% and 3.6% rises in Jun and Jul. Secondary school fees rose by 10.1% in Aug, contributing to the 5.7% rise in education costs. Separately, the central bank governor stated that inflation was still within a “reasonable” rate.
- Wholesale price inflation slowed to 5.6% yoy in Aug, with most categories easing – metal products which have a high weightage in the overall index eased to 3.16% (Jul: 5%); food products remained close to the 9% mark.Year-to-date, wholesale prices have increased by an average 11.4%.
- Saudi Central Bank licensed two fintech payment firms, Arab Sea Financial Co. (digital payments) and Fatoorah (e-invoicing), bringing the total number of licensed payment companies to 21; another 5 were granted “in-principle approval”.
- According to the capital market authority, foreign investors’ ownership in Saudi stock market rose by 31% yoy to SAR 284bn (USD 76bn) by end-Q2 2022. Ownership touched a record high of SAR 340bn in Apr 2022. Separately, over 300k investors exited the market in Q2, including 85k+ female traders.
- Data from SAMA showed that private mutual funds’ assets in Saudi Arabia grew by 22% yoy to SAR 333.6bn in Q2 while public funds’ assets fell by 10.7% qoq to SAR 192.5bn.
- Saudi investors’ trades in US stocks grew by 78% yoy to SAR 71bn (USD 19bn) at end-2022: this is the highest level in a year.
- Saudi Arabia overtook Russia to become India’s 2nd largest oil supplier, with shipments up 4.8% mom to 863,950 barrels per day in Aug, behind Iraq in the top spot.
- The PIF’s Saudi Company for Artificial Intelligence (SCAI) announced an investment of USD 776mn in a joint venture with China’s SenseTime to develop Saudi’s artificial intelligence ecosystem. The SCAI will also operate an AI lab serving as an R&D centre.
- Saudi Arabia plans to build 3 steel plants at a cost of SAR 35bn (USD 9.32bn) and is in discussions with investors, according to the industry minister. The plants’ production capacity would be about 6.2mn tonnes.
- Saudi Arabia produces around 20% of the world’s desalinated water (9mn cubic meters produced per day), according to the deputy minister of environment, water and agriculture.
- NEOM plans to build a water desalination plant by 2024 to combat water scarcity, revealed the CEO of its water and energy subsidiary ENOWA; he also disclosed that it will be powered by 100% renewable energy.
- S&P ratings boost for Saudi Arabia: the agency updated Saudi outlook to positive with the short and long term foreign and local currency sovereign credit ratings upgraded to A-/A-2.
UAE Focus![]()
- Dubai’s road toll operator Salik increased the size of its IPO to 24.9% of share capital from previously announced 20% given the strong investor appetite. About 1.87bn shares will be sold now, amounting to just higher than USD 1bn. Tranches for “cornerstone” investors would remain unchanged at USD 165mn.
- Dubai-based Al Habtoor Group is planning to list on the Dubai Financial Market within two years, the CEO disclosed on CNBC Arabia.
- UAE’s tourism revenues stood at AED 19bn (USD 5.17bn) in H1 2022, with hotel guests up 42% yoy to 12mn during the period, tweeted the nation’s vice president last week.
- Dubai tourism emerged strong even during the summer months: total visits touch 8.1mn in Jan-Jul, surpassing 2021’s total (7.28mn) & almost three times the 2.85mn visitors reported in Jan-Jul 2021. Regional tourism continues to dominate with Saudi and Oman tourists accounting for close to 1/5th of visitors. A stronger recovery is expected come winter, with lower temperatures & more events including Qatar’s World Cup.
- UAE Federal Tax Authority introduced the world’s first paperless tax refund system for tourists. The system will be linked with retailers, making receipts available online.
- In an ambitious move, UAE increased its greenhouse gas emissions reduction target to 31% (from 23.5% previously) by 2030.
- Dubai announced the completion of about 85% of the Dubai Waste Management Center, the world’s largest waste-to-energy project; construction of this project had started in 2021. Once completed, the center will convert 45% of the city’s waste into renewable energy.
- State-backed digital bank Wio launched in the UAE, with a focus initially on SMEs and plans to expand offerings to retail customers in “the next few quarters”.
- The number of Chinese firms in the Dubai Multi Commodities Centre stand at 703 firms currently, about 12% of all Chinese businesses in the country. Over the past 5 years, more than 2 Chinese firms have joined DMCC every week.
- Dubai launched a Research & Development programme, outlining four priorities – health and well-being, environmental technology, smart built infrastructure, and space and augmented human-machine intelligence.
Media Review
The Fed Should Wait and See
Ethereum’s “Merge” upgrade
Reuters Analysis: OPEC+ leaders like $100 oil, won’t necessarily defend it
FT climate graphic of the week: Record ice sheet melt in September as emissions rise
https://www.ft.com/content/7c75ff11-da59-49ed-9006-a6c33c45e216
China’s August gasoline exports nearly double from a year ago
Powered by:







