Markets
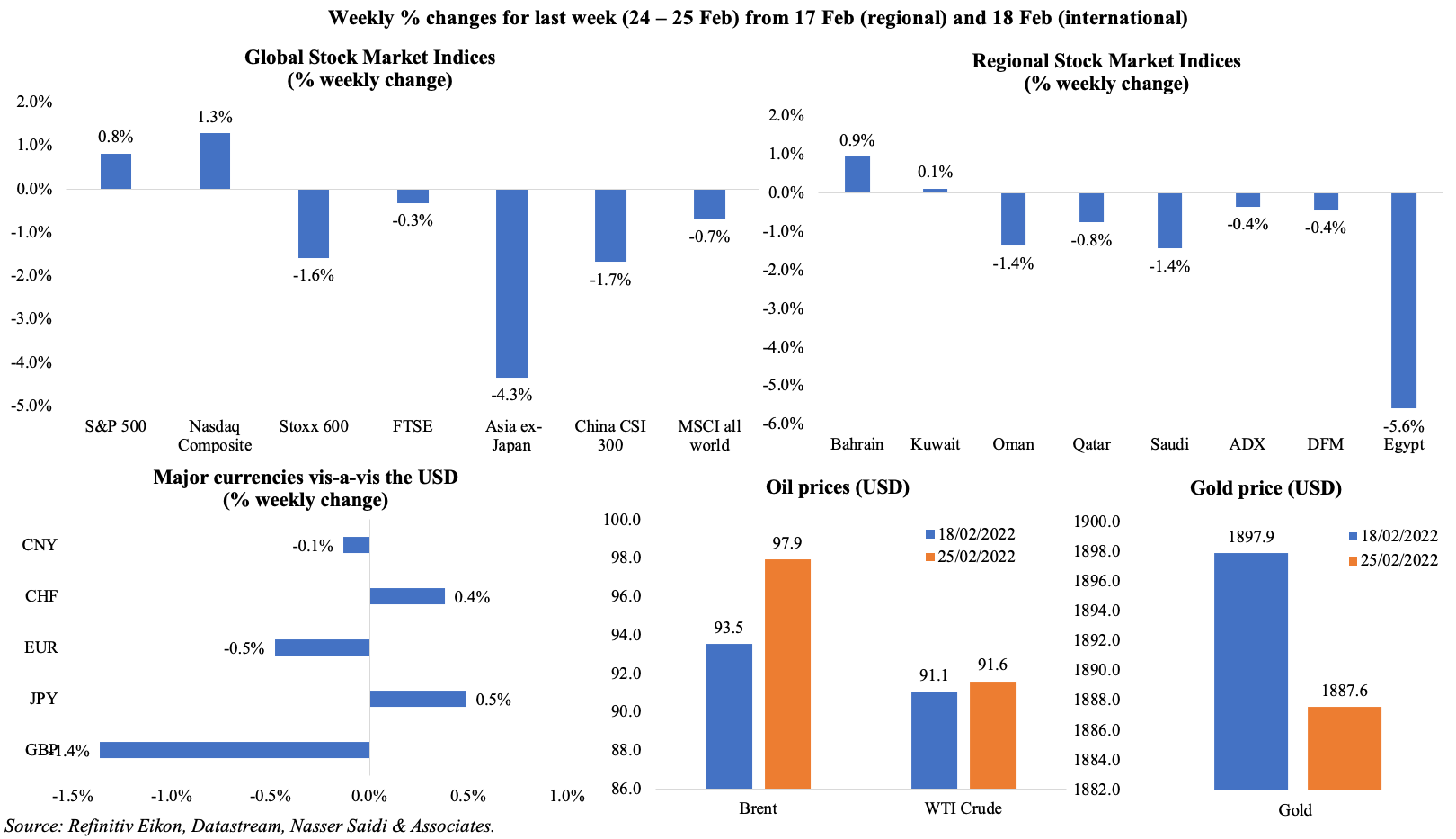
Global markets last week were in turmoil after the Russian invasion of Ukraine, which has since seen tight sanctions from the West including selected banks being banned from the Swift financial network. Thursday alone saw almost USD 1trn being wiped off the value of global stock market; many markets rebounded on Friday. At the end of the week, both S&500 and Nasdaq ended on a positive note while the MSCI World Index was down 0.7%. Most Middle East markets tumbled on concerns about disruptions to energy supply due to the invasion while UAE markets (which were open on Friday) stablised. The surge in oil and gas prices were the most dramatic: Brent almost reached USD 105 a barrel in early trading this morning; potential disruption of grain shipments from both Ukraine and Russia – which could affect countries in North Africa significantly (especially wheat) – also saw future prices rise higher (wheat prices touched the highest since mid-2008). Demand for safe haven assets weakened on Friday, including gold price: it had touched USD 1973.96 on Thursday, the highest since Sep 2020, but ended lower by end of the week.
Global Developments
US/Americas:
- GDP increased at a 7% annualized rate in Q4, slightly higher than the initial 6.9% estimate, supported by consumer spending (+2.1%) while inventories surged by a revised USD 238mn.
- Core PCE price index surged by 5.2% yoy in Jan, the highest increase since Apr 1983. Including both food and energy prices, headline PCE rose to 6.1%, the most since Feb 1982. Personal spending accelerated by 2.1% in Jan, reversing Dec’s 0.8% decline. Personal income was flat in Jan, following a 0.4% uptick the month before.
- Durable goods orders inched up by 1.6% mom in Jan (Dec: 1.2%), posting the 4th consecutive month of gains. Non-defense capital goods orders excluding aircraft grew by 0.9% (Dec: 0.4%).
- Flash manufacturing PMI in the US inched up to 57.5 in Feb (Jan: 55.5), supported by gains in factory orders and export sales. Input cost inflation eased to a nine-month low, but production continues to be hampered by scarcity of raw materials, supply chain disruptions and labour shortages.
- Richmond Fed manufacturing index fell to a 5-month low of 1.0 in Feb (Jan: 8.0), as new orders dropped (-3 from 6 in Jan) though employment gained (to 20 from 4 in Jan). Chicago Fed national activity index rose to 0.69 in Jan (Dec: 0.07), improving across all categories.
- New home sales fell by 4.5% mom to a seasonally adjusted annual rate of 801k in Jan, given high home prices and rising mortgage rates. Pending home sales fell for the 4th consecutive month in Jan, dropping by 5.7% mom – the steepest since a record drop in Apr 2020.
- S&P Case Shiller home price index increased by 18.6% yoy in Dec (Nov: 18.3%). The National Composite Index posted a gain of 18.8% in 2021, the highest calendar year increase in 34 years and much higher than 2020’s 10.4% uptick.
- Initial jobless claims slipped to 232k in the week ended Feb 18th from the previous week’s upwardly revised 249k; the 4-week average eased to 236.25k. Continuing claims eased to 1.476mn in the week ended Feb 11th – this is the lowest level since March 14th, 1970.
Europe:
- HICP in the euro area inched up 0.3% mom in Jan, the lowest monthly rate in 6 months.
- GDP in Germany grew by 2.9% yoy in 2021 (from the earlier estimate of 2.7%). In Q4, GDP declined by 0.3% (lower than the 0.7% estimated before), with the drop in consumer spending (-1.8%) slightly offset by government spending (1%).
- Producer price index in Germany surged to a new record high 25% yoy in Jan, with energy prices the biggest contributor to the uptick (+66.7%) in addition to upticks in intermediate goods (20.7%) and capital goods (5.3% – the biggest gain since Dec 1982).
- Germany’s flash manufacturing PMI slipped to 58.5 in Feb (Jan: 59.8) despite strong order growth given staff absenteeism due to infections. But the uptick in services PMI (to 56.6 from 52.2) supported the rise in composite PMI – up 2.4 points to 56.2.
- Flash manufacturing PMI in the eurozone eased to 58.4 in Feb (Jan: 58.7): while supply bottlenecks eased, respondents indicated that inflow of new orders exceeded gains in production. As in Germany’s case, the jump in services PMI (to 55.8 from 51.1) supported the climb in composite PMI (to 55.8 from 52.3).
- German Ifo business climate index inched up to 98.9 in Feb (Jan: 96). Both the current assessment and expectations increased to 98.6 and 99.2 (from 96.2 and 95.8 respectively), supported by the relaxation of restrictions and waning Covid numbers.
- GfK consumer confidence survey worsened to -8.1 in Mar (Feb: -6.7), given high inflation rates. The lifting of pandemic-related restrictions should lead to near-term improvements.
- Eurozone’s economic sentiment indicator edged up to 114 in Feb (Jan: 112.7). The final estimate of consumer confidence in Feb remained unchanged at -8.8 while the business climate edged down slightly to 1.79 from the previous estimate of 1.8.
- Flash manufacturing PMI in the UK stood unchanged at 57.3 in Feb from the month before while services PMI shot up to an 8-month high of 60.8 from 54.1. Output growth in the service economy (sub-index at 60.8) exceeded that seen in the manufacturing sector by a wide margin (sub-index at 56.7).
Asia Pacific:
- The People’s Bank of China left interest rates unchanged at 3.7% at the meeting; the apex bank on Friday pumped a net CNY 290bn through seven-day reverse repurchase agreements – the most since Sep 2020 – to keep liquidity stable at the end of the month.
- Flash manufacturing PMI in Japan declined to 52.9 in Feb (Jan: 55.4), the weakest since Sep 2021: output shrank for the 1st time in 5 months and new exports orders growth slowed.
- Inflation in Tokyo inched up to 1% yoy in Feb (Jan: 0.5%), the highest since Dec 2019. Excluding fresh food prices ticked up to 0.5% from 0.2% the month before – largely due to the 24.2% surge in energy prices. Excluding food and energy, prices fell by 0.6% (Jan: -0.7%).
- Japan’s leading economic index climbed to 104.8 in Dec – the highest level since Jul – up from the preliminary reading of 104.3 and Nov’s 103.9. The coincident index edged down slightly to 92.7 in Dec (Nov: 92.8).
- The Bank of Korea maintained the 7-day repurchase rate steady at 1.25% (after raising rates three times since Aug) while signaling tighter policy up ahead. Inflation is expected to touch 3.1% this year, much higher than the previous 2% estimate. Separately, the parliament approved another KRW 9trn (USD 14.2bn) in additional pandemic-related spending.
- Manufacturing output in Singapore plunged by 10.7% mom in Jan; excluding biomedical manufacturing, output fell by 0.2%.
Bottomline: Concerns about inflation rise as both energy prices and grain prices surge to multi-year highs and supply disruptions can be expected to linger. While release of oil from global strategic reserves is being planned, it seems unlikely that the OPEC+ will provide additional oil when it meets this week. Central banks are likely to continue tightening plans given inflationary pressures. Meanwhile, the Russian central bank doubled interest rates to 20% earlier today after the sanctions led to a plunge in the rouble (-29% to almost 118 vis-à-vis the dollar in early trading).
Regional Developments
- Revenues from online transactions in Bahrain surged by 116% yoy to BHD 498mn in 2021 from more than 3.7mn transactions. The digital transformation also saw 57 new government services migrating to online channels and 91% of the community opting to use eServices.
- Real estate transactions in Bahrain increased by 46% yoy to BHD 1bn (USD 2.7bn) in 2021, supported by government initiatives (especially National Real Estate Plan 2021-2024).
- Bahrain-based GFH Financial Group will discuss with its shareholders (on March 20th) its plans to list on Tadawul and Abu Dhabi Securities Exchange, reported Argaam.
- Egypt grew by 8.3% in Q2 of the current financial year (Oct-Dec 2021), up from 2% in the same quarter a year ago but lower than the 9.8% growth in Q1 of the current fiscal year. Growth is estimated to range between 6.2-6.5% this fiscal year.
- Bank deposits in Egypt rose by 22.3% yoy to EGP 5.7trn (USD 362bn), thanks to the retail sector deposits (up 20% to almost EGP 3.9trn). The highest growth was seen in public sector deposits (+43% to EGP 732bn) while the private business sector grew 18.3% to EGP 671bn.
- Bloomberg reported that Egypt has selected six international banks to manage the sale of its first sovereign Islamic bonds worth USD 2bn, with the issuance likely to happen in Q2.
- Egypt’s non-banking financial institutions are required to obtain the FRA’s prior approval before conducting due diligences, according to a statement published a week ago. The FRA will also be setting up two new dispute resolution committees for such firms.
- Egypt launched a USD 50mn venture capital fund to finance new and existing startups: the program is operating with the support of the World Bank.
- Mid-last week, Egypt’s minister of petroleum and mineral resources disclosed that an initial deal with Russia would be signed “soon” to start using natural gas in the transportation sector as engine fuel.
- Egypt’s current energy mix includes 20% of solar, wind and hydroelectric power, according to the minister of petroleum and mineral resources. The country aims to add 42% renewable energy to its energy mix by 2035.
- Egypt has achieved 62% self-sufficiency in wheat production, according to the agriculture minister. Currently, about 3.7mn acres in the country (the world’s largest wheat importer) are dedicated to producing about 9.5-10mn tons of wheat.
- Iraq’s oil minister revealed (at a gas exporters conference) that the nation aims to shift its investment priority from the oil sector to gas for the first time ever.
- Kuwait’s government owes KWD 2.35bn (USD 7.78bn) in late payments to public entities, revealed the finance ministry, due to the lack of liquidity in the Treasury’s accounts. The arrears are equal to nearly 11% of Kuwait’s budget for the fiscal year that starts on April 1st.
- Inflation in Kuwait increased to 4.3% in Dec (Nov: 3.9%), driven by higher costs for housing services (2.4% from Nov’s 0.8% gain). For the full year, overall inflation rose to 3.43% (2020: 2.1%); food prices jumped to 9.5% (2020: 4.9%) while housing services grew to 0.5% (2020: -0.2%).
- In a bid to strengthen strategic cooperation, Abu Dhabi’s stock exchange signed an agreement with the Kuwaiti bourse and Kuwait Clearing Co. to facilitate trading procedures.
- US approved a potential military sale to Kuwait worth USD 1bn for the design and construction of the defense ministry headquarters and related equipment.
- Reuters reported, citing sources, that the IMF has requested Lebanon to meet a set of pre-conditions before initiating bailout discussions. This includes a framework for fiscal reform, revamping the insolvent banking sector, implementing capital controls, amending, or lifting banking secrecy and audits of both the central bank and the state power company among others. Many of these measures would need parliamentary approval.
- Qatar’s energy minister revealed that neither Qatar nor any other single country has the capacity to replace Russian gas supplies to Europe with LNG. With existing long-term contracts to Asian buyers, Qatar can divert only 10-15% of volumes to Europe.
- Qatar’s Emir disclosed that the nation’s LNG production capacity will rise to 126mn tonnes a year by 2027 from 77mn tonnes now. He also revealed that Qatar is building a carbon capture facility which will isolate and store 2.5mn tonnes of carbon per year in four years (and 9mn tonnes per year by 2030).
- Negotiations on the Iran nuclear deal resume: though significant progress has been made, very tough issues remain, according to the US State Department.
- Moody’s expects global sovereign sukuk issuance to drop to USD 73bn this year (2021: USD 88bn). In 2021, issuance volumes had already dropped by 22% with declines largely from the GCC (mostly Saudi Arabia).
- The UN’s Government Electronic and Mobile Services Maturity Index ranks Saudi Arabia first in the MENA region for e-services availability for citizens and businesses. Separately, it also ranks 2nd globally among the G20 nations in the Digital Competitiveness Report 2021.
Saudi Arabia Focus
- Overall non-oil exports from Saudi Arabia grew by 37.7% yoy (to SAR 231.3bn) in 2021 and compares to a 73% hike in oil exports (to SAR 772.8bn). Oil exports continue to dominate overall trade in Saudi Arabia, accounting for just over three-fourth of total trade in Q4 2021 (more than its share in Q1 2020). Ratio of non-oil exports to imports increased to an average 47.3% in 2021 from 39.5% in 2020.
- Saudi energy minister cautioned that focusing only on renewable power sources was not right move now as it would not be able to produce all the energy needed for current recovery, also stating that lack of investments had led to the rise in energy prices.
- Aramco’s CEO disclosed that there are signs of more global demand amid supply close to pre-pandemic levels. But, he warned that the level of investment in the sector is inadequate to sustain short- to mid-term global demand. Separately, in an Argaam interview, he stated that Aramco is reviewing some assets to potentially sell in the future, without elaborating more.
- Saudi Arabia’s shipments of refined products grew by 32% yoy in 2021: exports of diesel (which accounts for 50%+ of refined oil products) grew by 35% to an average 682k bpd.
- Saudi PIF is exploring options to monetize its recent USD 86bn stake transfer from Aramco, reported Bloomberg. Separately, PIF opened 3 new subsidiary companies’ offices in London, New York and Hong Kong as part of its global expansion plans.
- Saudi Arabia’s Human Resources Minister revealed that some 1.95 million young Saudi nationals are working in real estate and related sectors in the country; he also highlighted that the tourism sector aims to create one million jobs by 2030
- Volume of construction contracting in Saudi Arabia is expected to reach SAR 275bn (USD 75bn) by 2024, according to the Governor of Saudi Contractors Authority.
- A study by Knight Frank showed that 44% of homeowners in Saudi Arabia plan to buy a second home for personal use. More than 80% of the respondents who are renting revealed plans to buy a home in the next 12 months. NEOM was named the most preferred location to buy a home by first time buyers and HNWIs.
- Aramco hit a record USD 2.2trn in market value last week, as it shares rose to the highest since listing.
UAE Focus![]()
- UAE’s non-oil foreign trade jumped by 27% yoy in 2021 to AED 1.9trn (USD 517bn), according to Dubai’s ruler. This places trade activity above pre-pandemic levels.
- The UAE is close to signing trade deals with Indonesia and Israel, revealed the foreign trade minister, in a Bloomberg interview. Negotiations with Colombia are expected to end by Mar.
- UAE does not plan to introduce income tax for now, disclosed the minister of state for foreign trade, stating “it is not at the table at all now”.
- Total revenue generated from services provided by the UAE’s federal government totaled AED 26bn in 2021, according to the finance ministry’s undersecretary. Revenue from the e-Dirham surpassed AED 14.3bn.
- UAE’s industry minister stated that it was critical that investments flow to the lowest-cost, lowest-carbon energy resources given that transitions towards net-zero emissions take time.
- The Dubai Water and Electricity Authority (DEWA) expects to launch its IPO in Mar, with a DFM listing in Apr, reported Reuters, citing sources. The company is expected to offer between 5-10% of its shares to investors and could be valued between USD 27-37bn. It may also triple its annual dividend payout to AED 6.2bn after IPO.
- Hospital operator across the Middle East VPS Healthcare is considering an IPO in Abu Dhabi, reported Reuters. It had planned a listing in 2019 in London, which did not go happen given Brexit-related uncertainty.
- Gulf Capital is considering the setup of a SPAC that will list on ADX, according to a Reuters report.
- UAE became the largest trading hub for rough diamonds in 2021, with over USD 22.8bn worth rough diamonds traded through the UAE, according to the head of DMCC (which houses the Dubai Diamond Exchange).
- Dubai retained its title as the world’s busiest for international travel for the 8th consecutive year, with 29.1mn passengers in 2021 (up 12% yoy). However, this is miles away from the pre-pandemic of 86.4 million in annual traffic in 2019. In Q4, the airport handled 11.8mn (+77% qoq), accounting for 40% of 2021 total: this was the first time since Covid hit that quarterly traffic surpassed 10mn passengers. Separately, Dubai Airports’ CEO revealed that passenger traffic was likely to reach pre-pandemic levels only by 2024.
- In a bid to diversify weapon suppliers, UAE plans to order 12 L-15 light attack planes from China with an option to purchase 36 more.
- UAE removed the requirement to wear face masks outdoors and ended the mandatory quarantine for Covid19 contact cases while also stating that “for economic and tourist sectors, physical distancing has been cancelled”. Furthermore, vaccinated passengers are no longer required to take PCR tests to travel to the country.
Media Review
Six factors to guide investors during Ukraine turmoil: El-Erian
https://www.ft.com/content/ad9bf55d-89a2-46c8-8106-4eb898d06c2e
Russia’s War and the Global Economy: Roubini
Oil’s journey from worthless in the pandemic to $100 a barrel: Reuters
https://www.reuters.com/business/energy/oils-journey-worthless-pandemic-100-barrel-2022-02-24/
If the supply of Russian gas to Europe were cut off, could LNG plug the gap?







