Markets
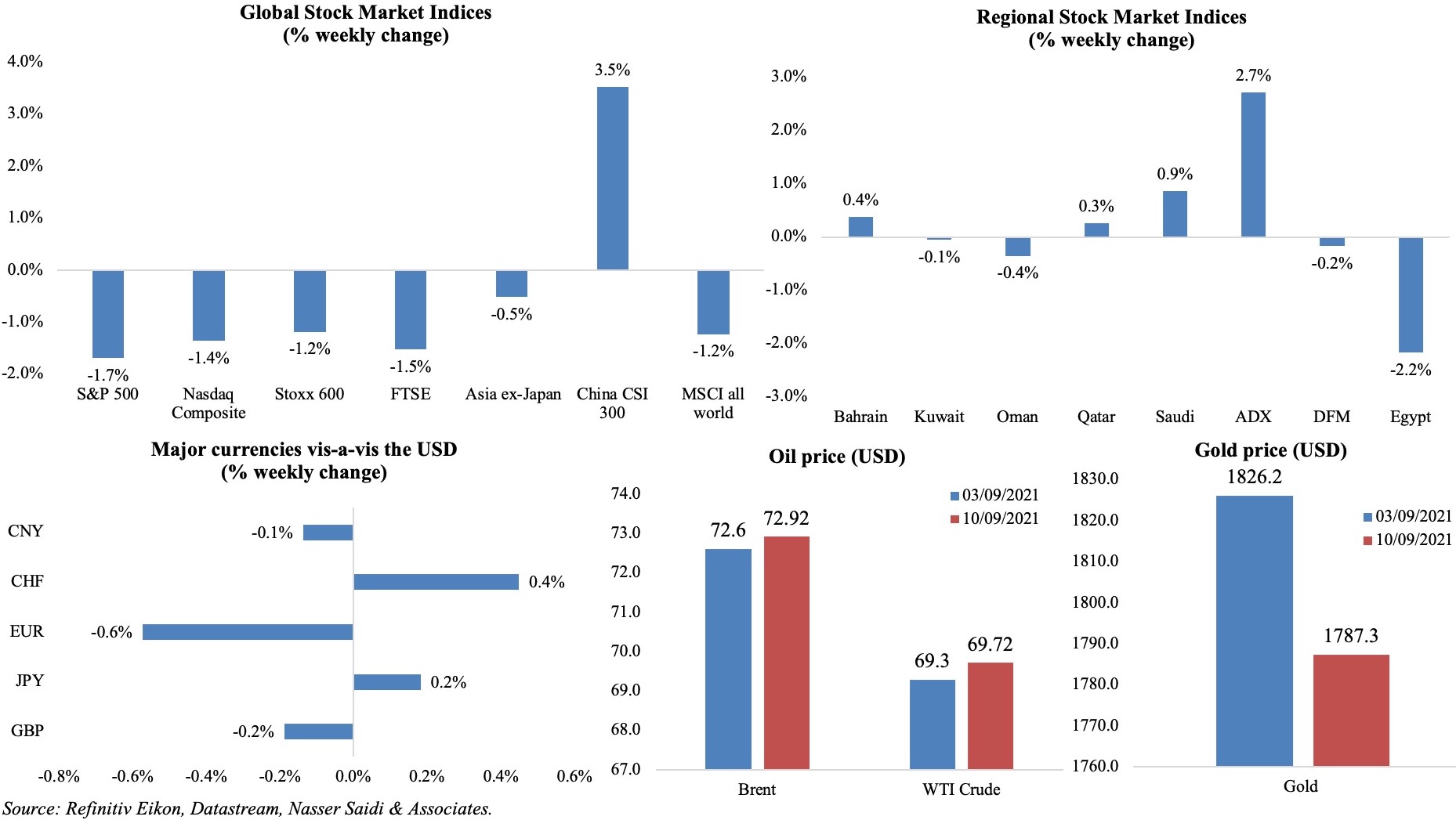
Renewed concerns over inflation dampened investor sentiment in the US, resulting in stocks posting their worst week in almost 3 months. In Europe, stock markets also ended in the red after ECB signaled a slowdown in bond purchases – Stoxx600 was down by 1.2% (steepest slide since mid-Aug). A call between Joe Biden and Xi Jinping eased tensions after trade negotiations remained unsuccessful; this helped China’s shares to rise (+3.5% in the week) and also lifted the overall MSCI World Index though the latter ended the week a tad lower. Among regional markets, 2 markets stood out: Tadawul closed at its highest level since Jan 2008 on Tuesday while Abu Dhabi closed at an all-time high on Thursday. The GBP fell after data showed a slowdown in recovery while the euro dropped by 0.6%. Oil prices ticked up on supply concerns, after production delays continued following Hurricane Ida while gold price ended lower (given uncertainties around Fed’s taper timeline).
Weekly % changes for last week (9-10 Sep) from 2 Sep (regional) and 3 Sep (international).
Global Developments
US/Americas:
- The Fed’s Beige Book stated that overall growth had “downshifted slightly to a moderate pace” while inflation is “steady at an elevated pace”. Business contacts cited “extensive labour shortages” despite “strong” wage growth particularly among lower earners.
- Producer prices in the US surged by 8.3% yoy in Aug, posting the biggest annual gain since Nov 2010 (Jul: 7.8%); in mom terms, PPI rose by 0.7% following two monthly increases of 1% each while transportation and warehousing prices quickened by 2.8%.
- Initial jobless claims eased to a new pandemic-era low of 310k in the week ended Sep 3rd, from an upwardly revised 345k the week before, slowing the 4-week average to 339.5k. Continuing claims edged down by 22k to 2.783mn in the week ended Aug 27th.
- JOLTS job openings increased to a record high of 10.934mn in Jul (Jun: 10.2mn): the rate of job openings swelled to 6.9% in Jul (Jun: 6.5%; Jul 2020: 4.6%).
Europe:
- GDP in the Euro area increased by 2.2% qoq in Q2 (Q1: -0.3%), with growth driven by the recovery in household final consumption expenditure (+3.7%) and government spending (+1.2%); employment grew by 0.7% qoq (Q1: -0.2%).
- The ECB plans to “moderately slow” its bond purchases under the EUR 1.85trn pandemic emergency purchase programme on the back of improving financing conditions and a rebound in recovery, while also signaling that it might continue in another form next year.
- German factory orders increased by 3.4% mom and 24.4% yoy in Jul (Jun: 4.6% mom and 26.5% yoy). New orders reached the highest level since 1991 (when the series began), thanks to foreign demand (+8%) and demand from outside the Eurozone surged (+15.7%) while domestic orders fell by 2.5%.
- Industrial production in Germany inched up by 1% mom in Jul, rebounding after three consecutive declines. Production of cars and car parts picked up by 1.9% and machinery rose by 6.9%. In yoy terms, IP grew by 5.7% (Jun: 5.4%).
- Trade surplus in Germany widened to EUR 17.9bn in Jul (Jun: EUR 13.5bn). Exports were marginally up by 0.5% and imports declined by 3.8%. Demand from the EU grew by 17.7% yoy while that from other countries climbed by 6.8%. July’s exports were 1.6% higher and imports 5.9% higher than in Feb 2020.
- The German ZEW survey showed an improvement in the current situation reading (31.9 in Sep vs Aug’s 29.3) while the economic sentiment reading dropped by 13.9 points to 26.5.
- The ZEW survey of economic sentiment fell to 31.1 in Sep in the Eurozone (Aug: 42.7). The current economic situation indicator in the Eurozone climbed 7.9 points to 22.5 while inflation is expected to decline over the next six months (inflation indicator dropped by 22.1 points to 20.1 in Sep).
- Sentix investor confidence in the eurozone eased to 19.6 in Sep (Aug: 22.2), the lowest reading since Apr. A gauge of investors’ future expectations dropped for the 4th consecutive month – to 9 from 14 the month ago – to its lowest level since May 2020.
- GDP in the UK inched up by 0.1% mom in Jul (Jun: 1%), with the services sector recording no growth overall on the month. Overall, growth remains 2.1% below its pre-pandemic level and grew by 3.6% in the 3 months to Jul 2021 (thanks to the easing of the lockdown).
- Trade deficit in the UK widened to GBP 3.12bn in Jul (Jun: GBP 2.51bn), recording the largest deficit since Dec 2020, after exports fell by 0.1% alongside a 1.1% gain in imports. Goods trade deficit rose to a 7-month high of GBP 12.7bn, as exports to the EU slowed given post-Brexit trade barriers.
- UK IP increased by 1.2% mom in Jul, with manufacturing posting no change while construction output was down by 1.6%.
Asia Pacific:
- China’s trade surplus widened to USD 58.34bn in Aug (Jul: USD 56.58bn). Imports surged by 33.1% yoy (Jul: 28.1%) while exports grew by 25.6% (Jul: 19.3%). Trade surplus with the US increased to USD 37.68bn from USD 35.4bn in Jul.
- Inflation in China ticked up to 0.1% mom and 0.8% yoy in Aug, remaining below the government target of 3% this year. Core inflation stood at 1.2% yoy (Jul: 1.3%). Producer price index climbed to 9.5% yoy (Jul: 9%) – the fastest pace since Aug 2008, thanks to higher prices of raw materials (coal, metals).
- Banks in China extended CNY 1.22trn in new yuan loans in Aug (Jul: CNY 1.08trn); money supply (M2) grew by 8.2% yoy (Jul: 8.3%). Growth of outstanding total social financing slowed to 10.3% in Aug – the lowest since Dec 2018 and from 10.7% in Jul.
- Q2 GDP in Japan accelerated by 0.5% qoq in Q2, up from the 0.3% preliminary estimate and Q1’s revised 1.1% dip. Household consumption (0.9%), fixed investment (2.3%) and government consumption (1.3%) supported the rebound as public investment shrank (-1.7%).
- Japan’s leading economic index declined to 104.1 in Jul from Jun’s 7.5-year high of 104.6. The coincident index fell by 0.1 points to 94.5.
- Overall household spending in Japan inched up by 0.7% yoy in Jul, rebounding from a 5.1% drop in Jun, thanks to food (+1.9% from -1.6% in Jun), clothing (+2.7% from -15.1%) as well as transport and communication (+14.2% from -5.8%). Month-on-month spending declined by 0.9% (Jul: -3.2%).
- India’s industrial production grew by 11.5% yoy in Jul, thanks to a low-base effect while manufacturing output climbed by 10.5%. Production of capital goods and consumer durables increased by 29.5% and 20.2% respectively while non-durable goods fell by 1.8%.
Bottomline: With Covid19 cases on the rise in the US (in unvaccinated pockets), the pace of economic recovery is coming increasingly under scrutiny. In the UK as well, the BoE governor warned that the economic bounce back was slowing. Inflationary pressures (from supply constraints to skills shortages and wage increases) continue to add uncertainty as to the timing of major central banks’ tapering measures. This week’s global data releases including inflation, consumer sentiment index and jobs (among others) will add flavour to the discussions (ahead of the BoE meeting next week).
Regional Developments
- Bahrain reported a 65% yoy surge in cashless payments in Aug: about 11.3mn point-of-sale and e-commerce transactions were reported, with a total value of USD 743.7mn; this follows a total of USD 3.62bn in cashless payments in H1 2021 from 53mn transactions.
- Bahrain was ranked 15th globally (and 2nd in the GCC and 3rd in the MENA region) in attracting direct investment, according to the FT’s Greenfield FDI Performance Index 2021.
- Annual urban inflation in Egypt increased to 5.7% in Aug (Jul: 5.4%), the highest since Nov, driven by increase in food costs (6.6% from 4.9% in Jul). In mom terms, prices were up by a marginal 0.1%, following Jul’s 0.9% gain while core inflation slowed to 4.5% (Jul: 4.6%).
- Egypt will resume its IPO programme for state-owned enterprises before end of this year, revealed the planning minister. The Daily News Egypt, citing sources, reported that e-finance company for digital payments infrastructure will be the first (up to 10% of the company’s shares) and to be implemented by Nov.
- No new taxes will be imposed on transactions on the Egypt’s stock exchange, stated the finance minister.
- Egypt plans to close an agreement with UAE’s Dragon Oil Co (the exploration and production platform of ENOC) to increase oil and gas production.
- Iraq and France’s Total will build 4 energy projects in Southern Iraq, as part of a USD 27bn deal signed last week. An initial investment of USD 10bn is expected, with engineering work to start “immediately”.
- Lebanon formed a government following a year of political impasse – to remain in power for 8 months, till elections in May. It is PM Mikati’s third government and the fourth under President Aoun. Immediately after the announcement, the pound rose to its highest rate vis-à-vis the dollar to LBP 15k from LBP 19k the day before.
- PMI in Lebanon stood at a 5-month low of 46.6 in Aug (Jul: 47), with outlook in “deeply negative” territory. Political and economic instability, fuel shortages and eroding purchasing power among domestic clients were cited as the main factors lowering demand.
- Lebanon is launching cash subsidy cards for over 500k families, which will provide each family with around USD 93 per month. The cash payments, estimated to cost USD 556mn, were approved by the Parliament in June, but with no sources of funding identified.
- Private generator owners in Lebanon hiked prices by more than 2-3 times in Sep, citing higher diesel prices after subsidies were lifted. The average prices of 5 and 10 amps of electricity are expected to reach LBP 2 and 4mn respectively even with the severe rationing.
- Data from the Planning and Statistics Authority showed that GDP in Qatar fell by 2.3% yoy and 0.8% qoq in Q1 this year, with both the oil and non-oil sectors declining by 2.3% (+4.0% qoq) and 2.4% (-3.6% qoq) respectively.
- Occupancy rates in Qatar averaged 60% in H1 2021 (vs 55% in H1 2020); hotel accommodation grew by 7% yoy during this period while the average room rate increased by 16% to QAR 438 and revenue per available room increased by 24% to QAR 266.
- Palestinian Authority pulled out of an agreement to provide funding from Qatar to the Gaza Strip “due to fears of legal prosecution and accusations that banks were “supporting terrorism””. Earlier in the week, QNA reported that Qatar had reached an agreement on a grant for reconstruction in the Gaza Strip and opening of crossings into the enclave.
- Getting serious about ESG: Kuwait launched an ESG reporting guide to “raise awareness” and “to promote environmentally conscious business practices in Kuwait’s capital market”; Oman is working on developing an ESG framework with an aim to to widen its funding base; Saudi Arabia’s PIF hired five international banks to advise on an ESG framework for public market capital raisings.
- According to Moody’s, Sukuk activity remained “solid” in H1 2021 with some USD 102bn; however, issuance is expected to fall to between USD 90-100bn in H2 (as higher oil price drove down sovereign funding needs in the GCC), resulting in a full year issuance much lower than the record USD 205bn issued in 2020. Separately, Fitch Ratings disclosed that though Green Sukuk issuances were rising (USD 6bn in H1 2021 from USD 3bn in 2020), it still accounted for just 2.5% of total outstanding sukuk.
Saudi Arabia Focus
- The Saudi government lent SAR 2.63bn (USD 701.2mn) to national development funds in 2020: the list was topped by the Real Estate Development Fund (SAR 155.02bn), the Saudi Industrial Development Fund (SAR 48.09bn) and the Social Development Bank (SAR 25.79bn).
- Investments of foreign non-founding investors in Tadawul reached a 20-month high of SAR 239bn (or 2.44%) in the week ending Sep 2nd. Investments of Gulf investors during the same week, at SAR 50.1bn, was51% of the total market value of the listed shares.
- Prices of construction materials in Saudi Arabia surged to record levels in Jul 2021, ranging between hikes of 4% to 40%. Price of a ton of national 18mm steel rebar increased by 29.39% to SAR 3505.45 while Romanian wood posted the largest increase (+40.7%).
- Aramco, as part of its industrial investment program (Namaat), signed 22 new MoUs and a joint venture agreement with companies including DHL, Samsung, Hyundai, and Honeywell among others: these focus on sustainability, technology, industrial and energy services, and advanced materials.
- Reuters reported that a consortium (led by EIG Global Energy Partners) with a stake in Aramco oil pipelines, plans to issue at least USD 4bn in bonds in Q4 to refinance a loan that funded the USD 12.4bn deal.
- A report from the Riyadh Chamber of Commerce revealed that the volume of e-commerce transactions touched SAR 21.375bn (USD 5.7bn) in 2020 and that the value of the e-commerce in the country contributed USD 10.4bn to the national accounts.
- The demand for guarantees from SMEs in Saudi Arabia (via the Kafalah program) grew by 106% (compared to 2019) to more than USD 4bn, as the firms tried to survive through the pandemic. According to the central bank, the amount of credit disbursed to SMEs grew by 39.74% to SAR 188.42bn in Q1 2021.
- Saudization programs will likely create 213k jobs for Saudis this year, disclosed the minister of human resources and social development.
- Saudi Arabia slashed official selling price of Arab Light crude for delivery to Asia in Oct by USD 1.30 to a premium of USD 70 per barrel: this was the first cut in the last 4 months.
- Saudi Algosaibi group finally reached a settlement with 95% of its creditors on debt that totaled SAR 28bn (USD 7.5bn), thanks to the new bankruptcy law which allowed for voting on the debt settlement plan.
- A silos project, constructed at a cost of more than SAR 364mn (USD 97mn), was inaugurated in Saudi Arabia last week. This has the capacity of storing 120k metric tons of grains and was built as part of the NTP towards ensuring food security.
- Saudi Arabia removed the travel bans imposed on UAE, Argentina and South Africa, allowing citizens to travel to these nations starting Sep 8th.
UAE Focus![]()
- UAE continues to reveal its list of 50 new economic initiatives to boost competitiveness and aid diversification. Announced earlier today were plans to increase the number of Emiratis in the private sector – this includes incentives like a boost to their salaries, support for pension fund of employees and payments for children in addition to allowing government employees to take sabbaticals on 50% of salary to start their own business among others (plan is to spend AED 24bn towards this effort). Private sector employers are expected to increase their Emirati workforce by 2% each year over five years. This set follows last week’s initiatives which focused on investment in technology and green, freelancer and part-time work visas. An investment of USD 36bn in the Emirates Development Bank was also announced.
- UAE’s minister of economy revealed that the country is estimated to grow by more than 4% this year – much more optimistic than the central bank’s Dec forecast of 2.5%. The country aims to attract AED 550bn (USD 150bn) in FDI in the next 9 years.
- UAE will allocate USD 2.6bn for industrial and technology projects, according to a senior official from the ministry of industry and advanced technology. The plan is to raise national value added to AED 55bn by 2025 from AED 33bn currently.
- Dubai PMI inched up to 53.3 in Aug (Jul: 53.2): there was a boost in consumer demand and the tourism sector gained, with its index rising to a 21-month high of 55.1 in Aug, thanks to the easing of travel restrictions. The output sub-index increased to its highest reading since Sep 2019, and the construction sector index rose to 53.3 in Aug (highest since Jul 2019).
- Bank deposits in the UAE increased by 0.3% mom to AED 1.915trn in Jul. Gross credit fell to AED 1.768trn from AED 1.769trn the month before: credit to the public sector was the only one that gained during the period, up by 0.8%.
- ADNOC plans to float 7.5% of its shares in ADNOC Drilling: the sale is expected to raise around USD 750mn. The plans to float part of the drilling unit is just part of the current trend of privatizing some of their fossil fuel assets.
- Holding company ADQ disclosed its plans to list Abu Dhabi Ports Co on the Abu Dhabi Exchange before end of the year.
- Abu Dhabi issued USD 3bn in multi-tranche bonds last week, its second of the year for which it received over USD 75bn in orders.
- The Abu Dhabi Investment Authority, in its Annual Review 2021, stated that technology and climate change are key investment areas for the SWF as part of its post-Covid19 strategy. The ADIA reported 20-year and 30-year annualised rates of return of 6% and 7.2% respectively in 2020, compared with 4.8% and 6.6% in 2019.
- Reuters reported that the UAE’s National Committee for Combating Money-Laundering and Financing of Terrorism and Illegal Organisations “announced the adoption of a regulatory framework for virtual assets in the UAE”. Both the central bank and SCA will oversee the implementation of the rules.
- UAE’s Barakah nuclear power station started operating its 2nd reactor (after the first started commercial operations in Apr this year). Once completed, Barakah will have 4 reactors will total capacity of 5600MW, equivalent to about 25% of UAE’s peak demand.
- DIFC reported a 59% yoy growth in new company registrations in the free zone in H1 2021, with about 492 new companies joining. Overall, there are 3292 active registered companies (+27%), allowing the centre to achieve one of the “2024 Strategy” targets of tripling in size (compared to 2014).
- The CEO of Etihad revealed that the airline performed the strongest in Jul since the start of the pandemic: in Jul, just over 40% of its seats were filled vs just 24.9% over H1 2021.
- On Sep 9th, more than 1.3mn persons used Dubai’s public transport facilities: the most since the beginning of the pandemic.
- UAE will allow entry of all fully WHO-approved vaccinated persons as of Sep 12th, including from previously suspended countries in advance of the opening of Expo 2020.
Media Review
Why nations that fail women fail
https://www.economist.com/leaders/2021/09/11/why-nations-that-fail-women-fail
From Afghanistan to the World Cup, Tiny, Wealthy Qatar Steps Up
https://www.nytimes.com/2021/09/07/world/middleeast/afghanistan-qatar-airlift.html
This SDR Allocation Must Be Different
Lebanon’s billionaire PM forms government after 13-month deadlock
https://www.ft.com/content/bf1691aa-dc3e-4eff-bfc2-b5ed49406b2a
Lebanon’s economic woes
https://www.reuters.com/world/middle-east/how-bad-is-crisis-lebanon-2021-09-10/
Powered by:







