Markets
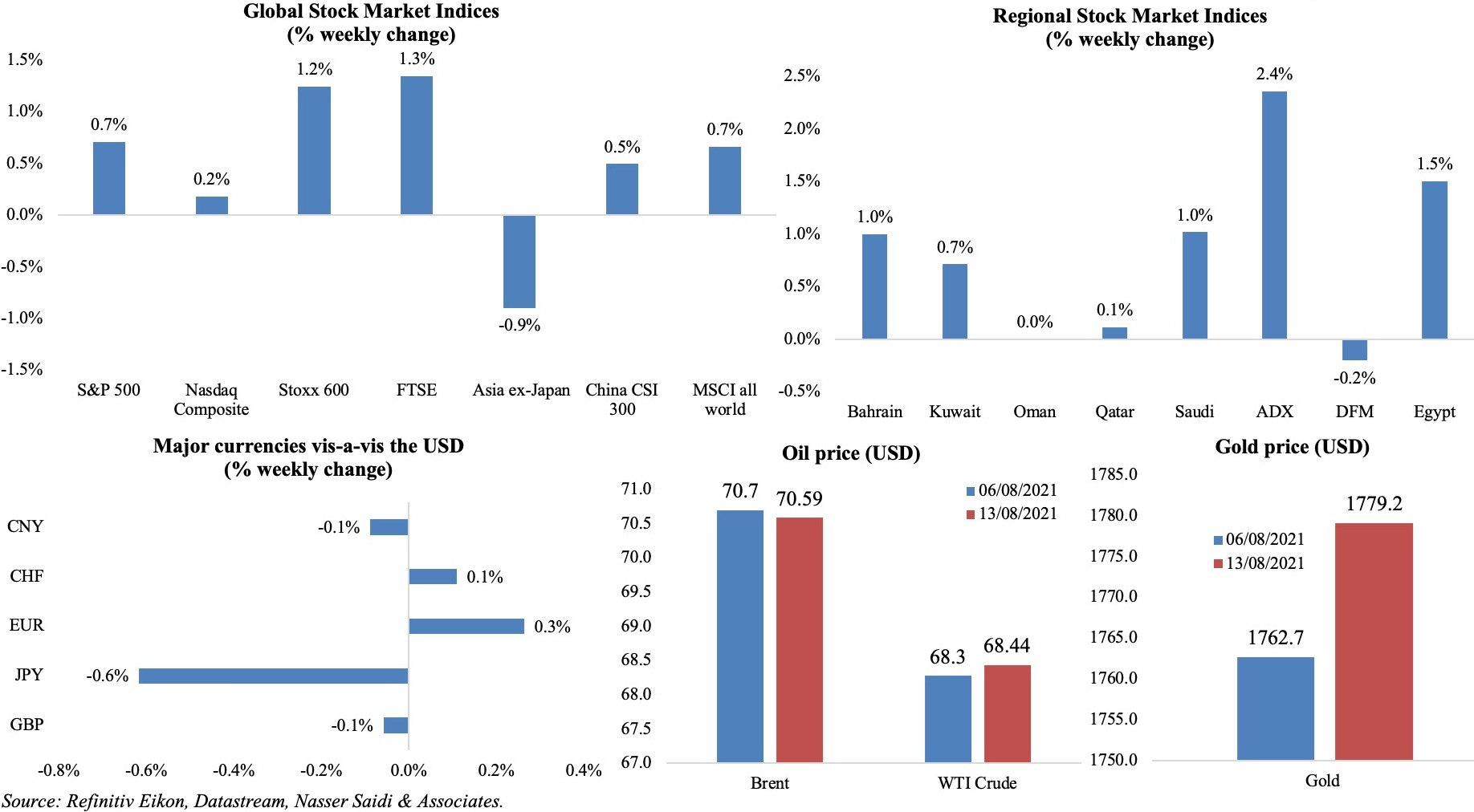
Global stock markets – including S&P 500, Dow Jones Industrial, Stoxx600, MSCI World – continued an upward trajectory posting new record highs thanks to stronger-than-expected earnings results. Meanwhile, surging Covid19 cases in wider Asia-Pacific and regulatory crackdown in China cast a shadow on equities. Regional markets were mostly up: corporate earnings supported the uptick and Abu Dhabi gained the most, also hitting a record high early in the week (thanks to International Holding (IHC)). The dollar strengthened and the euro was down (inching near a 4-month low) for the second consecutive week. Brent was relatively stable around the USD 70-mark while WTI edged up slightly in spite of the IEA’s warning of slowing oil demand and gold price rose by 0.9%.
Weekly % changes for last week (12-13 Aug) from 5 Aug (regional) and 6 Aug (international).
Global Developments
US/Americas:
- Inflation in the US moderated slightly to 0.5% mom in Jul (Jun: 0.9%) while in yoy terms, inflation held steady at 5.4% (a 13-year high). Excluding food and energy, prices eased to 0.3% mom from 0.9% the month before. In yoy terms, core inflation stood at 4.3%, down from Jun’s 4.5%.
- Producer price index increased to 7.8% yoy in Jul (Jun: 7.3%), the largest increase in more than a decade. Excluding food and energy, PPI inched up to 6.2% (Jun: 5.6%).
- Initial jobless claims fell for a 3rd straight week, declining to 375k in the week ended Aug 6th, from an upwardly revised 387k the week before, raising the 4-week average to 396.25k. Continuing claims slipped to 2.866mn in the week ended Jul 30th. Separately, JOLTS job openings increased to a record 10.073mn in Jun (May: 9.483mn), higher than the 8.7mn persons are officially unemployed.
- The preliminary reading for non-farm productivity in the US increased at a 2.3% annualized rate in Q2 versus Q1’s 4.3% gain. Unit labour costs increased to 1% from a revised 2.8% fall the quarter before (a bit misleading given the higher impact on lower-wage sectors during the pandemic). Overall output is now 1.2% above pre-pandemic levels but hours worked remain 2.8% below it.
- Budget deficit in the US widened to USD 302bn in Jul (Jun: USD 174bn), a record for the month. Overall federal deficit touched a total USD 2.5trn for the first 10 months. More fiscal expansion is underway: the Senate passed the USD 1trn infrastructure package last week and this includes USD 550bn in new spending, as well as USD 450bn in previously approved infrastructure investment.
- Michigan consumer sentiment index declined to 70.2 in Aug (Jul: 81.2), posting the lowest reading since 2011.
Europe:
- Germany’s exports grew by 1.3% mom while imports were up by 0.6% in Jun, widening the trade surplus to EUR 13.6bn. Exports to non-EU nations grew by 23.7% yoy and 3.1% mom to EUR 53.5bn, largely due to the low base year effect.
- The ZEW Economic sentiment index for Germany plunged to 40.4 in Aug (Jul: 63.3) while the current situation reading improved to 29.3 from 21.9 the month before.
- Eurozone’s ZEW Economic sentiment index also slipped to 42.7 in Aug (Jul: 61.2). The indicator for the current economic situation climbed 8.6 points to 14.6 compared to Jul.
- The harmonized index of consumer prices in Germany remained steady at 3.1% yoy and 0.5% mom in Jul. Separately, wholesale price index inched up to 11.3% yoy in Jul (Jun: 10.7%), recording the fastest pace since Oct 1974 (largely a low base effect). Wholesale prices have been on the rise since Feb 2021.
- Industrial production in the Eurozone unexpectedly declined by 0.3% mom in Jun, recovering from the 1.1% drop the month before. Production of capital goods and energy declined by 1.5% and 0.6% respectively but this was partially offset by increases in non-durable (+1.6%) and durable consumer goods (+0.1%) and intermediate products (+0.1%).
- GDP in the UK rebounded in Q2, rising by 4.8% qoq from Q1’s 1.6% dip. Overall, GDP remained 2.2% below the pre-pandemic reading. June’s 1% growth was a result of the easing of lockdown restrictions: services sector expanded by 1.5% (restaurants and cafes were up by over 10%) and a 4.5% rise in health services.
- Industrial production in UK shrank by 0.7% mom in Jun, due to maintenance in oil field production sites and the volatile pharmaceutical sector; manufacturing production ticked up by 0.2% mom and 13.9% yoy while construction output fell by 1.3% mom.
Asia Pacific:
- Inflation in China eased to 1% yoy in Jul (Jun: 1.1%), as food prices fell by 3.7% from a year ago (Jun: +1.7%) while non-food prices increased by 2.1% (Jun: 1.7%). while core CPI rose to 1.3% (Jun: 0.9%). Producer price index remained high, inching up to 9% from 8.8% the month before, as prices of crude oil, coal and related products rose.
- Money supply in China increased by 8.3% yoy in Jul, posting a 17-month low, and slowing from the 8.6% growth reported in Jun. New loans almost halved to CNY 1080bn from Jun’s CNY 2120bn and is the lowest since Oct 2020. Growth of outstanding total social financing (TSF), slowed to 10.7% – the weakest since Feb 2020 – and from 11% in Jun.
- FDI into China increased by 25.5% yoy to CNY 672.19bn (USD 103.69bn) in Jan-Jul this year. FDI from both Belt and Road nations and the ASEAN grew by 46.3% during the period.
- Current account surplus in Japan surged by 50.3% yoy to JPY 10.5trn in H1 this year, thanks to an expansion of exports (up 22% to JPY 39.2trn) while imports also grew (+11.6%). This overtakes the pre-pandemic surplus level of a JPY 10.3trn posted in H1 2019. However, the services trade deficit, at JPY 2.1trn in H1 2021, was the worst reading since H2 2012.
- Industrial output in India increased by 13.6% yoy in Jun, due to a low base effect, and following a 29.3% rise the month before. Manufacturing output grew by 13% from 34.5% in May. The cumulative growth during Apr-Jun was 45% versus a contraction of 35.6% in the same period a year ago. It remains 7% lower compared to pre-Covid levels.
- GDP in Singapore fell by 1.8% qoq in Q2, following a 2% dip in Q1. In yoy terms, GDP rebounded by 14.7% (higher than the advance estimates of 14.3%), thanks to increases in manufacturing (+17.7% yoy) and services producing industries (+10.3%) while construction more than doubled from a year ago. In absolute terms, GDP remained 0.6% below Q2 2019. Overall GDP growth forecast for 2021 was raised to 6-7%, citing “a gradual recovery in the second half of the year, supported in large part by outward-oriented sectors”.
Bottomline: With Covid19 cases topping 206mn globally, the Delta variant continues to play havoc. In the US, cases and hospitalizations continued to rise among the unvaccinated, with the number of children hospitalized rising to a record high of just over 1900 on Saturday. Southeast Asia continues to be bogged down by an increase in daily cases, resulting in extension of lockdowns. The pace of vaccination makes a difference: Singapore’s relatively high rate (close to 60% fully vaccinated) is allowing it to ease restrictions albeit slowly. China meanwhile closed a terminal at the Ningbo-Zhoushan port (the 3rd busiest globally) after detecting a single case, a move that is likely to reverberate in further delays and rising shipping costs. Meanwhile, the IEA slashed its oil demand forecast given the virus outlook, in contrast to the OPEC which raised non-OPEC supply forecast. Separately, the US has called on the OPEC and allies to pump more oil to allow for lower fuel prices – a strange move considering the Biden administration’s push for combating climate change.
Regional Developments
- Annual rate of urban inflation in Egypt increased to a 7-month high of 5.4% in Jul (Jun: 4.9%), largely due to the increase in food costs (+4.9%), transport (+6.6%) and alcohol and tobacco (+2.9%). Fuel and utilities prices had been hiked in Jul, but the rate is still at the lower end of the central bank’s target range of between 5-9%.
- Egypt’s Industrial Development Authority is building 17 industrial complexes, comprising 5,046 units, at a cost of EGP 10bn and expected to create about 48k direct jobs.
- Egypt plans to expand urban development nationwide to accommodate nearly 10mn persons by 2022.
- Exports of agricultural produce from Egypt increased by 10% yoy to USD 2.215bn during the period Sep 2020-Jun 2021, with Arab nations the largest destination for the exports (USD 741mn). Russia was the largest importer agricultural crops (USD 307mn), followed by Saudi Arabia (USD 252mn) and UAE (USD 116mn).
- One person is dying of Covid19 every two minutes in Iran, reported state TV early last week. With just under 4% of the population fully vaccinated, a new 6-day “general lockdown” will be imposed from Monday.
- Iraq plans to increase oil production to 8mn barrels per day (bpd) by 2027, according to the country’s oil minister.
- US plans to provide over 500k vaccine doses to Iraq under the global COVAX vaccine sharing program. This is part of the over 110mn doses donated by the US globally.
- Iraq needs nearly IQD 34trn (USD 29bn) to build houses for citizens made homeless during the war, reported Alsabah daily.
- Bilateral trade between Jordan and China rebounded this year, rising by 21.4% yoy to USD 2.004bn in H1 2021. Exports to China grew by 14.1% to USD 235mn.
- Net domestic borrowing in Jordan amounted to JOD 638mn this year, versus about JOD 1461mn at end-Jul 2020.
- Volume of registered investments in Jordan’s free and development zones reached JOD 1.434bn (USD 2bn), with the number of companies operating in the zones touching 1953 at the end of 2020 (+0.2%).
- Budget deficit in Kuwait widened to a record-high KWD 10.8bn (USD 35.5bn) in 2020-21. Revenue plunged by 38.9% to KWD 10.5bn, with oil revenues down by 42.8% to KWD 8.8bn. Expenditures rose by 0.7% to KWD 21.3bn last year, with wages and subsidies accounting for 73% of the total. According to the finance ministry, average Kuwaiti crude selling price for the fiscal year stood at USD 36 per barrel, with average oil production of 2.5mn barrels per day.
- Kuwait Petroleum Corporation qualified about 70 SMEs to work with the oil sector since the launching of ‘Badir’ initiative for the qualification and registration of SMEs in oil tenders. These SMEs are registered in 4 activities: manufacturing (11), supply (20), business contracting (19) and services (20).
- Kuwait plans to vaccinate 70% of its population by end-Sep, stated the PM at an event. According to the health ministry, more than 2.5mn citizens and residents have been vaccinated so far (accounting for 66% of the population).
- The crisis worsens in Lebanon: the central bank announced an end to financing fuel subsidies, also revealing that more than USD 800mn had been spent on fuel in Jul. The government opposed this move, stating that prices should not change till prepaid cash cards are issued to the needy (approved by parliament in Jun, but not rolled out yet due to the dollar debate). This move will lead to accelerating inflation, further depreciation of the LBP as well as severe disruption of economic activity & food security.
- Saudi Arabia, while expressing solidarity with Lebanon, explicitly stated that any assistance to the current or future governments was dependent on the rollout of “serious and tangible reforms”.
- Oman’s fiscal deficit touched OMR 1.1bn (USD 2.86bn) in H1 this year, according to the finance ministry.
- The Capital Market Authority in Oman approved licensing for crowdfunding platforms, citing potential to create more jobs, allow for financial inclusion of SMEs and overall economic development. Regulations are in the final stages of revision and the first platform is expected to launch by end-2021.
- About 123k tourists visited Oman in Jun 2021, with Indians and GCC nationals accounting for 34.5% and 30.6% of the total.
- Oman aims to vaccinate 320k students aged 12 and above ahead of the start of the new school year.
- Oman has established a national hydrogen alliance including 13 institutions from the public and private sectors.
- Qatar recorded a surplus of QAR 3.8bn (USD 1.04bn) in Q2 2021, according to the finance ministry. Revenues touched QAR 50.1bn (+10.7%, with oil and gas revenues fell by 22.6% qoq) while expenditures touched QAR 46.2bn.
- In the latest edition of the Conference Board’s consumer confidence in the GCC, Saudi Arabia and UAE posted the highest consumer confidence (both at 130) followed by Bahrain and Qatar (both at 104), Oman (98) and Kuwait (96).
Saudi Arabia Focus
- Saudi Arabia grew by 1.5% yoy in Q2 2021, supported by non-oil sector’s 10.1% expansion while the oil sector shrank by 7%.
- Fiscal deficit in Saudi Arabia stood at SAR 4.6bn (USD 1.23bn) in Q2 2021, narrowing from the SAR 109.2bn deficit posted in Q2 2020. Revenue from oil increased by 38% yoy to SAR 132.15bn while non-oil revenues increased just over 3-fold to SAR 115.96bn. Expenditure in Q2 grew by 4% to SAR 252.7bn.
- Foreign investor licenses issued in Saudi Arabia grew by 2.6% qoq to 478 in Q1: this is the highest number since records began in 2005. Of these, almost one-fourth (114 licenses) were for the manufacturing sector while industrial investments in Q1 grew to almost USD 4.7bn – more than 4 times the amounted invested last year. The construction sector saw 78 permits being issued.
- A recent report titled “Privatisation Program 2025” identified 59 initiatives in Saudi Arabia to generate SAR 143bn (USD 42bn) in cumulative revenues via asset sales and Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) by 2025. In 2020, revenues from asset sales stood at SAR 75bn while PPP investments generated SAR 13.46bn.
- Saudi Arabia’s General Authority for Competition announced that it had issued no objection certificates to the merger of 32 firms and local currency exchange trading companies to form a closed joint-stock company.
- Industrial production in Saudi Arabia increased by 11.9% yoy and 3.6% mom in Jun, largely due to the uptick in mining and quarrying (19.3% yoy and 4.5% mom). Non-oil manufacturing activity declined by 4.2% yoy and 0.4% mom.
- Saudi Arabia’s industrial sector comprised 10,138 factories as of the end of Jul, according to the Ministry of Industry and Mineral Resources, and 40% of these were located in Riyadh.
- Saudi Arabia deposited SAR 100bn (USD 26.6bn) into the accounts of beneficiaries of its Citizen Account Program since its establishment in 2017. More than SAR 9bn was paid out in Aug and arrears worth SAR 10.5mn was also paid.
- Saudi Aramco reported a 4-fold increase in net profits in Q2, supported by higher oil prices and recovery in oil demand. The CEO stated that the company is on the lookout for potential deals to offer to investors (similar to the USD 12.4bn deal in Jun for its crude pipeline network) and is also looking to tap the hydrogen market (on this note, the Saudi Cabinet approved an MoU with Germany for cooperation in hydrogen projects).
- Saudi Arabia aims to attract USD 7.3bn into the health sector from private investors, revealed the health minister. The plan is to increase private sector participation in the sector to 35% by 2030, from 25% currently.
UAE Focus![]()
- Dubai PMI increased to 53.2 in Jul (Jun: 51), posting the quickest expansion since Nov 2019. Both travel and tourism and the wholesale and retail sectors picked up during the month, with businesses citing growth in demand and improving economic conditions. In line with rising demand, employment picked up, rising at the fastest pace since Nov Despite rising input prices, companies continued to absorb costs in a bid to stimulate sales.
- Dubai’s non-oil external trade grew by 10% yoy to AED 354.4bn in Q1, revealed the DG of Dubai Customs.
- Abu Dhabi is planning to introduce a professional license allowing foreigners 100% ownership of businesses related to 604 activities including accounting, training, consultancy, beauty centres, computer and internet network companies. Such licenses will however require a local service agent who will be responsible for managing licensing requirements, according to the Abu Dhabi Department of Economic Development.
- Dubai’s e-commerce business licenses surged by 63.05% yoy to 3243 in H1 2021, according to Dubai Economy. While IT topped the list of licensed activities, followed by ready-made garments and ladies tailoring and design among others, male entrepreneurs accounted for 63% of licenses issued during the period.
- Bilateral trade between UAE and Israel currently stands at USD 712mn; it plans to boost this to USD 3bn in three years.
- Dubai Airports CEO disclosed that an estimated 56mn passengers are likely to pass through the airport next year. In H1 this year, 10.6mn passengers passed through Dubai International (-40.9% yoy) while it had handled 25.9mn persons last year and 86.4mn in 2019. Passenger traffic through the airport is expected to cross more than a million in the Aug 12-22 week) given the recent ease in restrictions and ahead of schools’ opening.
- Etihad Airways halved its core operating losses to USD 400mn in H1 2021. Operating costs were reduced by 27% to USD 1.4bn in H1, supported by grounding of its aircrafts. Separately, Etihad Cargo posted a 20% increase in tonnage compared to pre-Covid volumes.
- Hot on the heels of the first sale of UAE’s blue ammonia cargoes to Itochu, it was announced that ADNOC and Fertiglobe agreed to sell blue ammonia to Japan’s Idemitsu for use in its refining and petrochemicals operations.
- Majid Al Futtaim’s latest report revealed that consumer retail spending in the UAE was up by 4% in Q2 (faster than the 3% rise in Q2 2019); it was however down by 3% in H1 2021 compared to the same period in 2019. E-commerce sales surged by 17% yoy in H1 while online sales accounted for 9% of overall consumer spending.
- From Friday, Abu Dhabi will restrict access to certain public spaces (including universities, public and private schools) only to vaccinated persons. Separately, Dubai has further relaxed restrictions: hotels can operate at full capacity while shopping malls and restaurants can operate at 80% capacity with seating limit at 10 per table.
Media Review
For many, hydrogen is the fuel of the future. New research raises doubts.
https://www.nytimes.com/2021/08/12/climate/hydrogen-fuel-natural-gas-pollution.html
China Signals Regulatory Crackdown Will Deepen in Long Push
Will Central Bank Digital Currencies Doom Dollar Dominance?
IPCC’s AR6 Climate Change 2021 report
https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/
Kuwait’s economic makeover under threat as small businesses fight for life
How sustainable are sovereign wealth funds?
Powered by:







