Markets
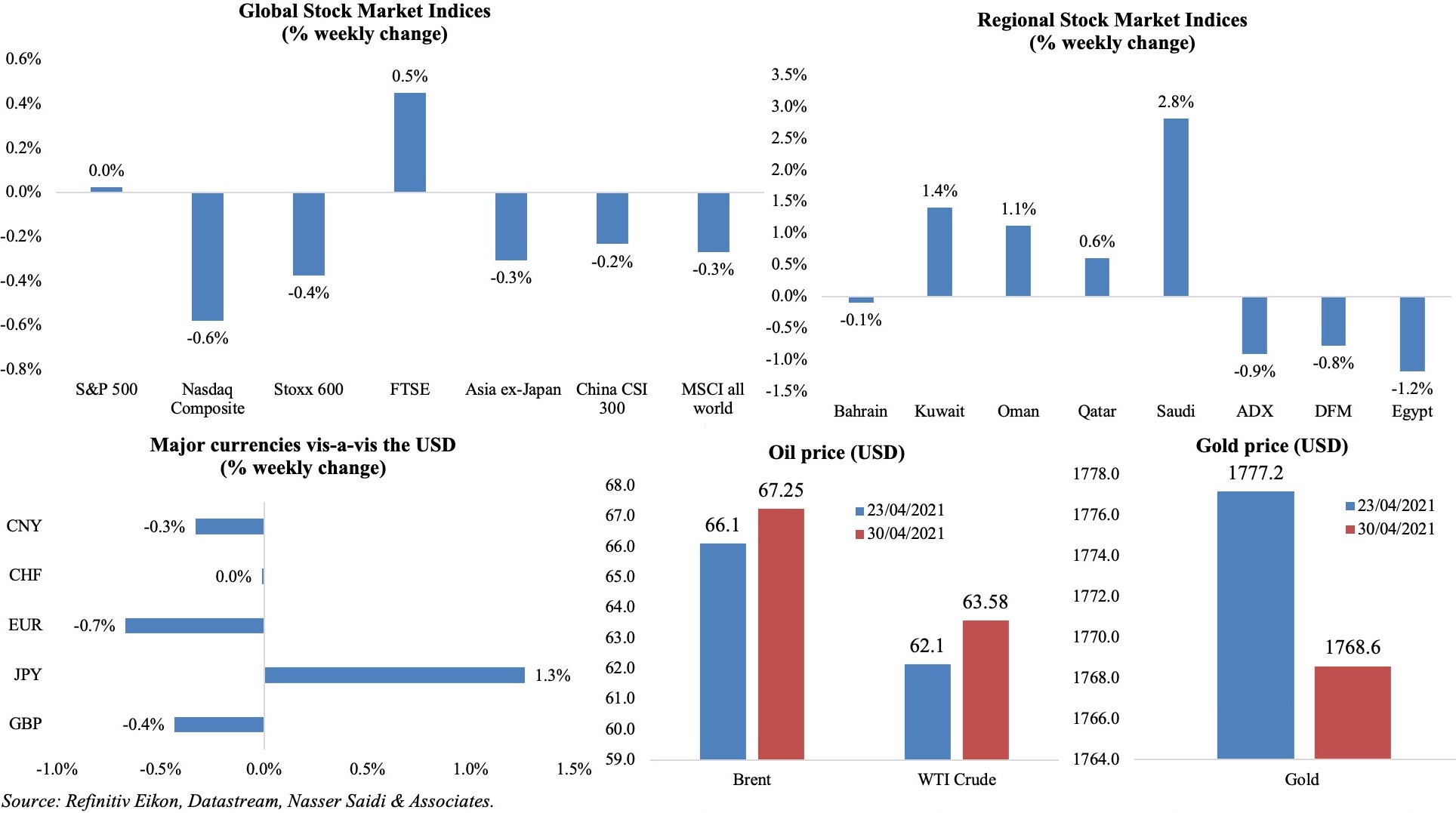
Equity markets fell across the board last week, with only FTSE in the green among major markets, as economic data weighed in on sentiment (while the US seems to be on a strong recovery path, Q1 growth dipped in the Eurozone and China’s PMI fell below levels seen last year). Though Stoxx fell compared to a week ago, it was just below its all-time high while the MSCI’s world stocks gauge hit a historic high during the week. Regional markets were mostly subdued while Saudi Arabia ended the best performer (following an uptick on Wednesday, thanks to the Crown Prince’s views during a televised interview). The dollar posted its largest monthly fall since Dec at end of Apr while the yen hit a 2-week low versus the greenback. Oil prices were at near 6-week highs on strong US data and a weaker dollar and gold was down by 0.5%. Meanwhile, copper and aluminum prices have been rallying, with the former above the USD 10k per tonne mark for the first time in over 10 years.
Weekly % changes for last week (29-30 Apr) from 22 Apr (regional) and 23 Apr (international).
Global Developments
US/Americas:
- The Fed held interest rates steady (at close to zero) and will continue with bond purchases (at least USD 120bn each month); though the Fed forecasts faster growth and higher inflation (the latter reflecting “transitory factors”), Powell stated that it was a “long way from our goals” and hence withdrawing monetary support.
- Preliminary GDP in the US increased by 4.1% yoy in Q1 (Q4: 1.9%). In annualized terms, GDP grew by 6.4% in Q1 – posting the second-fastest pace for growth since Q2 2003 (highest being the reopening surge recorded in Q3 2020) – and up from 4.3% in Q4. Consumer spending grew by an annualized 10.7%, with households spending more on goods (+23.6%) versus services (+4.6%), while government expenditures and investment increased 6.3%.
- Personal income surged by 21.1% mom in Mar (Feb: -7%), thanks to the stimulus checks (stimulus payments accounted for USD 3.948trn of the overall USD 4.213trn rise in Mar) while personal spending increased by 4.2%. The PCE Price Index rose 0.5% in Mar, while the core PCE Index, which excludes food and energy, rose 0.4% in the month.
- The Chicago Business Barometer jumped to 72.1 in Apr (Mar: 66.3), posting the highest level since Dec 1983. New orders rose 9.9 points to a near 7-year high, the production index ticked up 0.9 points to the highest level since Jan 2018 and employment, up by 1.7 points, touched the highest since Aug 2018.
- Michigan consumer sentiment index increased to 88.3 in Apr, from a preliminary reading of 86.5 – the highest since Mar 2020.
- Durable goods orders rebounded by 0.5% mom in Mar (Feb: -0.9%), with orders for new cars and trucks rising by 5.5% while semiconductor shortages continued to play havoc. Non-defense capital goods orders excluding aircraft increased by 0.9%, reversing the 0.8% drop the month before (orders for commercial airlines plunged by 47%).
- S&P Case Shiller home price indices accelerated by 11.9% yoy in Feb (Jan: 11.1%).
- Pending home sales increased by 1.9% mom in Mar, following the 11.5% drop in Feb. Sales were 23.3% higher compared to Mar 2020.
- Goods trade deficit widened by 4% to a record high USD 90.59bn in Mar (Feb: USD 88bn). Exports of goods grew by 8.7% to USD 142bn and imports were up by 6.8%.
- Initial jobless claims fell by 13k to 553k in the week ended Apr 17 holding below 600k for the 3rd straight week. Continuing claims fell to 3.660mn in the week ended Apr 10 compared to the previous week’s downwardly revised 3.651mn.
Europe:
- Eurozone’s GDP slipped into a double-dip recession, with growth declining by 1.8% yoy and 0.6% qoq in Q1 (Q4: -0.7% qoq). While Spain contracted by 0.5% and Italy’s GDP fell by 0.4%, France posted a 0.4% growth (given its delayed lockdown). The wider EU-27 nations fell into recession as GDP declined by 0.4% in Q1, following a 0.5% contraction in Q4 2020.
- Inflation in the Eurozone increased by 1.6% yoy in Apr (Mar: 1.3%); core inflation eased – down to 0.8% in Apr from Mar’s 0.9% reading. Energy prices were up by 10.3% in Apr (Mar: 4.3%) while services costs were up by 0.9% and food and beverages up by 0.7%.
- Q1 GDP in Germany fell by 3% yoy and 1.7% qoq: Destatis disclosed that household consumption was negatively affected, while exports of goods supported the economy. Separately, the government raised its growth forecast to 3.5% from a previous estimate of 3% given expectations of higher household spending once lockdowns and restrictions are lifted.
- The harmonized index of consumer prices in Germany increased by 2.1% yoy and 0.5% mom in Apr. This is above the ECB’s target of close to but below 2%.
- The Ifo business climate for Germany inched up by 0.2 points to 96.8 in Apr – the highest since Jun 2019; current assessment improved by a full point to 94.1 though expectations slowed to 99.5 (Mar: 100.3) on fears of a new wave of infections and bottlenecks in intermediate products.
- The German GfK consumer confidence survey weakened in May, with the reading falling to -8.8 from Apr’s -6.1 on rising infections and negative impact from the lockdown.
- Unemployment rate in Germany stayed unchanged at 6% in Apr, with some 2.77mn persons registered as unemployed. Separately, unemployment rate in the wider eurozone slowed to 8.1% (Feb: 8.2%) and youth unemployment rate fell to 17.2% from 17.3% in
Asia Pacific:
- China’s official NBS manufacturing PMI slowed to 51.1 in Apr (Mar: 51.9): while output, new orders and export sales softened (to 52.2, 52 and 50.4 respectively), employment fell to 49.6. Caixin manufacturing PMI rose to 51.9 from Mar’s 11-month low reading of 50.6, with new orders rising for the 11th consecutive month while input costs hit the highest level since Nov 2017. Non-manufacturing PMI slowed to 54.9 in Apr (Mar: 56.3), as new order growth eased (51.5 from 55.9) and new export orders fell (48.1 from 50.3); but it was still the 13th consecutive month of above-50 in the service sector.
- BoJ kept policy rates unchanged at the latest meeting and maintained its stimulus measures while raising growth forecasts for the current fiscal year (4% vs. 3.9% predicted in Jan) amid weak inflation views – revising core inflation downward to 0.1% (from 0.5% projected in Jan).
- Inflation in Tokyo unexpectedly fell by 0.6% yoy in Apr (Mar: -0.2%), as major carriers slashed mobile phone fees. Excluding food and energy, prices were unchanged (Mar: 0.3%).
- Industrial production in Japan increased by 4% yoy and 2.2% mom in Mar (Feb: -2% yoy and -1.3% mom). Overall industrial output fell by 9.5% yoy in the fiscal year 2020, with output of autos as well as oil and coal products both down by 16.7% in the year.
- Japan’s leading economic index eased to 98.7 in Feb from a preliminary reading of 99.7 (Jan: 98.1), the highest reading since Oct 2018. Meanwhile, coincident index stayed at 89.9.
- Manufacturing PMI in Japan inched up to 53.6 in Apr (Mar: 52.7) – touching the highest level in 3 years – as new orders expanded at the fastest pace in 38 months and output grew at the fastest since Apr 2018.
- Retail trade in Japan increased by 5.2% yoy in Mar (Feb: -1.5%) – the first uptick in retail trade since Nov 2020. Large retailer sales picked up by 3% following the 4.8% drop in Feb.
- South Korea’s preliminary GDP increased by 1.6% qoq and 1.8% yoy in Q1 this year (Q4: 1.2% qoq), recovering to pre-pandemic levels, supported by private consumption (+1.1%) and government spending (+1.7%) while exports surged 1.9%.
- Exports from South Korea expanded by 41.1% yoy in Apr – the most since Jan 2011 – thanks to semiconductors, cars and petrochemical products while imports grew by 33.9%. Exports to China, the US and EU increased by 31.7%, 43.0% and 43.0% each.
- Singapore industrial production picked up by 7.6% yoy in Mar though down by 1.7% mom; excluding the volatile biomedical manufacturing, output grew by 14.9%.
Bottom-line: India’s Covid19 cases have continued to rise at 300k+ daily cases for 10 days now, and yet another state announced a 2-week lockdown today (many others have imposed night and/or weekend lockdowns) that will sharply affect growth and recovery prospects. Amid the Covid19 rising cases (in Brazil, the death toll crossed 400k), at last week’s OPEC+ meeting it was decided to stick to the current plan to gradually raise production. Demand threat notwithstanding (India is the 3rd largest oil importer), there are also supply threats given the ongoing Iran-US nuclear talks – a potential lifting of sanctions would allow Iran to supply its oil in the global market. On the calendar this week is the Bank of England meeting – watch out for whether the Bank decides to slow pace of its bond purchases (like Canada did a few weeks back).
Regional Developments
- More than 60% of Bahrain’s adult population (estimated at 1.12mn) have received the first dose of the Covid19 vaccine and 47% have received both doses, according to a senior government official.
- Trade between Bahrain and GCC grew by 6% yoy to USD 1.76bn in Q1. Bilateral trade with Saudi Arabia accounted for about 45% of the total trade (USD 789mn) and with the UAE accounted for another 36% (+15% to USD 639mn).
- Egypt outlined a three-year structural reform plan, focusing on boosting private sector growth, increasing exports and accelerating digitization. Economic growth of between 6-7% is targeted in the next three years.
- Economic losses from the Covid19 pandemic in Egypt amounted to EGP 370bn (USD 23.6bn), according to the finance minister. He also stated that fiscal deficit for the current fiscal year is about EGP 500bn and public debt fell to 87.5% of GDP in June 2020 from 108% in June 2017 (it is forecast to reach 89% in Jun 2021).
- Egypt’s draft budget for 2021-22 has been submitted to the House of Representatives for discussion and approval: it aims to reduce budget deficit to 6.7% of GDP, clock in primary surplus of 1.5% and achieve GDP growth of 5.4%. Revenues are estimated to touch EGP 1.36trn alongside expenditures of EGP 1.8trn.
- The central bank of Egypt kept interest rates on hold for the fourth consecutive meeting: the overnight lending rate stands at 9.25% and overnight deposit rate at 8.25%.
- Money supply growth in Egypt surged by 20.06% yoy to EGP 5.13trn in Mar, revealed the central bank.
- Egypt’s external debt increased by about 1.5% qoq to USD 125.3bn as of Sep 2020, with long-term external debt (at USD 113bn) accounting for 90.2% of the total.
- Non-oil trade between Egypt and Saudi Arabia increased by 6.8% yoy to USD 4.4bn in 2020; Egypt’s exports to Saudi Arabia surged by 13% to USD 2.6bn, making the country the second largest destination for Egypt’s exports last year.
- Bilateral trade between Egypt and Jordan grew by 8.6% yoy to USD 616.3mn in 2020, with exports to Jordan up 12.2% yoy to USD 495.4mn while imports fell by 4.5%.
- Further to having signed an agreement to create a cross-border link with Euroclear in 2019, Egypt expects its domestic debt to be “Euroclear–able” and open to a larger number of foreign investors by Nov, according to the finance minister. He also disclosed that Egypt will likely join JPMorgan’s GBI-EM investment index, supporting its local currency bond markets.
- Egypt will invest USD 7.5bn to build the largest petrochemical complex in Africa and the Middle East in the Ain Sokhna Industrial Zone of the Suez Canal Economic Zone.
- Tourism revenues in Egypt are expected to increase to USD 6-7bn this year, revealed the deputy tourism minister, with tourist arrivals anticipated to recover to 60% of 2019 levels.
- Iraq’s crude oil exports from the southern ports averaged 2.7mn barrels per day in Apr, in line with its commitment with OPEC+.
- According to the minister of planning, Iraq requires IQD 136trn (USD 93.19bn) to complete ongoing (6000+) projects; oil and electricity projects are the most in number.
- Kuwait aims to vaccinate 70% of the target population within 2 months provided it receives the anticipated number of doses on time, reported Al-Qabas daily.
- The 2021-22 development plan in Kuwait envisions 132 projects with a combined value of around KWD 1.8bn (USD 6bn), reported Al-Anba daily, citing a government document. This also includes the construction of an “international economic zone” though related costs or location are not disclosed.
- Bank lending to the property sector in Kuwait plunged by 64.6% ytd to KWD 224.6mn as of end-Feb. Mortgage finance declined by 16.8% mom in Feb.
- Oman’s fiscal deficit expanded to OMR 751.4mn in Q1 (Q1 2020: OMR 26.3mn): revenues were down by 30.5% yoy to OMR 1.82bn while spending slipped by 2.73% to OMR 2.57bn.
- Oman’s state-oil firm OQ will be tapping the international bond market for the first time to raise at least USD 500mn from the issuance. This forms part of OQ’s larger plans to sell assets, issue bonds and refinance debt to fund a USD 7.9bn spending plan over next five years.
- The supply and transportation of goods and services in Oman’s “special zones” – Special Economic Zone at Duqm and free zones in Salalah, Sohar and Al Mazunah – are zero-rated for VAT.
- Qatar posted a QAR 200mn (USD 55mn) surplus in Q1 2021, supported by an oil price recovery in the quarter, according to the finance ministry; revenues touched QAR 45.2bn.
- Qatar’s Emir met with Saudi Arabia’s minister of state, reviewed “issues of common interest” and discussed “enhancing and developing bilateral relations” in various fields.
- Qatar Petroleum is planning its first ever USD-denominated public international bond sale, reported Reuters. The company has more than USD 25bn in outstanding loans and bonds.
- Exports from Brazil to the Arab region surged by 22.5% yoy to USD 2.91bn in Q1 this year; Saudi Arabia accounted for about 18% of this total, while Bahrain, Egypt and the UAE came next. Iron ore and food products (sugar, poultry, beef, cereals) were the major exports.
Saudi Arabia Focus
- The highlight of last week was the Saudi Crown Prince’s TV interview, given the fifth anniversary of Vision 2030: he disclosed that discussions are ongoing to sell 1% of Aramco to a leading global energy company and sale to international investors could happen in the next one year or two; no plans were underway to introduce an income tax and that the VAT hike to 15% was temporary; a Budget Bureau has been set up to take over from the finance ministry’s budget setting role; a new Policies Office will be launched by end of this year; importantly, there was a softened stance regarding Iran.
- Saudi Arabia’s trade surplus widened by 22.1% yoy to SAR 25.4bn in Feb: non-oil exports rose by 16.2% to SAR 18.6bn, oil exports fell by 1.4% and imports fell by 6% to SAR 40.4bn.
- Foreign reserves in Saudi Arabia grew by 1.7% mom to SAR 1.683trn (USD 448.9bn) in Mar; reserves were down by 5% yoy.
- Consumer spending in Saudi Arabia increased by 2.08% yoy to SAR 260.8bn in Q1, though declining by 1.6% in qoq terms. Point of sales transactions surged by 37.7% yoy while cash withdrawals declined by 13.96%.
- Saudization rate nudged up to 22.75% in Q1 from 20.37% a year ago; financial and insurance sector achieved the highest rate at 83.6%, followed by public administration, defense, and mandatory social insurance (71.9%).
- Saudi Arabia’s Tourism Development Fund, along with Riyad Bank, launched the SAR 2bn (USD 530mn) Tourism Partners Program to develop key tourism destinations.
- Bloomberg reported Saudi Arabia is planning to establish a homegrown electric-car maker, in a bid to boost local manufacturing, with BCG as advisers.
UAE Focus![]()
- Preliminary results from the Federal Statistics and Competitiveness Centre show the UAE’s economy shrank by 1% last year and non-oil gross domestic product contracted 6.2%. GDP last year stood at almost AED 1.42trn at constant prices, with non-oil GDP making up just over AED 1trn of this.
- Inflation in Abu Dhabi fell by 0.46% yoy in Q1: prices of food and beverages as well as utilities increased (by 1.4% and 0.3% respectively), while recreation costs plunged by 17.3%.
- Dubai unveiled the Food Tech Valley: aiming to triple UAE’s food production, it will host R&D facilities, an innovation centre, a smart food logistics hub and areas for vertical farming. It is expected to “serve as a global destination for start-ups and industry experts in the food ecosystem”.
- The UAE Central Bank’s Q1 2021 Credit Sentiment Survey showed a strong demand for personal loans alongside a moderate rise in business loans in Q1; overall demand was for housing, personal and credit card loans – most significantly in Dubai.
- The number of patents registered in the UAE reached 25,598 by end-2020, while the number of live patent applications stood 1,971.
- One of Israel’s biggest energy companies plans to sell 22% share of the offshore Tamar gas field to UAE’s Mubadala for an estimated USD 1.1bn. The Tamar field, which went online in 2013, is believed to hold more than 300bn cubic meters of gas.
- Early evidence of the impact of Covid19 pandemic on companies: the 2009-crisis hit Dubai property developer Limitless disclosed a reduction of about 31% “in key asset values since year end 2019”.
- S&P affirmed Ras Al Khaimah’s sovereign credit ratings of “A-/Stable/A-2” given expectations that the government will maintain its “prudent fiscal stance” over the next 2 years. It also affirmed Sharjah’s “BBB-” long-term sovereign credit rating with a stable outlook, on expectation that government debt will remain below 60% of GDP through 2024.
Media Review
Mideast Petrostates Ramp Up Oil-Asset Sales to Raise Billions
https://www.bloombergquint.com/business/mideast-petrostates-ramp-up-oil-asset-sales-to-raise-billions
Iran negotiator: based on accords so far, U.S. sanctions on oil, banks would be lifted
https://www.reuters.com/world/middle-east/iran-nuclear-talks-make-progress-will-resume-friday-russia-says-2021-05-01/
Saudi crown prince softens Iran rhetoric in balancing act
https://www.reuters.com/world/middle-east/saudi-crown-prince-softens-iran-rhetoric-balancing-act-2021-04-28/
Entire TV interview (in Arabic): https://youtu.be/fwn1Cusx_Rk
UAE and UK set to sign multibillion-pound clean energy and tech investment deals
https://www.thenationalnews.com/business/economy/uae-and-uk-set-to-sign-multibillion-pound-clean-energy-and-tech-investment-deals-1.1211510
Tracking the economic impact of India’s second covid wave
https://www.economist.com/finance-and-economics/2021/05/01/tracking-the-economic-impact-of-indias-second-covid-wave







