UAE, Covid19 & economic activity after re-opening post-lockdown
With UAE easing restrictions imposed due to the Covid19 outbreak and opening the economy in phases, a pickup in economic activity is inevitable. The Oxford Government Stringency Index (which records the number and strictness of government policies) scores the UAE at 69.44 in the beginning of Jul, down from a high of 89.81 recorded during the first two weeks of Apr (a higher score indicates a stricter government response). The question however remains whether residents have embraced the “re-opening” and gone back to “business as usual”.
Few economic indicators are released monthly in the UAE and hence the availability of Google and Apple Mobility numbers offer a good perspective of where the economy is headed to, reopening after the lockdown. Google Mobility indicators show trends over several weeks on how visits to various sectors – retail & recreation, grocery and pharmacy, parks, transit stations, workplaces – compare to a baseline value for that day of the week [1] while residential shows a change in duration of time spent at home. Apple Mobility indicators track resident activity – walking and driving – which can also be read into as “confidence” indicators i.e. you are more likely to be out exercising if you have accepted the new Covid19 realities (social distancing, wearing masks etc).
These high-frequency indicators offer an insight into retail behaviour (visit to recreation, retail outlets, groceries), as well as economic activity (transit stations, workplaces and residential) while parks and walking can be interpreted as “social well-being”, an equally important measure.
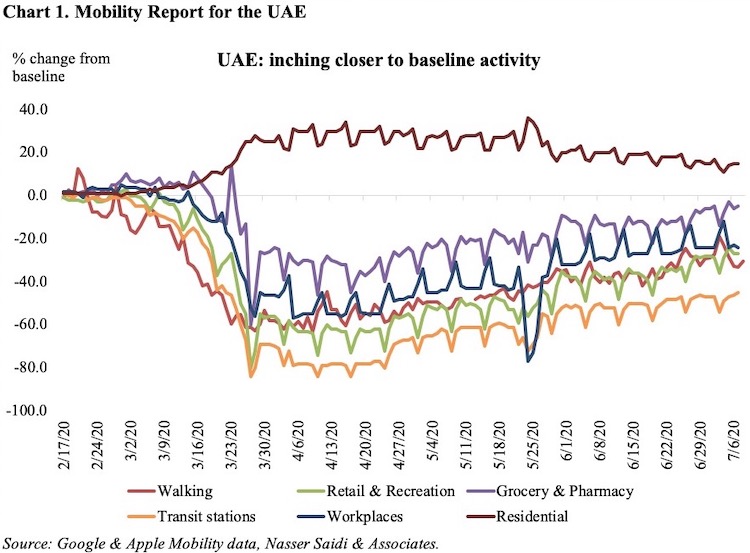
The lockdown phase in the UAE (towards the end of March) is evident from Chart 1, with the various indicators dipping to near -100%. Of the indicators, the two that are inching back to baseline are visits to groceries and pharmacies as well as workplaces. During the peak of the outbreak, when severe restrictions were in place, there was a surge e-commerce activity (especially online shopping platforms) which still continues, and could explain the current gap to baseline activity.
Workplaces are still 24% below the baseline, implying that working from home is still an option being provided by many offices. If companies continue to offer flexible work options, this would reduce office space and rents, while employees can stay at cheaper home locations, save on rents, and telecommute. Congestion statistics already show a return to normal, more so in Dubai than Abu Dhabi (Chart 2). However, to fully realise the benefits of telecommuting, it requires removing barriers by amending labour laws (e.g. part-time work/ freelancing options versus being tied to a specific company) and liberalising VoIP services (for businesses, especially for SMEs).
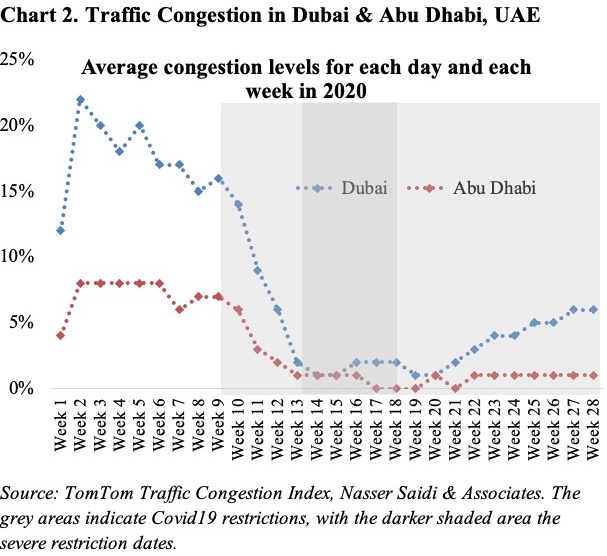
The uptick in “workplaces” has not been mirrored in “transit stations”. This is likely the result of a combination of two factors: (a) prevalence of using cars to travel – a report in Dec 2018 disclosed that UAE had an average ratio of one car to every three residents; average congestion is picking up faster in Dubai than in Abu Dhabi; (b) public transport is more frequently used by those without the option of personal transport, and who are more likely working in the services sector (e.g. in retail, hospitality sector and the like). Working in the hardest hit sectors during the Covid19 outbreak, these persons could have witnessed job losses or reduced working hours resulting in a slower uptick in “transit stations” category.
In spite of retail and recreation outlets operating at full capacity now, the return to baseline hasn’t been as smooth. One of the reasons could be the launch of online shopping by many retailers; another restriction is related to F&B operations: social distancing rules mean curtailed capacity, implying it will take longer for the sector to recover. Even during the Eid holidays in end-May, the uptick in this category was muted though lifting of restrictions mid-Jun on entry of kids and persons aged 60+ seems to have had a positive impact. With tourists back in Dubai starting Jul 7, the picture could change in the retailers’ favour.
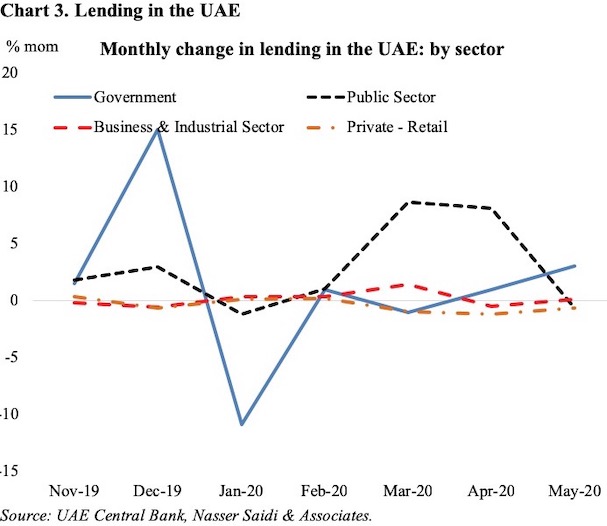
Last, but not the least, the UAE central bank has released monthly statistics for May – the 2nd month after lockdown was initiated towards end-Mar. The Central Bank had launched a AED 256bn Targeted Economic Support Scheme for banks to provide temporary financial relief for individuals, SMEs and other private businesses affected by the pandemic, following which banks offered relief for customers’ loans. Alongside, support was specifically initiated for SMEs – be it to open new bank accounts faster to providing credit guarantees. However, this does not seem to be reflected in the gross credit disbursed to UAE firms (Chart 3). Loans to the government rose by 3.06% mom in May while loans to the retail sector declined in month on month terms (-0.6%). Public sector entities (i.e. state-owned enterprises/ GREs) saw two consecutive 8%+ mom increase in loans before dropping by -0.7% mom in May.
So, what does all this mean from a policy perspective? The UAE’s drive to greater digitalization will gain traction in the new Covid19 normal: from varied e-commerce offerings to creating innovative payment systems to neo-banking options (ADGM announced associated regulations last year). A future UAE where work from home is commonplace, delinking jobs and visas are norm, and online payments are king (vs cash currently) is not far-fetched any more. The role of the private sector (including investments) is critical in achieving this goal alongside government support, and to this extend might need specific support for the SME sector which is oft sidelined given relatively lower turnover, lack of security/ collateral as well as potential for non-performing loans (and “absconding” owners).
[1] The baseline is the median value, for the corresponding day of the week, during the 5-week period Jan 3–Feb 6, 2020.
Weekly Insights 20 Jul 2020: UAE, Covid19 & economic activity after re-opening post-lockdown
20 July, 2020
Apple Mobility central bank Covid19 Google Mobility Government Stringency Index SMEs Traffic congestion UAE
read 4 minutes
Read Next
publication
Weekly Insights 25 Jul 2024: GCC are adjusting to lower oil revenues
Dubai GDP & inflation. Saudi foreign trade. Kuwait 2023-24 fiscal deficit. GCC US Treasury holdings.
25 July, 2024
publication
Weekly Economic Commentary – Jul 22, 2024
Download a PDF copy of the weekly economic commentary here. Markets Major equities
22 July, 2024
publication
Weekly Insights 19 Jul 2024: MENA growth projections lowered by the IMF; GCC’s non-oil sector growth will stay robust
IMF growth downgrades. UAE monetary stats. Abu Dhabi GDP. Saudi consumer & wholesale price indices.
19 July, 2024






