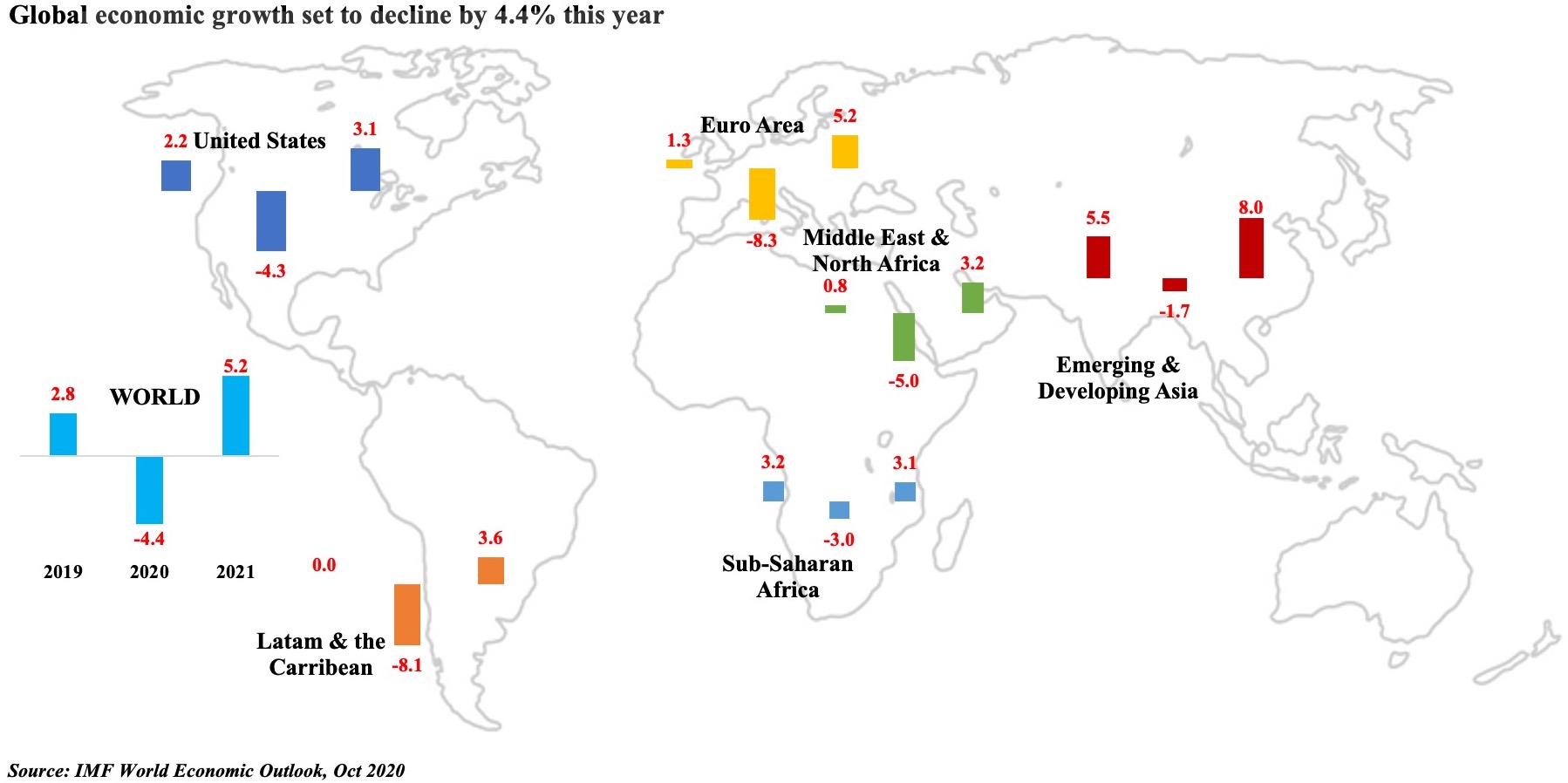
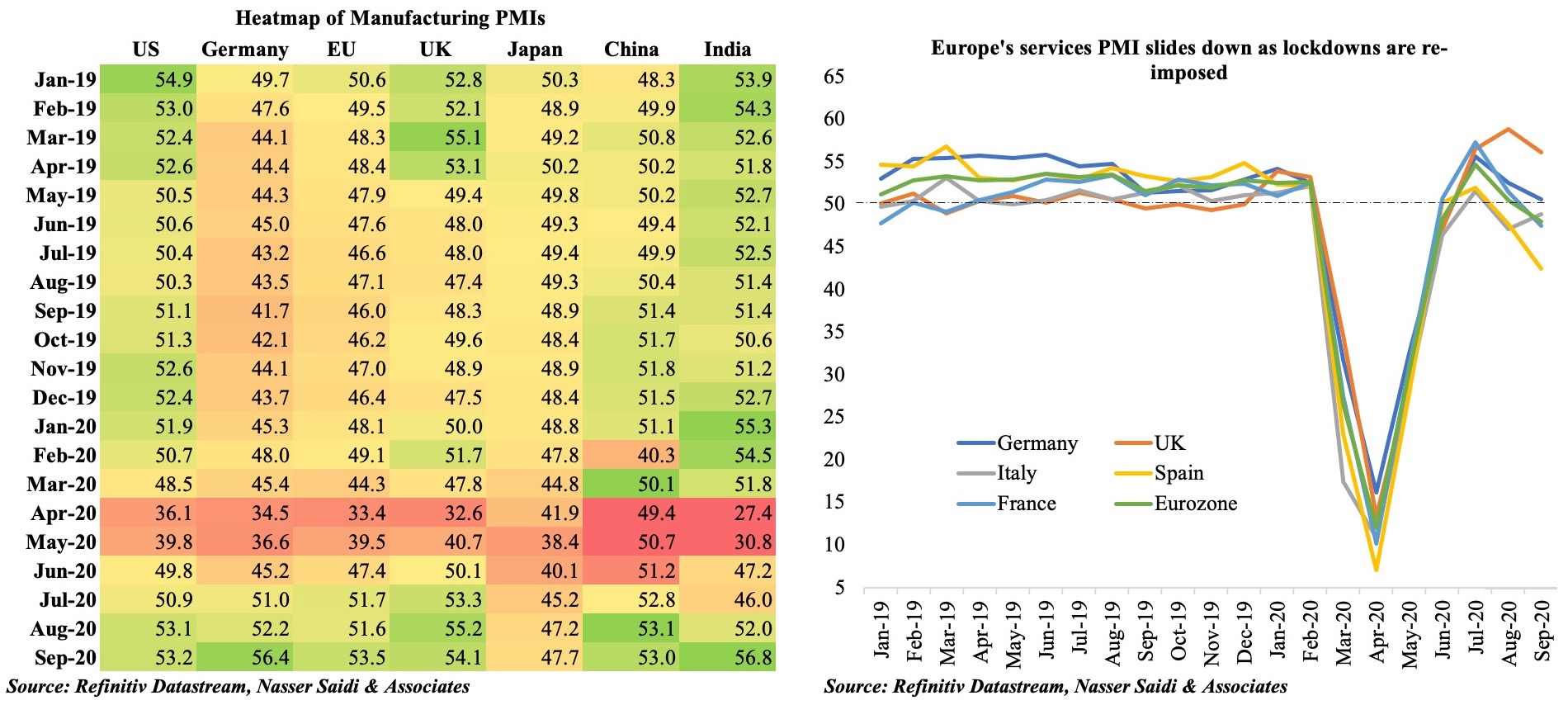
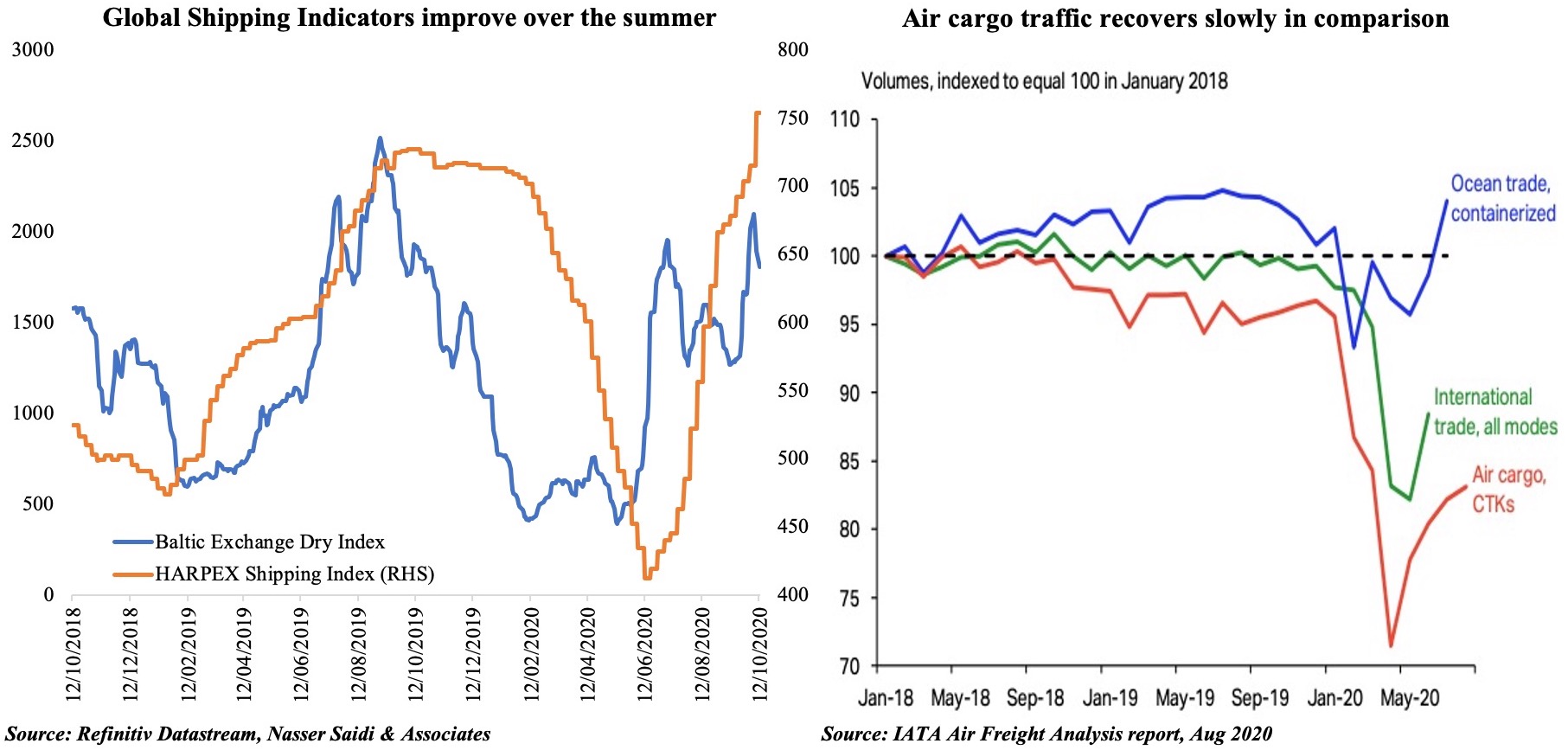
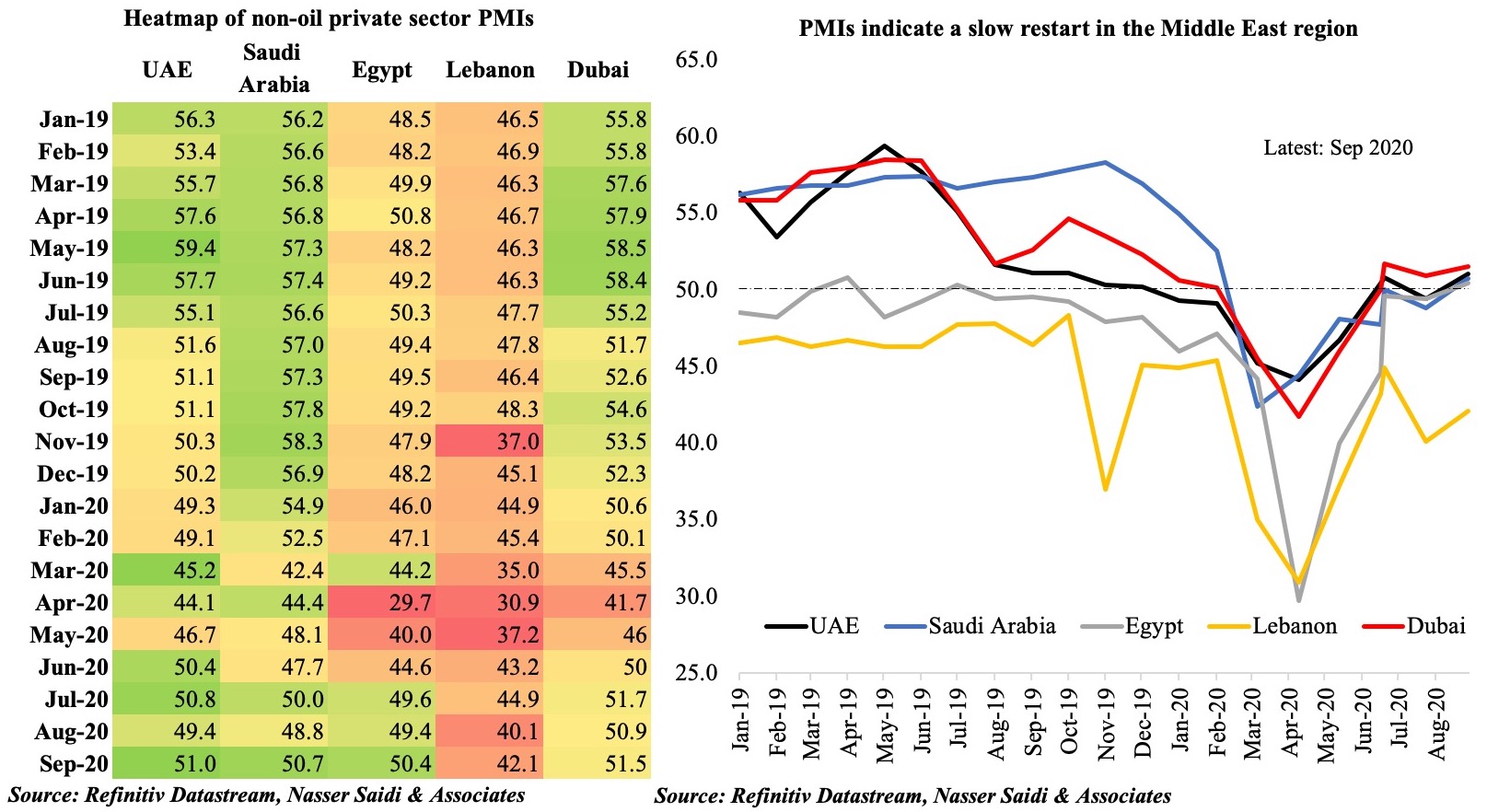
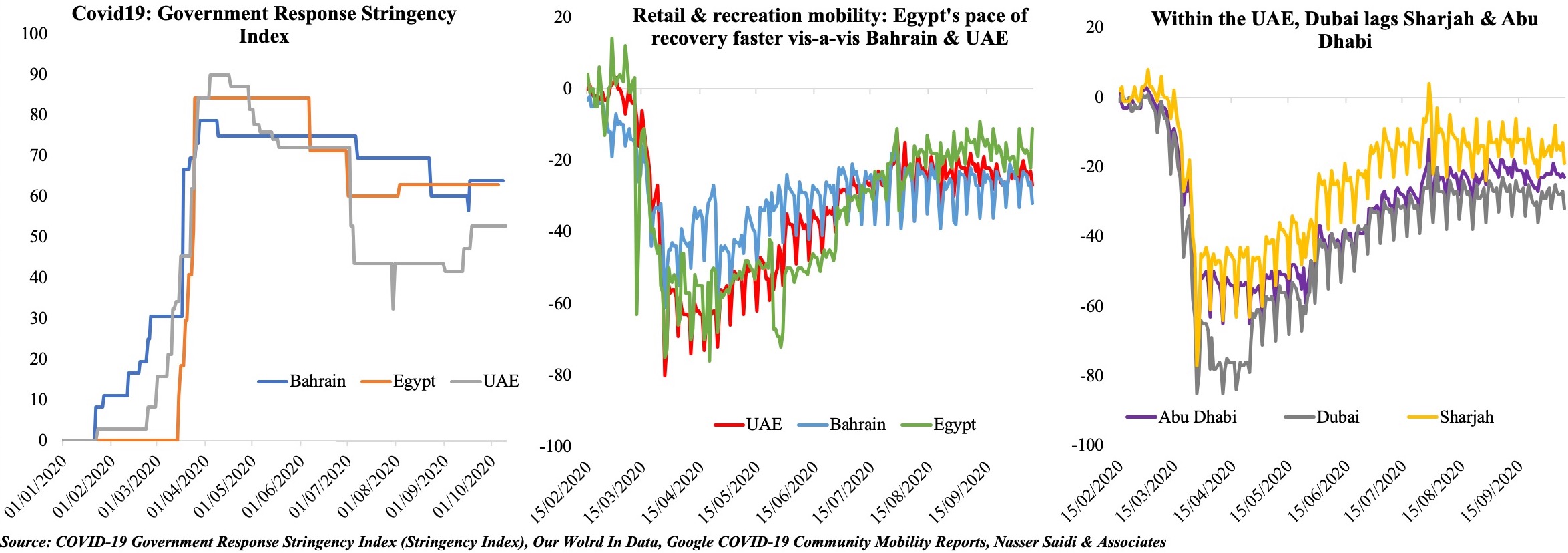
Charts of the Week: Last week, both Bahrain and Saudi Arabia released Q2 GDP numbers: as expected, overall growth contracted, with private sector activity significantly affected. The initial sections offers a forward-looking perspective on the two nations based on more recent data and proxy indicators. Saudi Arabia also disclosed a medium-term fiscal strategy, which forms the last section of this Insights’ edition.
- Bahrain GDP & economic activity
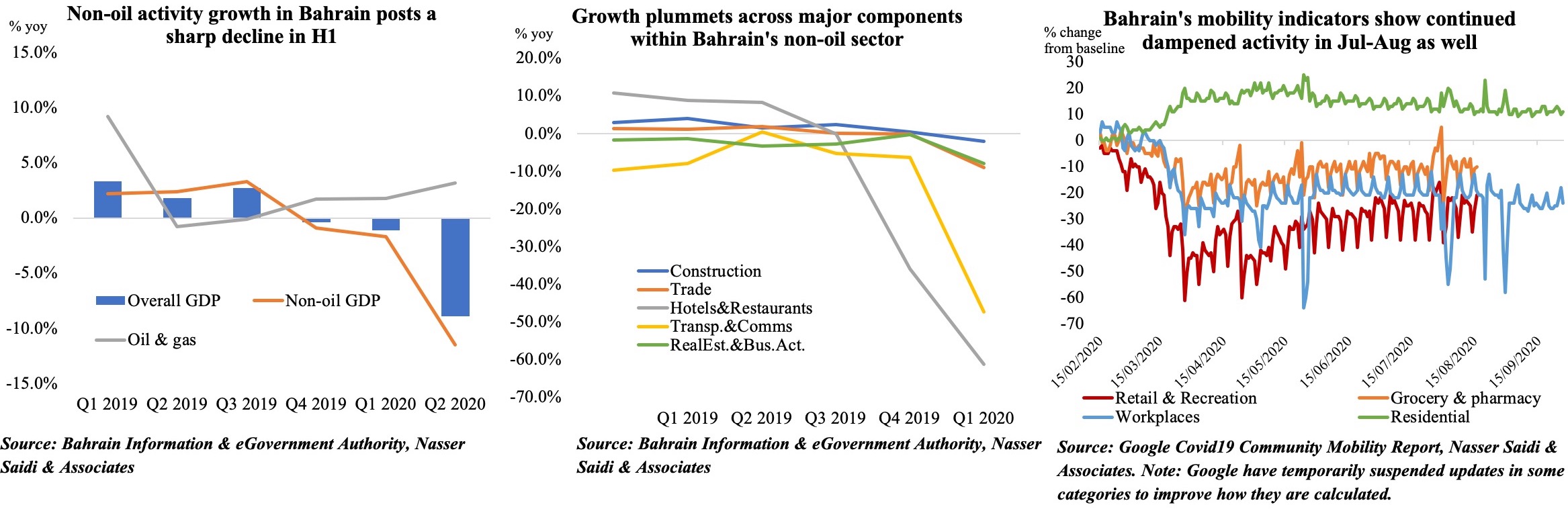
GDP in Bahrain declined by 8.9% yoy in Q2 2020, following a 1.1% drop the previous quarter. This was primarily due to the non-oil sector which plummeted by 11.5%. As expected, the largest dips in GDP came from the hotels and restaurants (-61.3%) and transport & communication (-47.4%) – both directly affected by the Covid19 outbreak. Spillover effects were also visible across the board: the financial sector, which accounts for the largest share of non-oil GDP (16.8% in Q2), posted a 5.8% drop while the sub-sectors real estate and business activities and construction slipped by 7.9% and 2.1% respectively.
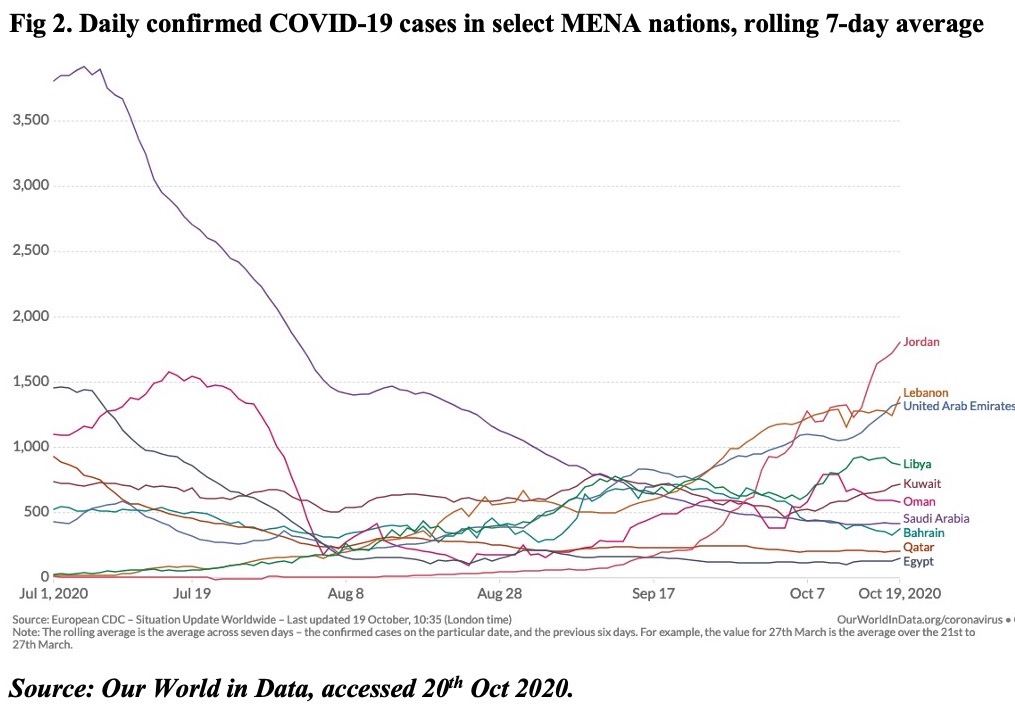
With Covid19-related restrictions slowly being phased out in Bahrain, can we expect a resumption of economic activity? The data for Jul-Aug show the pace of recovery has been slow, with readings for retail and recreation still at an average 26% below the baseline data (pre-Covid19). Recent announcements of extended government support – be it the exemption of tourism levies for 3 more months or extended support to KG & nursery teachers, taxi drivers or Bahraini citizens’ payment of utility bills and about 50% of salaries in the private sector (only those affected) – will provide direct support and likely nudge recovery. hotel occupancy rates in four- and five-star hotels increased by 13.3% mom and 17.6% in Jul and Aug respectively. Opening borders with Saudi Arabia will not only increase the number of trucks crossing the King Fahd Causeway (improving transport/ trade) but will also attract visitors from Saudi Arabia (supporting hospitality and retail).
- Saudi Arabia GDP & economic activity
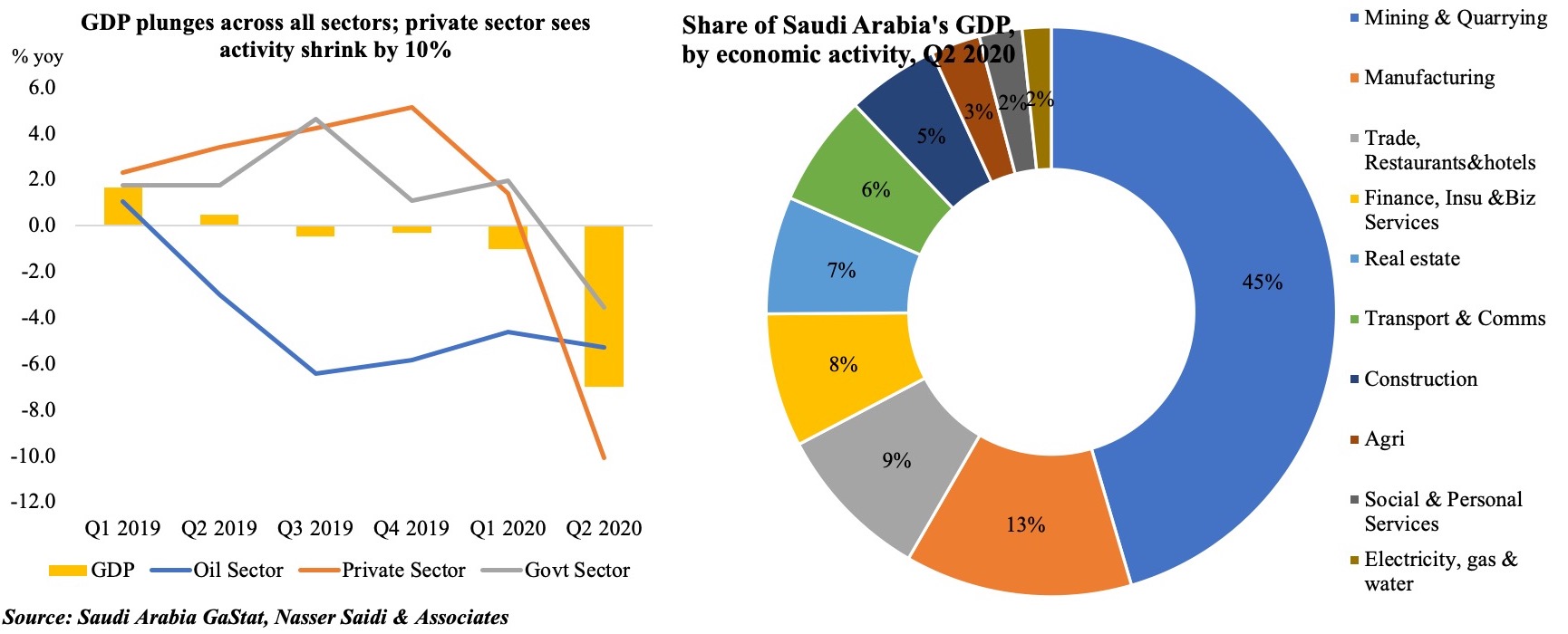
Saudi Arabia’s overall GDP plunged by 7% yoy in Q2 2020, with falls in both the oil and non-oil sectors. The oil sector’s 4.9% drop in H1 is a result of the reduction in oil production in line with the OPEC+ agreement. Within the non-oil sector, all sub-sectors posted declines in Q2 ranging from trade and hospitality (-18.3%) to finance, insurance and real estate (-0.7%). The share of GDP by economic activity shows that the oil sector continues to dominate (45% of overall GDP), closely followed by manufacturing (13%) and trade and hospitality (9%).
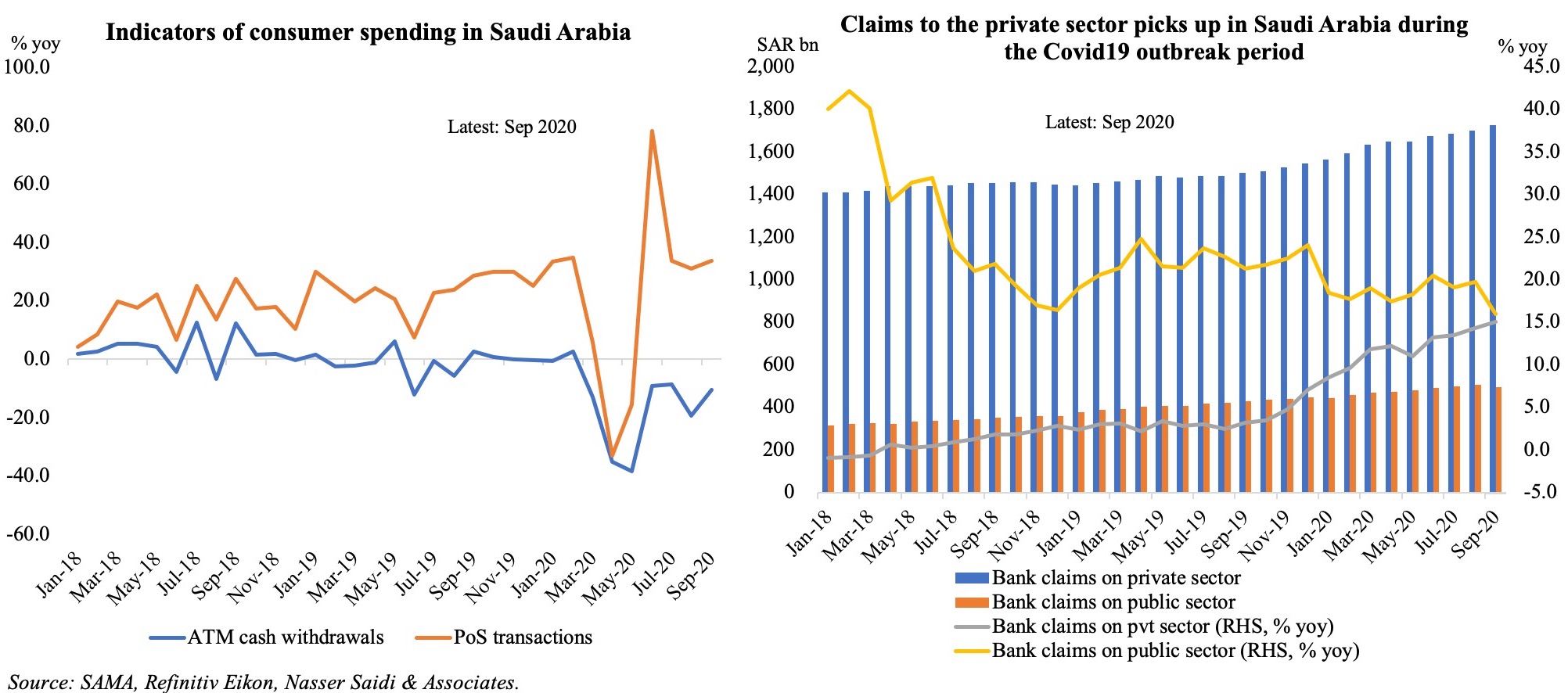
To gauge any underlying change in activity during Q3, we refer to the central bank’s data on consumer spending and point-of-sale (PoS) transactions by category. There is a spike before the VAT hike came into place in Jul, as expected, but the Aug data seems to indicate a slight recovery for hotels (+2.6% yoy, following 6 months of double-digit declines) while items like jewelry and clothing continue to register negative growth. The construction and real estate sector look well-placed to improve in H2 this year: not only has letters of credit opened for building materials imports increased by 64% yoy in Aug (following 5 months of double-digit declines), cement sales has also been picking up during Jun-Aug; a temporary boost for the sector will also come from the recent announcement that real estate would be exempt from the 15% VAT (to be replaced instead by a 5% tax on transactions, of which the government would bear the costs for up to SAR 1mn for the purchase of first homes).
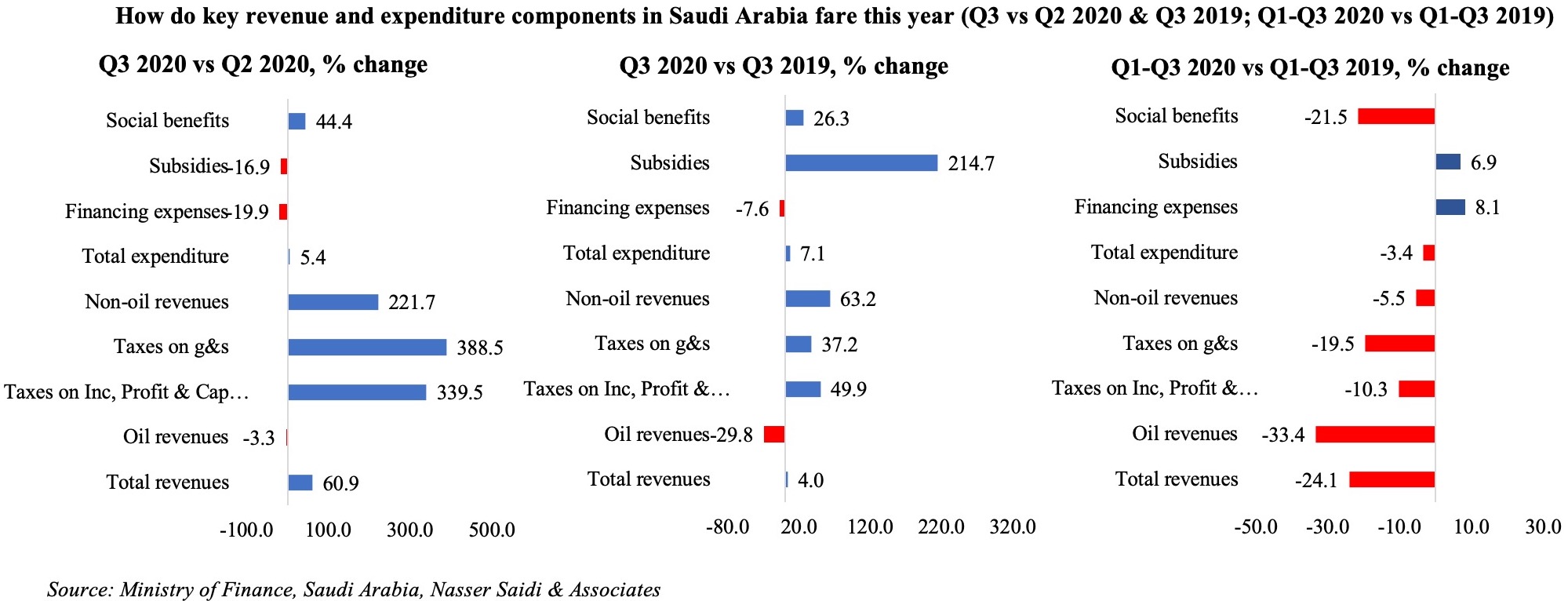
- Saudi Arabia’s fiscal space
With oil prices around the USD 40-mark, extended government support in Saudi Arabia during the Covid19 outbreak will put a strain on finances. From the H1 2020 estimates disclosed by the Ministry of Finance, it is noticeable that the share of taxes as % of overall revenue has declined to 18% (H1 2019: 23%). Compensation of employees remain the biggest strain on the expenditure side, with the single component accounting for 53% share, though it is commendable that subsidies have declined by 27.8% yoy to SAR 13bn.
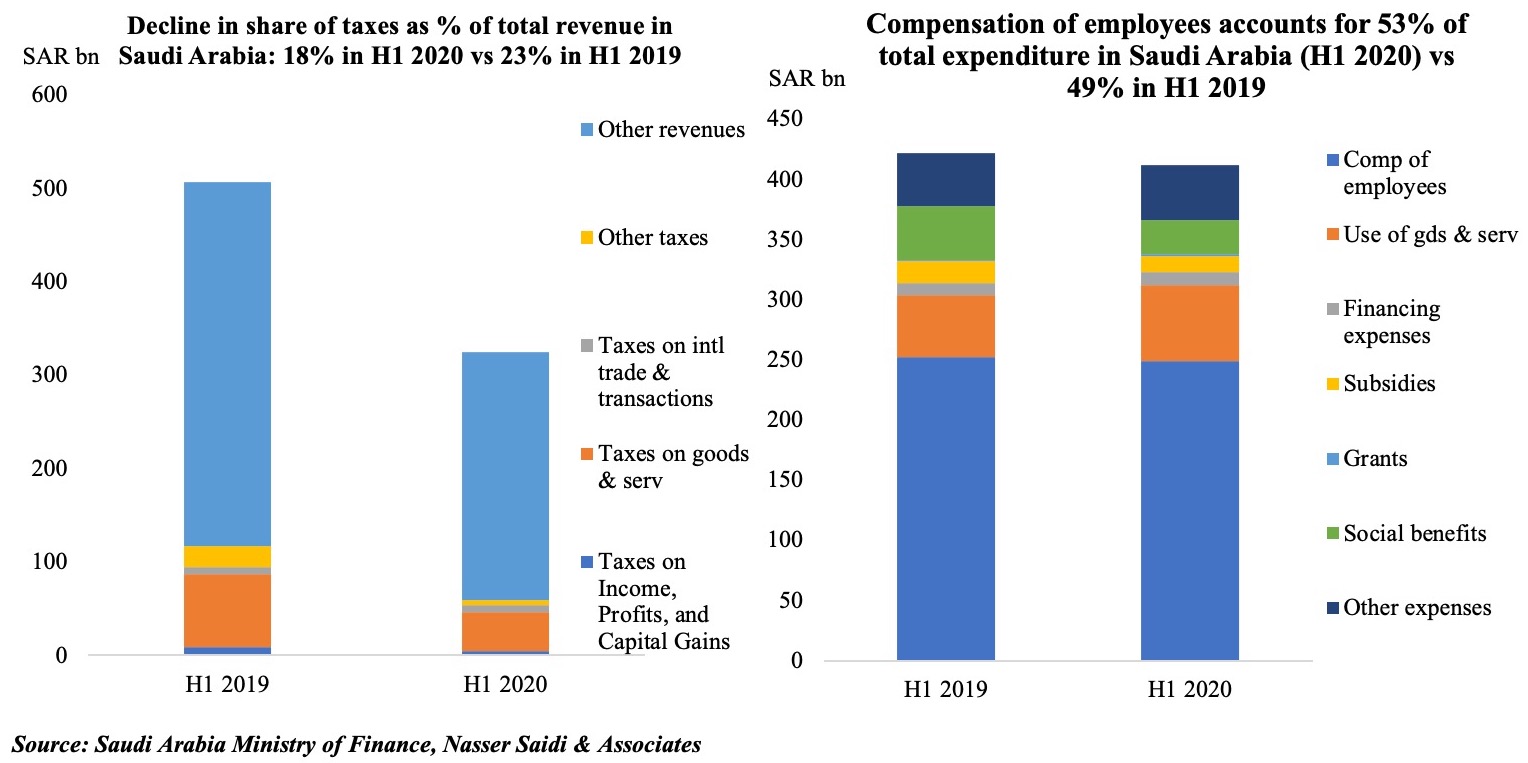
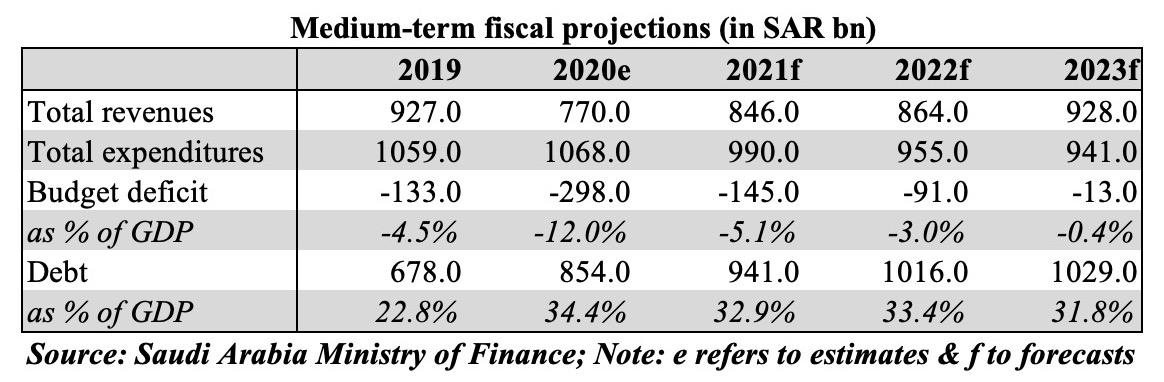
If Saudi Arabia’s fiscal consolidation plans are to be met, reforms are required on both revenue and expenditure side. The Kingdom has already increased VAT to 15% from Jul: however, with subdued demand and consumer spending, it seems unlikely that this move will add substantial revenue this year. We have highlighted in previous editions that Saudi Arabia can benefit from the introduction of other more revenue-generating taxes – e.g. carbon taxes, which will also contribute towards a cleaner environment. Additional measures could include energy price reforms (thereby reducing subsidies) as well as a consolidation or removal/ reduction of various small fees and taxes after undertaking an impact exercise (i.e. do these fees raise significant revenues or do they hinder development of the related sector?). The other major route to take is lowering “compensation of employees”: this can be done either by reducing the public sector workforce (and increasing productivity through increased digitalization) or by decreasing wages (and synchronizing public holidays) to be on-par with the private sector – these moves could also support creation of jobs in the private sector, lead to higher productivity levels and growth.
Powered by:

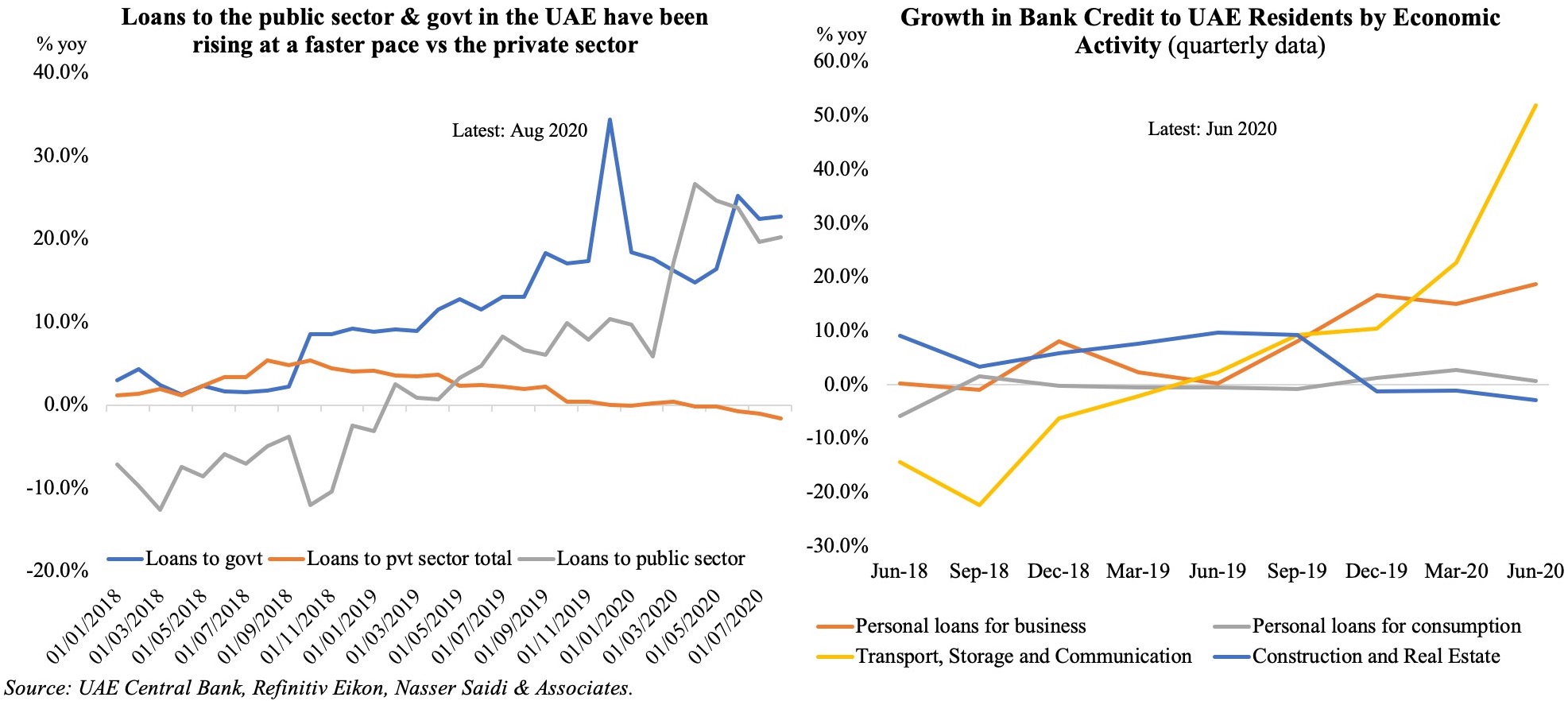
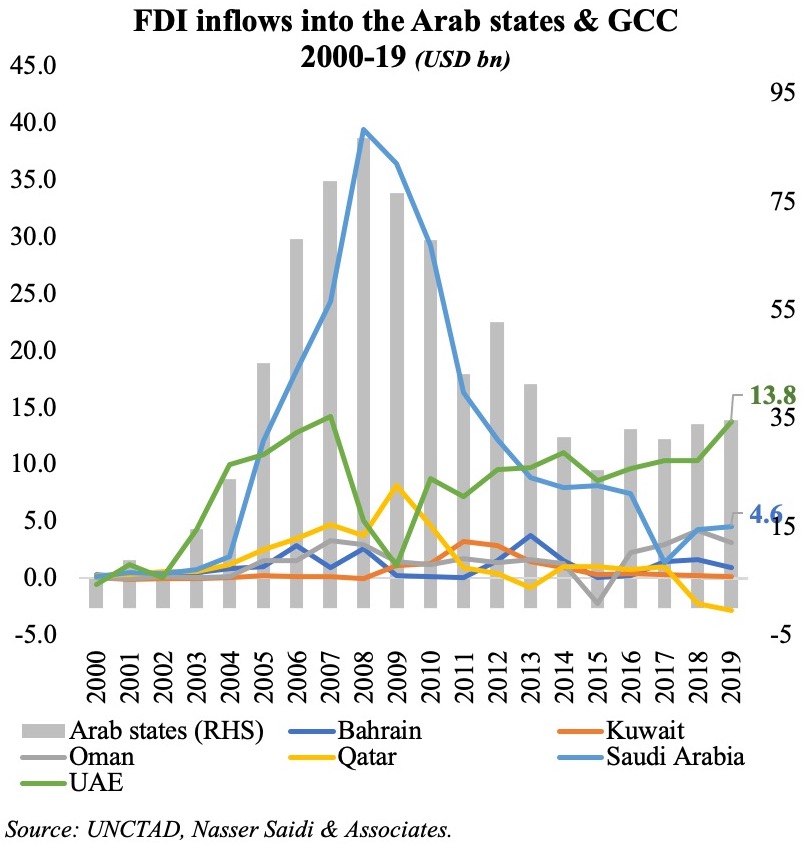 We focus on FDI in this Weekly Insight piece. FDI inflows are essential to the UAE’s diversification efforts, as it would not only create jobs, raise productivity and growth, but could also lead to transfer of technology/ technical know-how and promote competition in the market. According to the IMF, closing FDI gaps in the GCC could raise real non-oil GDP per capita growth by as much as 1 percentage point.
We focus on FDI in this Weekly Insight piece. FDI inflows are essential to the UAE’s diversification efforts, as it would not only create jobs, raise productivity and growth, but could also lead to transfer of technology/ technical know-how and promote competition in the market. According to the IMF, closing FDI gaps in the GCC could raise real non-oil GDP per capita growth by as much as 1 percentage point.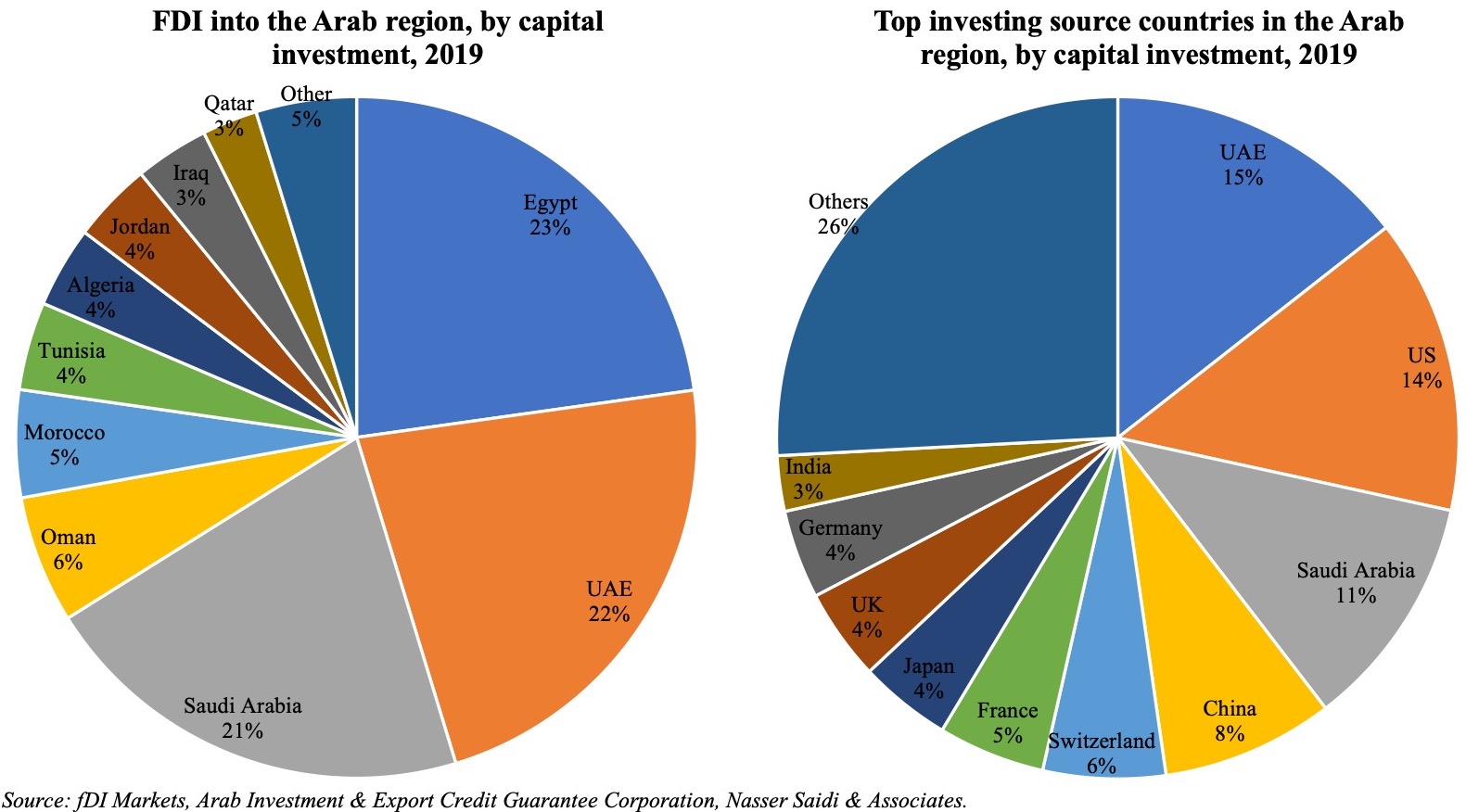
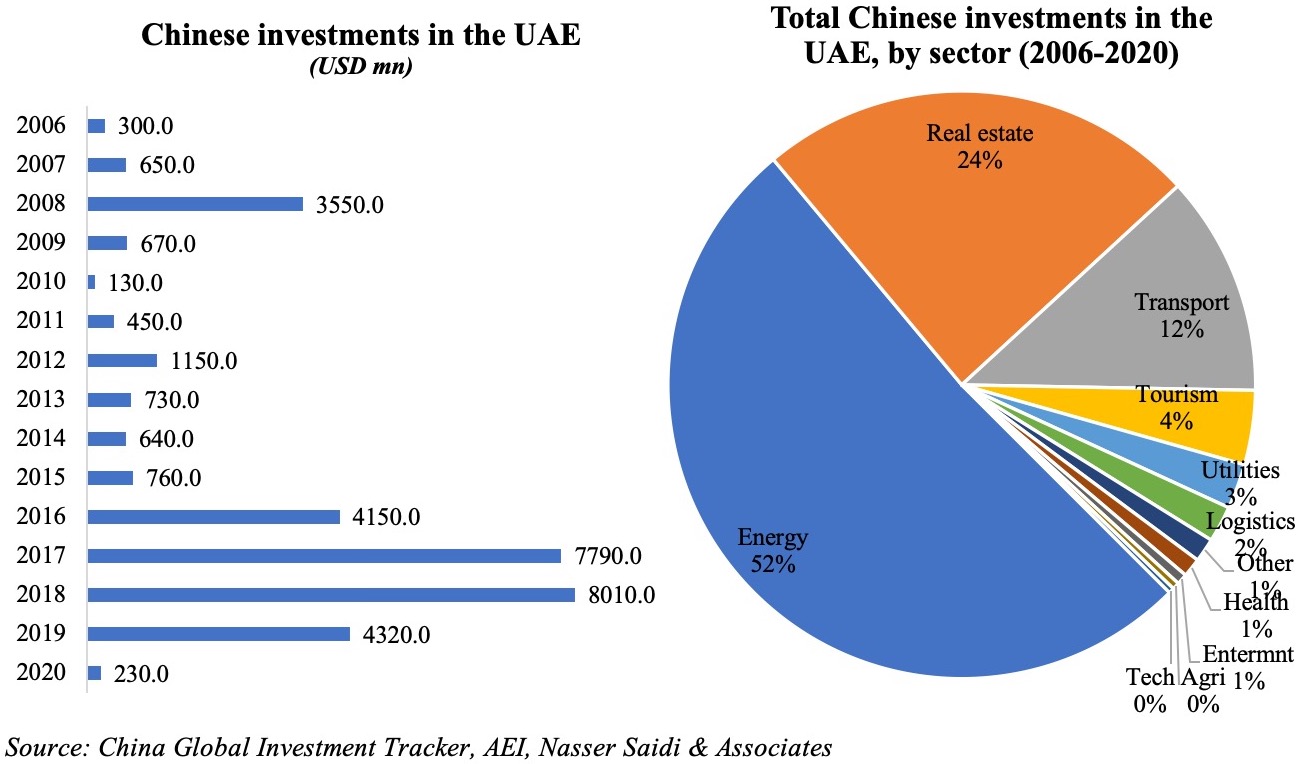
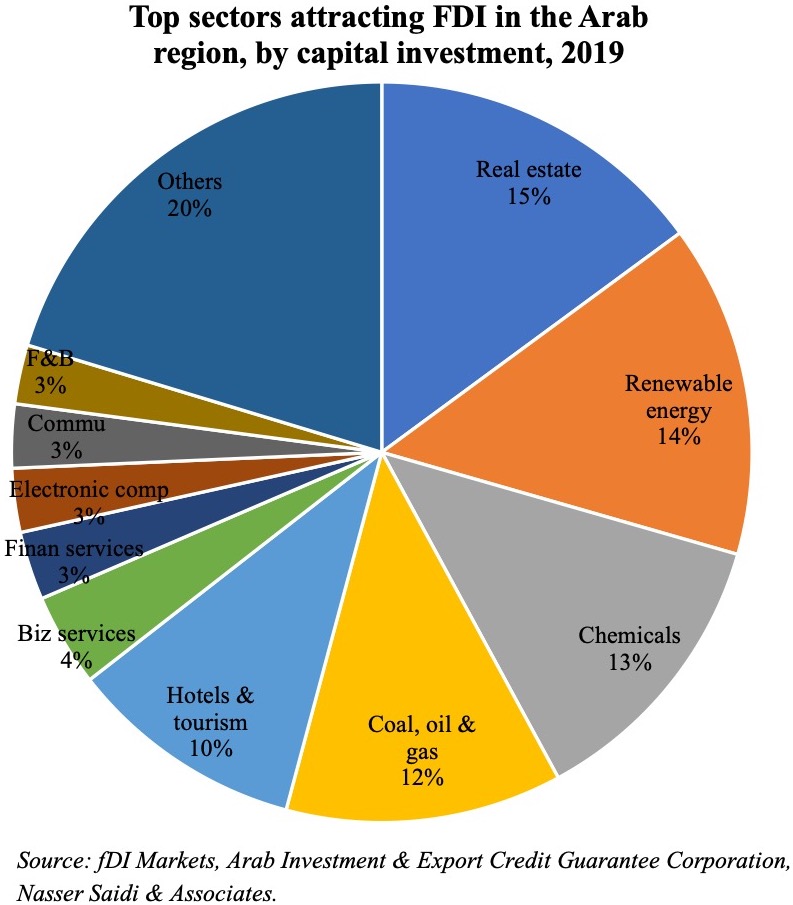 hinese projects tracked during Jan 2003-Mar 2020 (with the number of projects in double-digits in 2018 and 2019). According to AEI’s China Global Investment Tracker, the value of Chinese investments touched a high of USD 8bn in 2018, thanks to a handful of large projects (including with ACWA Power and Abu Dhabi Oil). Sector-wise, investments were concentrated in energy (both oil and gas as well as renewables), real estate and transport – together accounting for 87.8% of total investments during 2016-2020. This is largely in line with FDI inflows into the Arab region as well, with the top 5 sectors (real estate, renewables, chemicals, oil & gas and travel & tourism) accounting for close to two-thirds of total inflows in 2019.
hinese projects tracked during Jan 2003-Mar 2020 (with the number of projects in double-digits in 2018 and 2019). According to AEI’s China Global Investment Tracker, the value of Chinese investments touched a high of USD 8bn in 2018, thanks to a handful of large projects (including with ACWA Power and Abu Dhabi Oil). Sector-wise, investments were concentrated in energy (both oil and gas as well as renewables), real estate and transport – together accounting for 87.8% of total investments during 2016-2020. This is largely in line with FDI inflows into the Arab region as well, with the top 5 sectors (real estate, renewables, chemicals, oil & gas and travel & tourism) accounting for close to two-thirds of total inflows in 2019.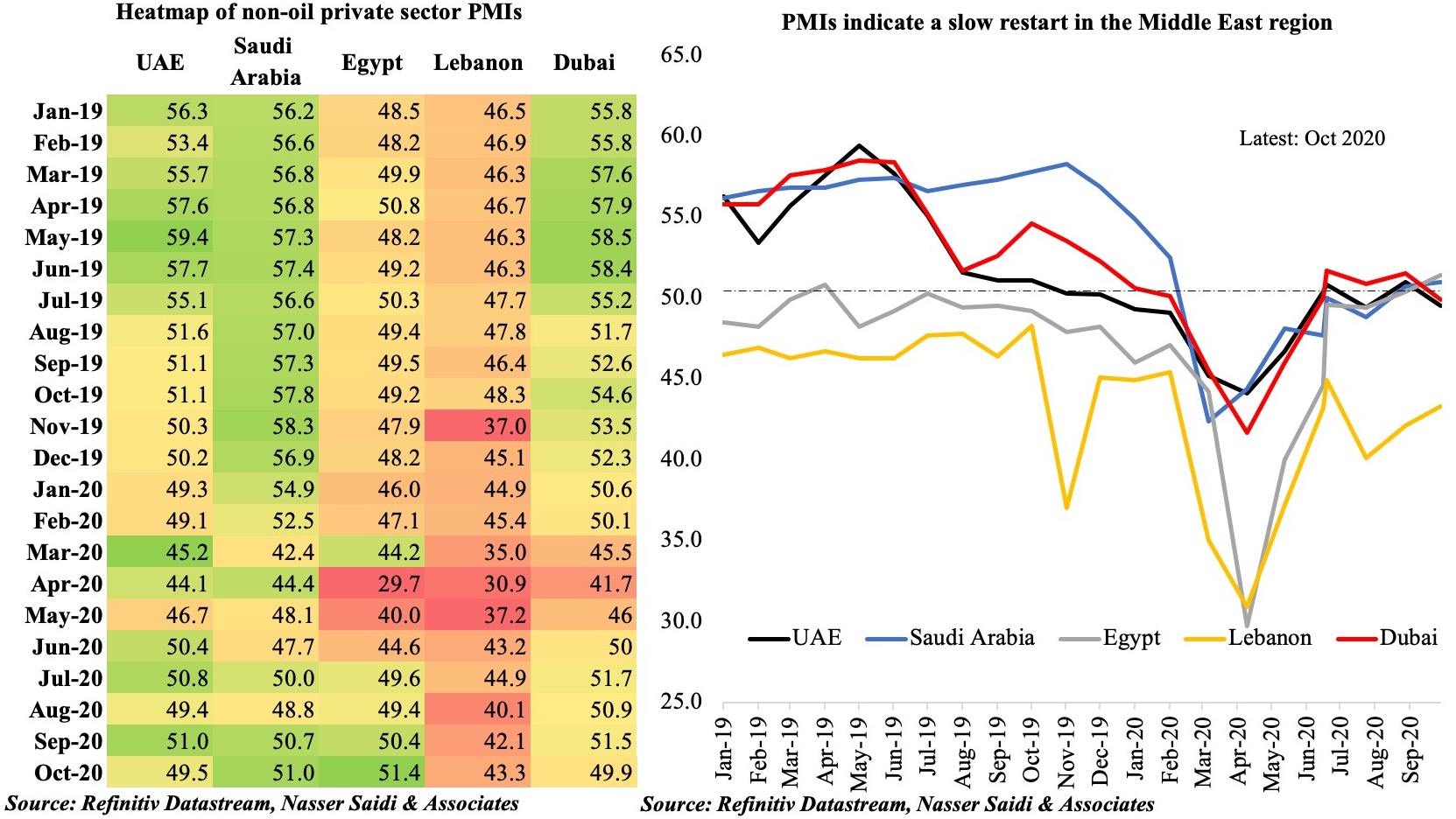
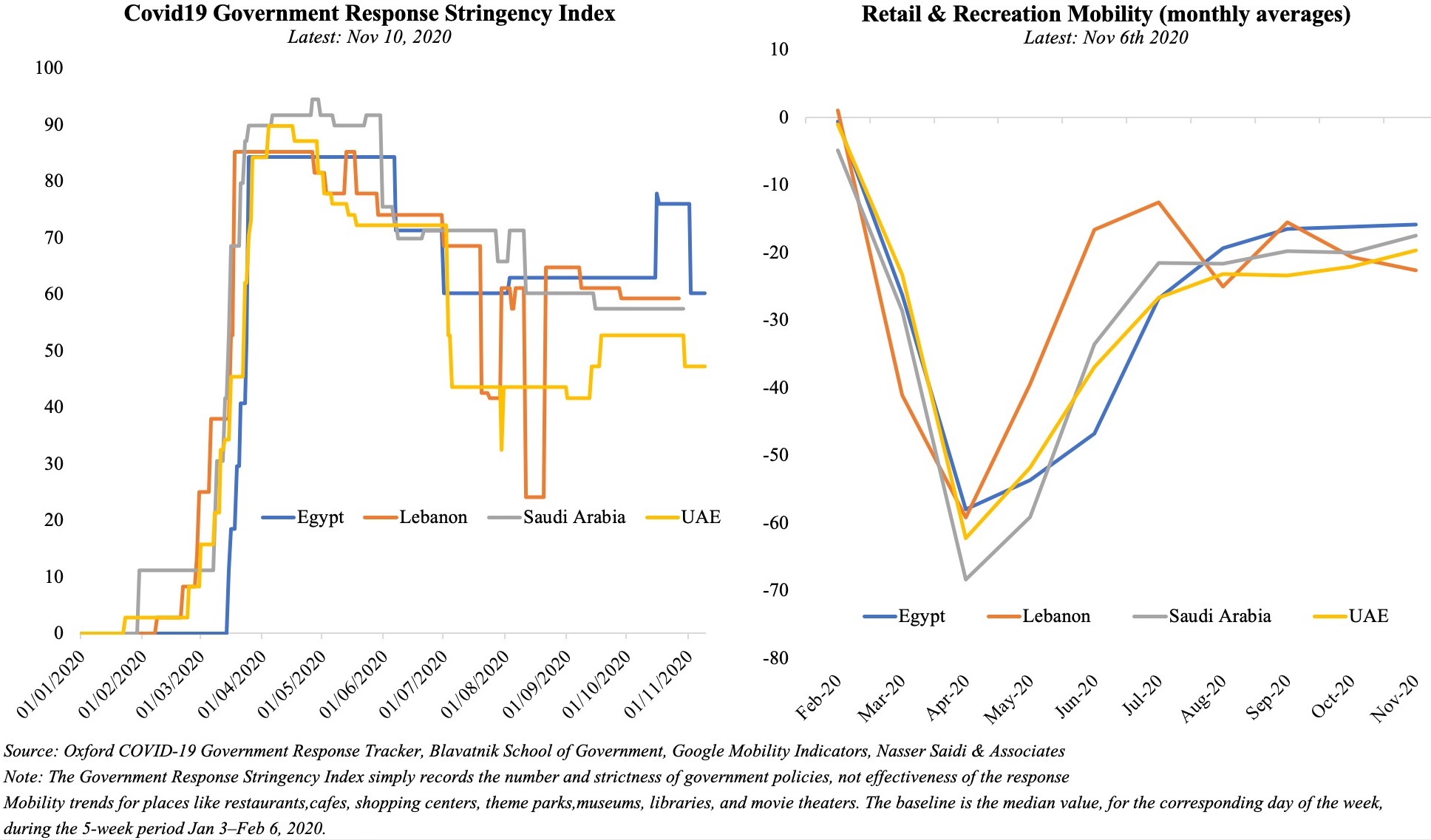

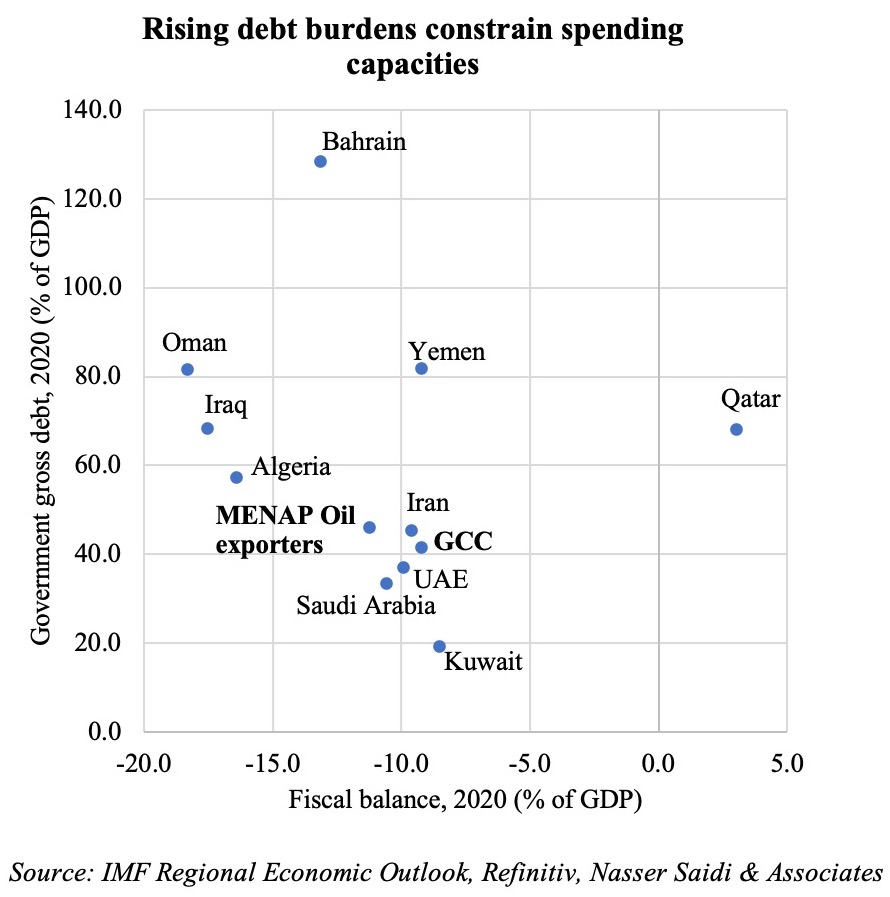
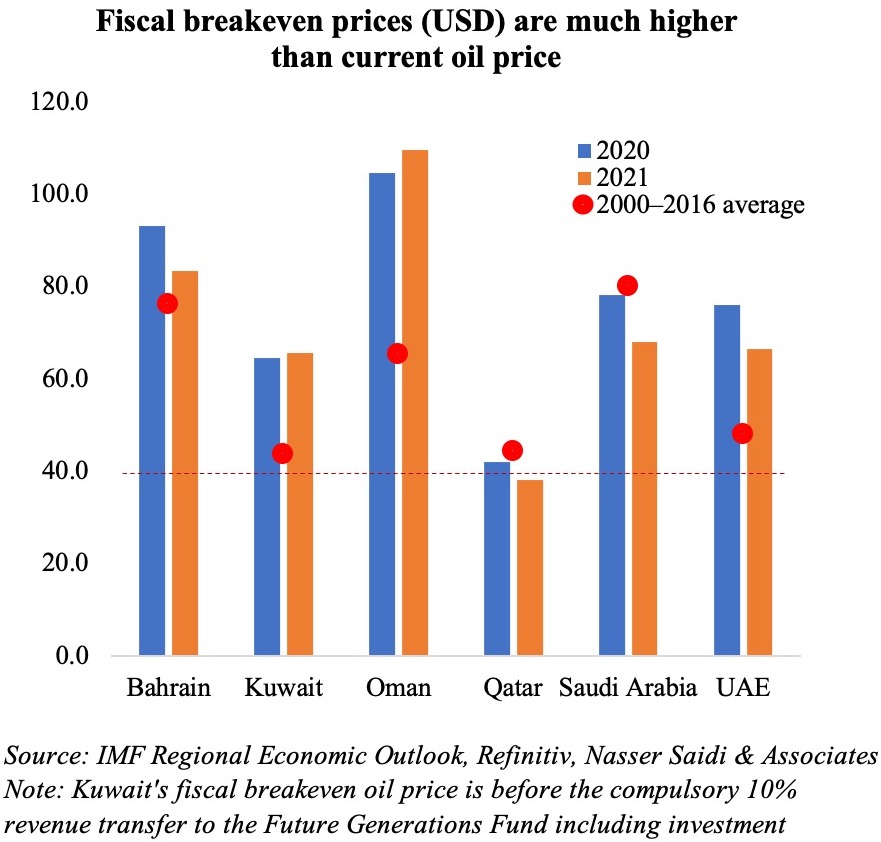 Given the resurgence in Covid19 cases and renewed lockdown measures and the global energy transition away from fossil fuels, it is unlikely that oil prices will revert to the levels seen a few years ago, given weaker demand – the IMF’s latest World Economic Outlook puts oil prices, based on futures markets at USD 41.69 in 2020 and USD 46.70 in 2021 (versus an average price of USD 61.39 last year). Fiscal breakeven oil prices in the GCC range between USD 42 for Qatar to USD 104.5 for Oman this year, exerting additional pressure on most oil producers as they ramp up spending to support the economy (UAE’s emirates Dubai and Sharjah announced USD136Mn and USD139Mn respectively in additional stimulus in the last few days).
Given the resurgence in Covid19 cases and renewed lockdown measures and the global energy transition away from fossil fuels, it is unlikely that oil prices will revert to the levels seen a few years ago, given weaker demand – the IMF’s latest World Economic Outlook puts oil prices, based on futures markets at USD 41.69 in 2020 and USD 46.70 in 2021 (versus an average price of USD 61.39 last year). Fiscal breakeven oil prices in the GCC range between USD 42 for Qatar to USD 104.5 for Oman this year, exerting additional pressure on most oil producers as they ramp up spending to support the economy (UAE’s emirates Dubai and Sharjah announced USD136Mn and USD139Mn respectively in additional stimulus in the last few days).