Weekly Insights 28 Jan 2021
Download a PDF copy of this week’s insight piece here.
1. Global Recovery in 2021, albeit divergent & uncertain
The IMF, in its latest World Economic Outlook update, forecasts global recovery at 5.5% this year and 4.2% in 2022, from a contraction of 3.5% in 2020. There is a divergence in recovery: advanced nations, where growth plunged by 4.9% last year, will recover at a slower 4.3% while emerging markets recover at a faster 6.3% in 2021 (2020: -2.4%). Much of the emerging market recovery is thanks to the effective containment of Covid19 in China and many of the South-east Asian nations. The growth estimates are based on continuing policy support (and its effectiveness) and roll-out of vaccines (though its pace and logistics issues are identified as a concern) and “supportive financial conditions” (thanks to major central banks’ maintaining current policy rates through to 2022).
While over 150 economies are expected to have their per capita incomes below the 2019 levels in 2021, the projected cumulative output loss over 2020–2025 is forecast to be USD 22trn (relative to the pre-pandemic projections).
Fig 1. Global economic growth set to recover by 5.5% this year
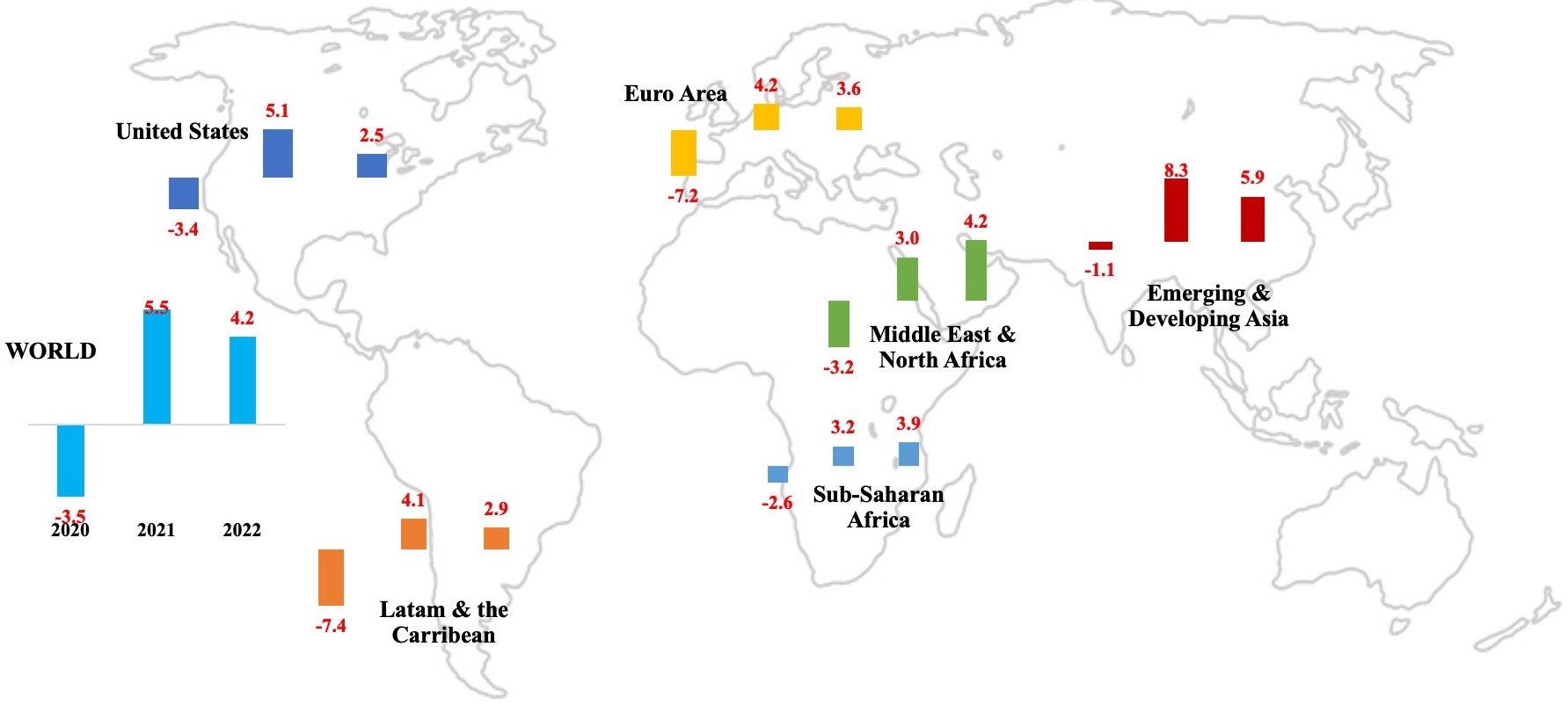
Source: IMF World Economic Outlook, Jan 2021
The slowest pace of recovery among the regions is in the Middle East (+3% growth this year), a result of the shocks from both Covid19 and lower oil prices. The average price of oil last year was USD 41.29 (simple average of Brent, Dubai Fateh and WTI) and this is estimated to rebound by 21.2% yoy to USD 50.03 this year. As Covid19 cases surge globally, leading to newer restrictions/ lockdowns, the demand for oil is likely to stay subdued: consequently, OPEC+ monthly meetings are unlikely to result in production increases anytime soon. Even if vaccines are distributed quicker-than-expected, resulting in an increase in economic activity earlier than anticipated, there are multiple other factors that are likely to keep oil prices within the USD 50-55 mark (Figure 2).
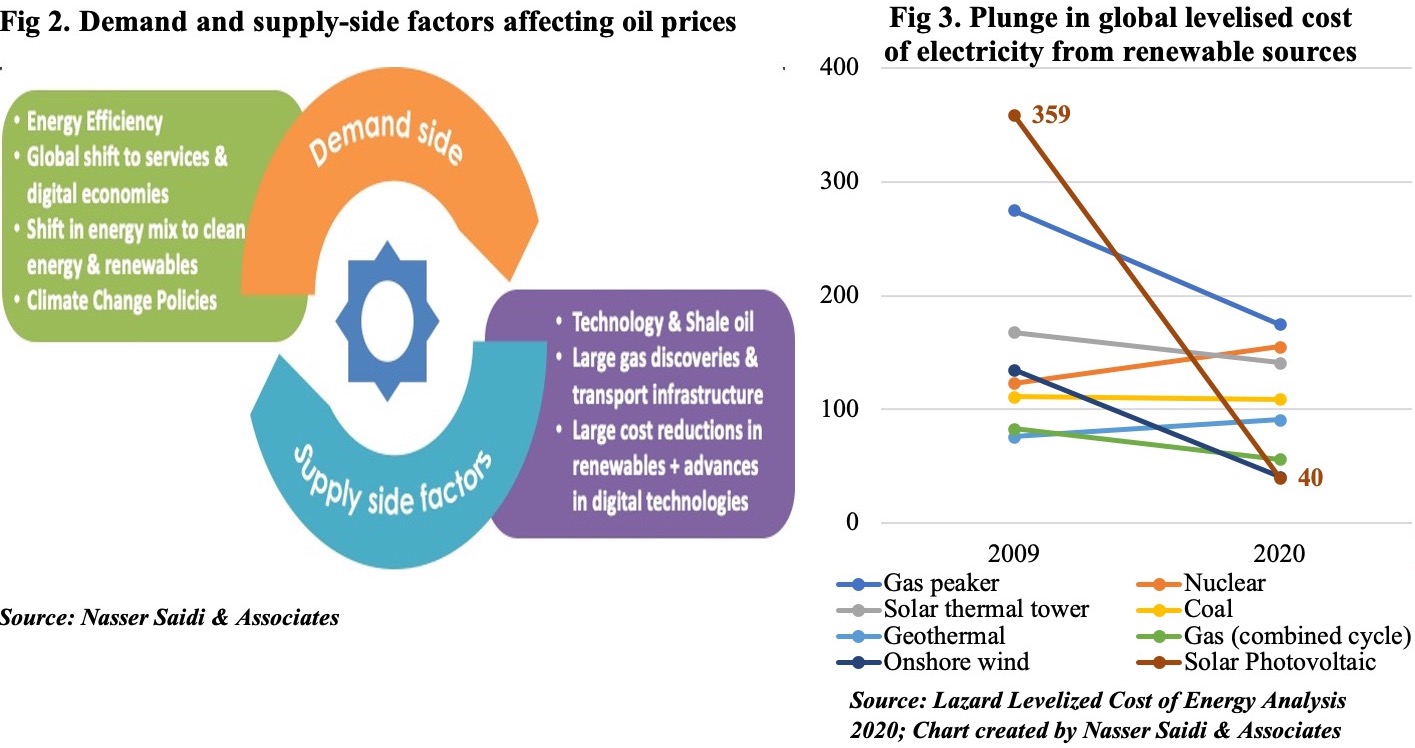
In addition to lower demand due to Covid19 restrictions, growing awareness of climate change risks (& related policy changes) and energy efficiency policies will also affect the demand for oil. On the supply side, technological innovation and rapidly falling costs for solar and wind power has made renewables more competitive. Figure 3 shows the plunge in price of electricity from renewable sources: onshore wind fell by 70% to USD 41 last year from USD 135 in 2009; the dive in solar PV was more eye-popping – it fell by a massive 89% to USD 40 last year from USD 359 in 2009.
2. Services trade continues to drag
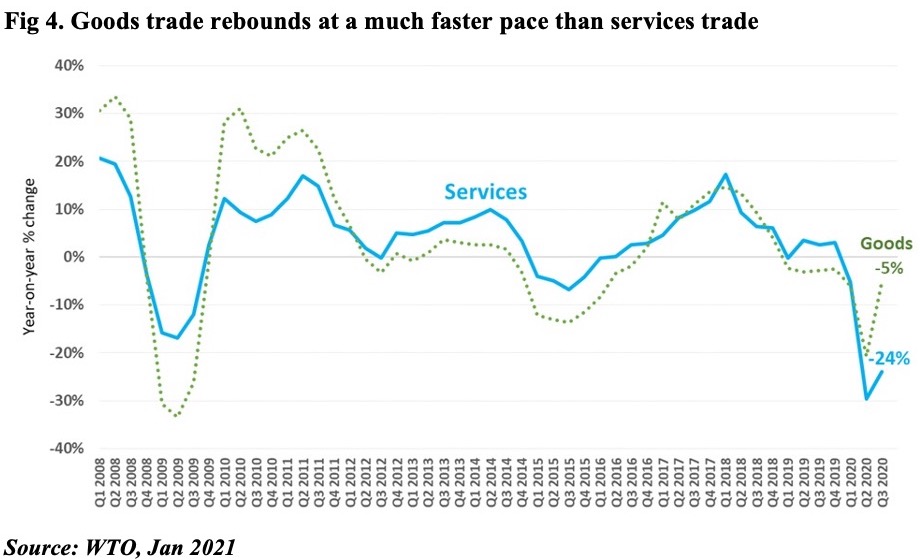
The WTO, in its latest report on services trade, highlights that the recovery has been slow: the decline in global services trade eased to a 24% yoy decline in Q3, from the 30% drop posted in Q2. This compares to the goods trade recovery which was down by just 5% yoy in Q3. Sector-wise, unsurprisingly, travel is the most affected, down by 68% yoy while among “other services”, computer, insurance and financial services increased in Q3 (+9%, 3% and 2% respectively). Global PMI indicators also suggest that economic recovery is driven by manufacturing vis-à-vis services: in Dec, output across manufacturing sector outperformed the services sector for the 6th straight month. Within the services index, respondents expect growth in future activity though optimism levels waned towards the end of last year.
3. Labour market recovery in 2021?
A key sub-indicator within PMI is employment – one of the main components dragging down the headline index. According to the ILO, about 8.8% of global working hours were lost for the whole of last year (relative to Q4 2019), roughly equivalent to 255mn full-time jobs. To put this in perspective, this was four times more than what was lost in the 2009 financial crisis period. In turn, labour income witnessed a decline of 8.3% – equivalent to USD 3.7trn or 4.4% of GDP!
In the Arab states, total estimated decline in working hours was 9% versus the global loss of 8.8% (Figure 5 below). However, these are ILO’s own estimates, as no labour force surveys were available for any country in the region during this time. According to these estimates, Iraq and Saudi Arabia registered losses of 8.3% and 10.8% respectively.
Fig 5. Quarterly & annual estimates of working hour losses, world vs. Arab states
| Percentage of working hours lost (%) vs pre-crisis quarter Q4 2019 | Equivalent number of full-time jobs (48 hrs/ week) lost (mns) | |||||||||
| Q1 2020 | Q2 2020 | Q3 2020 | Q4 2020 | 2020 | Q1 2020 | Q2 2020 | Q3 2020 | Q4 2020 | 2020 | |
| World | 5.2 | 18.2 | 7.2 | 4.6 | 8.8 | 150 | 525 | 205 | 130 | 255 |
| Arab states | 3.3 | 18.8 | 9.4 | 4.7 | 9.0 | 2.0 | 10.0 | 5.0 | 2.0 | 5.0 |
Source: ILO Monitor: COVID-19 and the world of work, seventh edition, Jan 2021
Recovery is expected in 2021 as mobility restrictions are lifted and vaccine roll-out leads to a slow return of business/economic activity. With young persons and women as well as the informal sector and low-skilled workers more affected than the rest during the Covid19 period, it is imperative to target the return of these groups into the labour market. Without this, the outlook will be more inequality and instability (remember that youth unemployment was one of the factors leading up to the Arab Spring 10 years ago) in the most affected nations. As it stands, the IMF estimates that close to 90mn persons are likely to fall below the extreme poverty threshold during 2020–21.
4. Employment in Saudi Arabia
Separate data releases from Saudi Arabia give us an insight into employment trends in the country, which can be explained by a combination of Covid19, travel restrictions and Saudization policies:
- Unemployment in Saudi Arabia dropped to 14.9% in Q3 from 15.4% the previous quarter, though higher than Q1’s 11.8%. The gap between male and female unemployment remained significant, with the former at 7.9% and latter at 30.2%.
- The most recent labour force survey shows that the number of expats working in the country fell by 257,170 (qoq) to 10.2mn in Q3 while citizens grew by 81.9k to 3.25mn. Expat males account for two-thirds of the workforce versus Saudi males and females at 15.6% and 8.6% respectively in Q3.
- There was a 58% yoy decline in work visas issued to expats to 611,185 in Jan-Sep 2020.
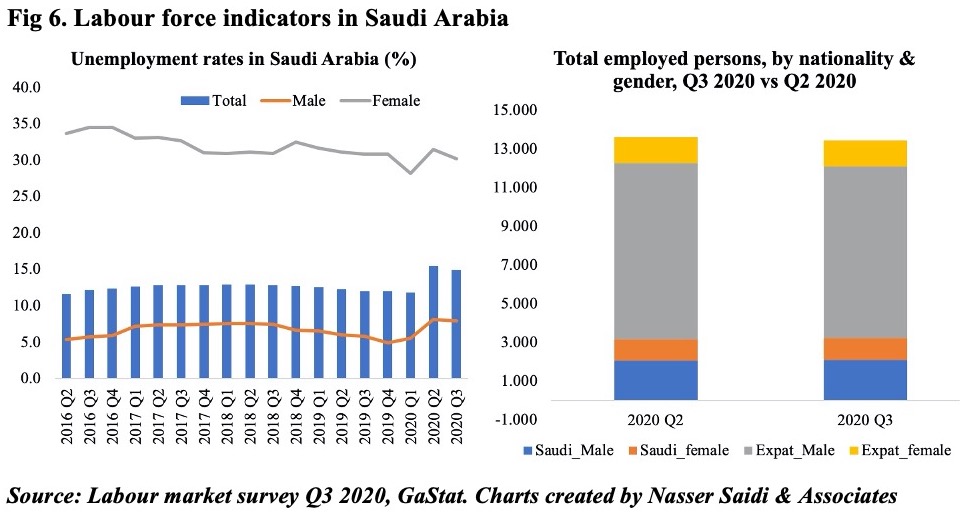
While on the one hand, the country has an aim to support female employment (an objective within the Vision 2030 document is to raise women’s participation to 30% by 2030), there seems to be a major disconnect: female employment in the private sector is less than 10% of total, and the additional hurdles – like costs of employing women (separate floors/ work areas from the male counterparts), social customs, technical skills (focus on degrees in education, humanities) – may be putting off prospective employers.
Independently, the Public Investment Fund (PIF) disclosed that it had generated over 331k jobs in the past 4 years either directly or indirectly through its investment policies. The PIF’s recent commitment to not only invest USD 40bn every year for the next five years but also create close to 1.8mn jobs by end-2025 will support the economy going forward.
According to UNCTAD’s latest “Investment trends Monitor”, FDI into Saudi Arabia increased by 4% yoy to an estimated USD 4.7bn last year – this is in spite of the 42% drop in global FDI flows (with further weakness expected in 2021) and the 24% decline in flows to West Asia. With various ongoing projects related to Vision 2030 and megaprojects in NEOM, as well as the revamp of over 200 FDI regulations, the Kingdom’s ability to woo investors is explicable: Egypt, India and the UK were the most active investors in the country. Care must be taken to attract FDI into more job-creating sectors than the oil & gas sector (which is more capital intensive). Given the country’s commitment to support clean/renewable energy, it is pertinent to focus on the creation of green jobs, thereby leading to sustainable economic recovery.
Powered by:

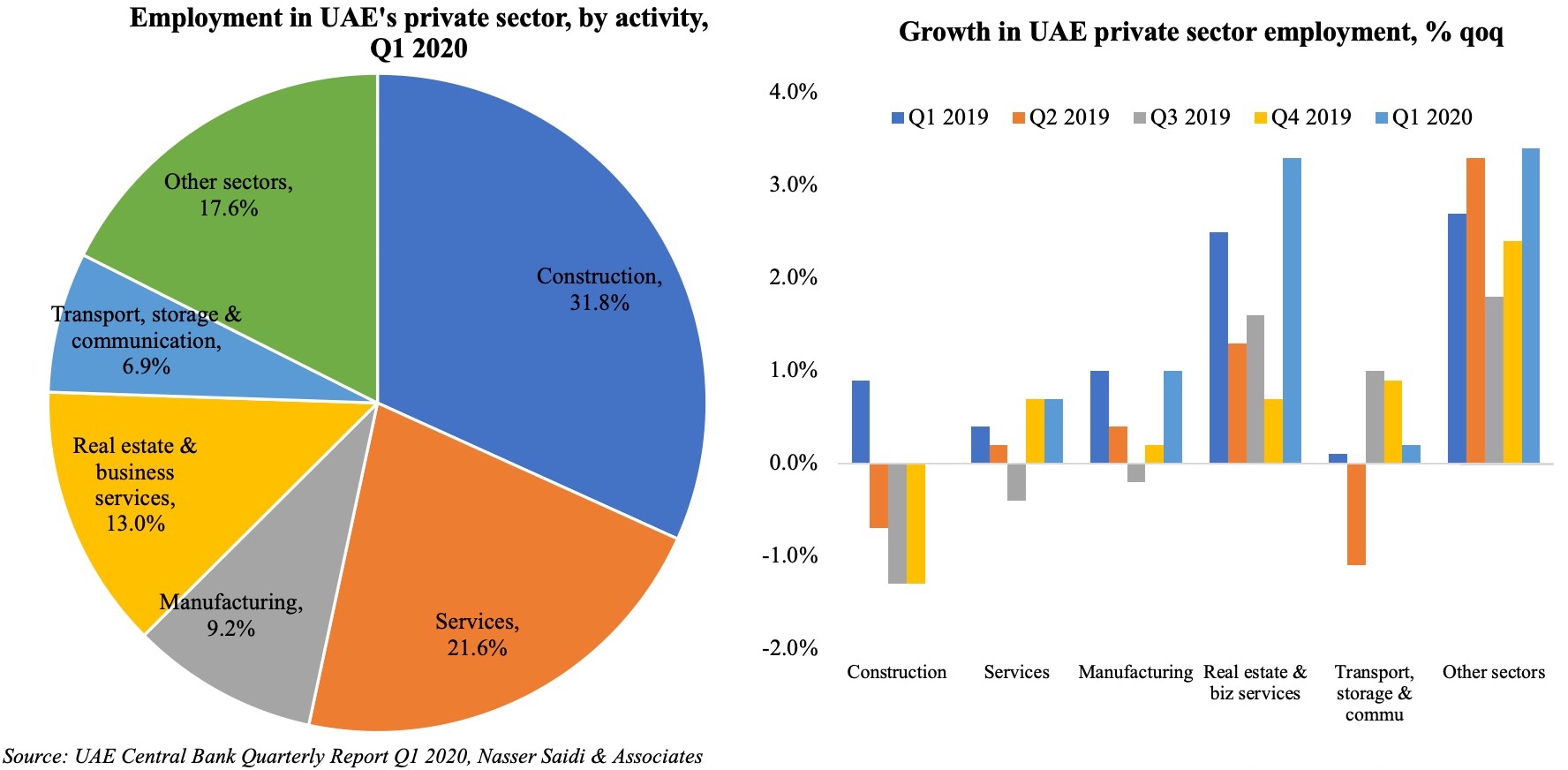
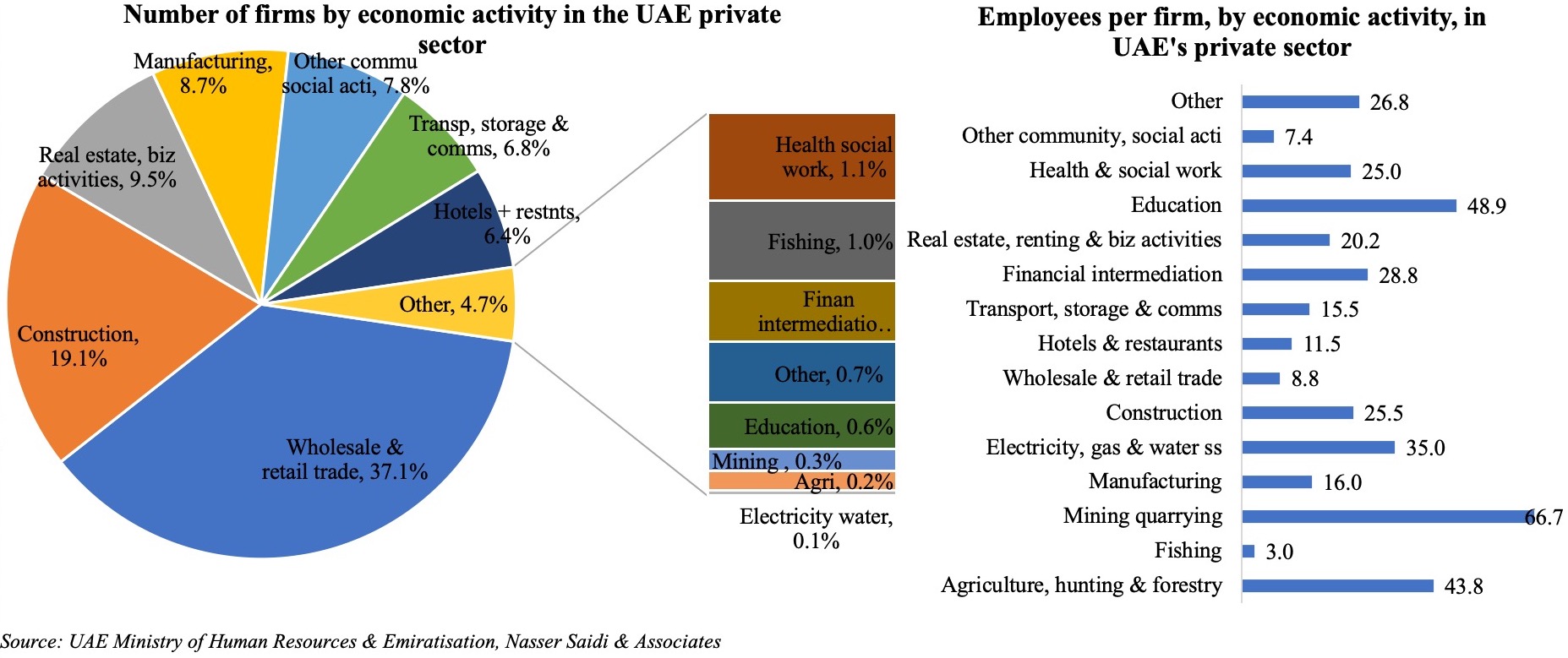
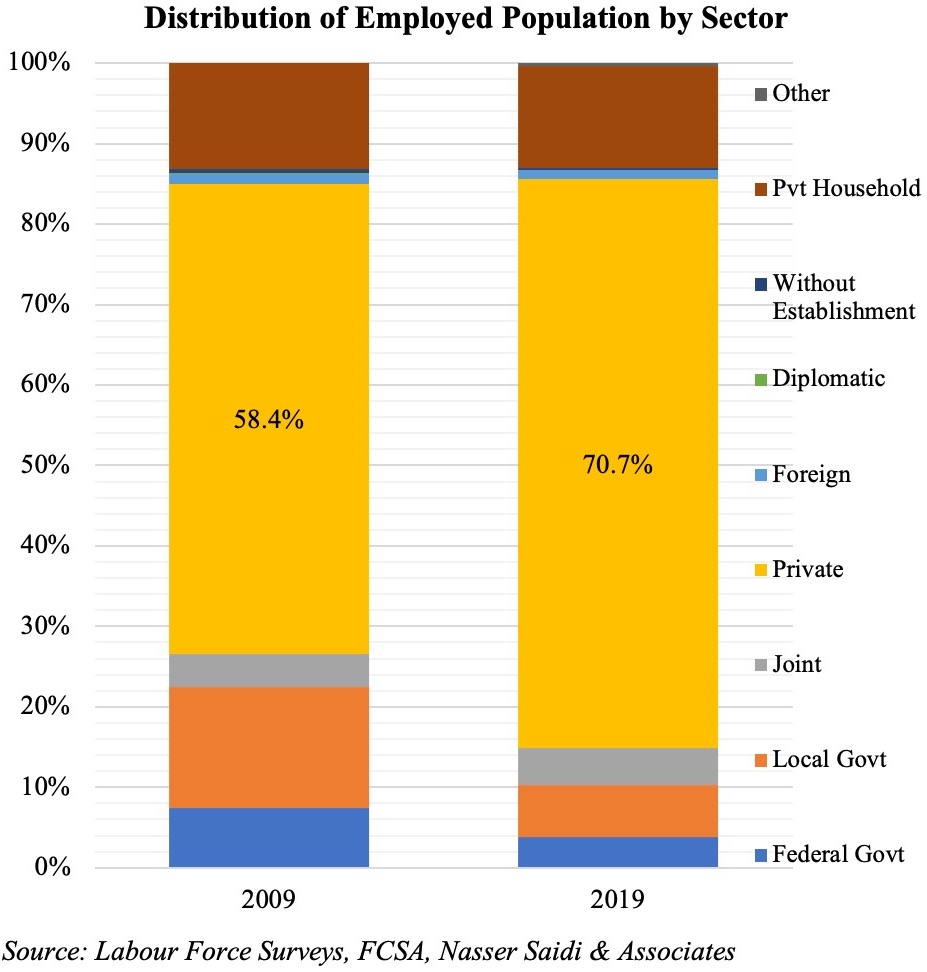
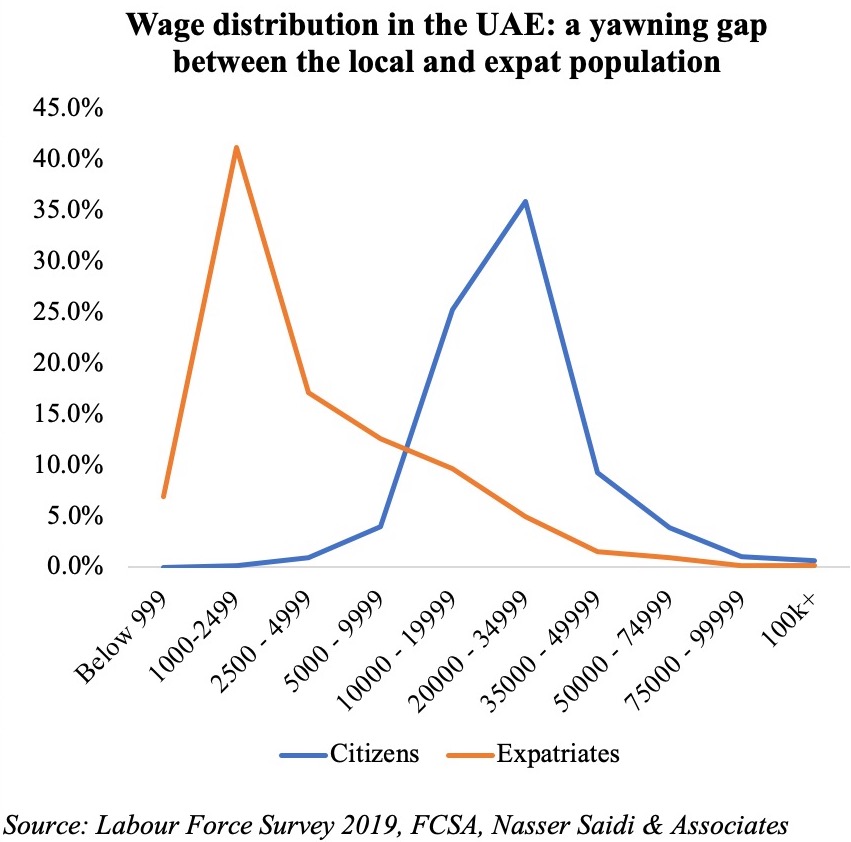 The Survey also confirms the disparity in wages between local and expat population: more than one-third of Emirati respondents disclosed receiving monthly wages between AED 20-35k (versus just 5% of expats in the same income bracket). This brings to the forefront two issues:
The Survey also confirms the disparity in wages between local and expat population: more than one-third of Emirati respondents disclosed receiving monthly wages between AED 20-35k (versus just 5% of expats in the same income bracket). This brings to the forefront two issues: